Eric Yuan
ByteSized32: A Corpus and Challenge Task for Generating Task-Specific World Models Expressed as Text Games
May 24, 2023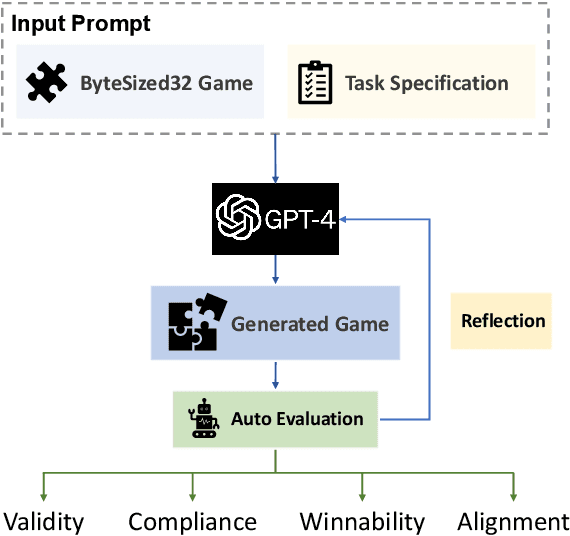
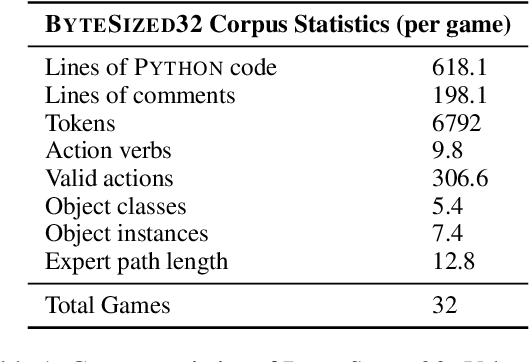

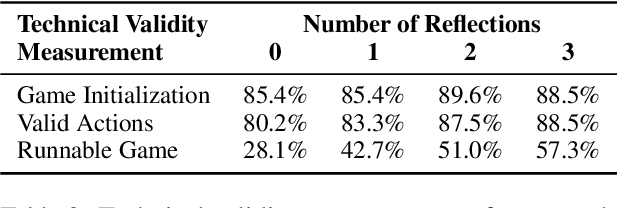
Abstract:In this work we examine the ability of language models to generate explicit world models of scientific and common-sense reasoning tasks by framing this as a problem of generating text-based games. To support this, we introduce ByteSized32, a corpus of 32 highly-templated text games written in Python totaling 24k lines of code, each centered around a particular task, and paired with a set of 16 unseen text game specifications for evaluation. We propose a suite of automatic and manual metrics for assessing simulation validity, compliance with task specifications, playability, winnability, and alignment with the physical world. In a single-shot evaluation of GPT-4 on this simulation-as-code-generation task, we find it capable of producing runnable games in 27% of cases, highlighting the difficulty of this challenge task. We discuss areas of future improvement, including GPT-4's apparent capacity to perform well at simulating near canonical task solutions, with performance dropping off as simulations include distractors or deviate from canonical solutions in the action space.
Automatic Exploration of Textual Environments with Language-Conditioned Autotelic Agents
Jul 08, 2022Abstract:In this extended abstract we discuss the opportunities and challenges of studying intrinsically-motivated agents for exploration in textual environments. We argue that there is important synergy between text environments and autonomous agents. We identify key properties of text worlds that make them suitable for exploration by autonmous agents, namely, depth, breadth, progress niches and the ease of use of language goals; we identify drivers of exploration for such agents that are implementable in text worlds. We discuss the opportunities of using autonomous agents to make progress on text environment benchmarks. Finally we list some specific challenges that need to be overcome in this area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge