Erasmo Tani
Learning Multinomial Logits in $O(n \log n)$ time
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:A Multinomial Logit (MNL) model is composed of a finite universe of items $[n]=\{1,..., n\}$, each assigned a positive weight. A query specifies an admissible subset -- called a slate -- and the model chooses one item from that slate with probability proportional to its weight. This query model is also known as the Plackett-Luce model or conditional sampling oracle in the literature. Although MNLs have been studied extensively, a basic computational question remains open: given query access to slates, how efficiently can we learn weights so that, for every slate, the induced choice distribution is within total variation distance $\varepsilon$ of the ground truth? This question is central to MNL learning and has direct implications for modern recommender system interfaces. We provide two algorithms for this task, one with adaptive queries and one with non-adaptive queries. Each algorithm outputs an MNL $M'$ that induces, for each slate $S$, a distribution $M'_S$ on $S$ that is within $\varepsilon$ total variation distance of the true distribution. Our adaptive algorithm makes $O\left(\frac{n}{\varepsilon^{3}}\log n\right)$ queries, while our non-adaptive algorithm makes $O\left(\frac{n^{2}}{\varepsilon^{3}}\log n \log\frac{n}{\varepsilon}\right)$ queries. Both algorithms query only slates of size two and run in time proportional to their query complexity. We complement these upper bounds with lower bounds of $Ω\left(\frac{n}{\varepsilon^{2}}\log n\right)$ for adaptive queries and $Ω\left(\frac{n^{2}}{\varepsilon^{2}}\log n\right)$ for non-adaptive queries, thus proving that our adaptive algorithm is optimal in its dependence on the support size $n$, while the non-adaptive one is tight within a $\log n$ factor.
Learning-Based Algorithms for Graph Searching Problems
Feb 27, 2024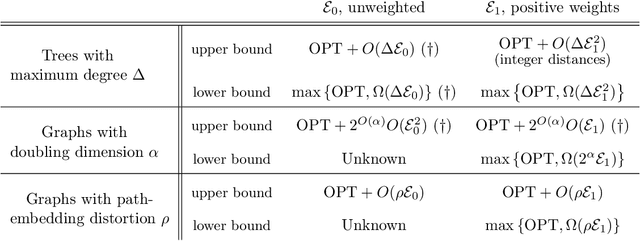
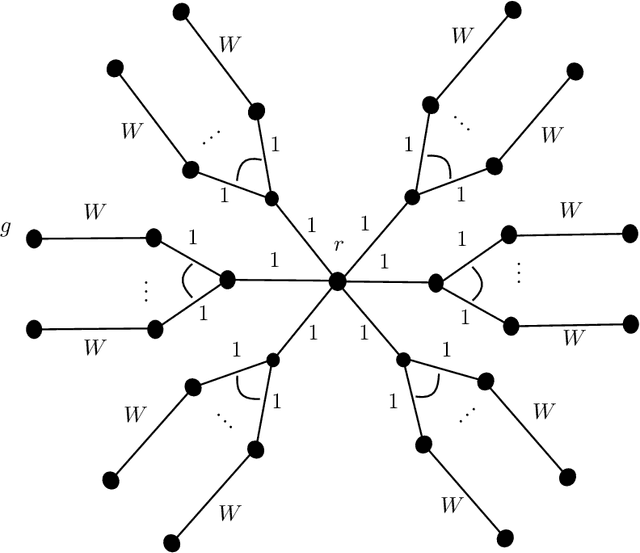
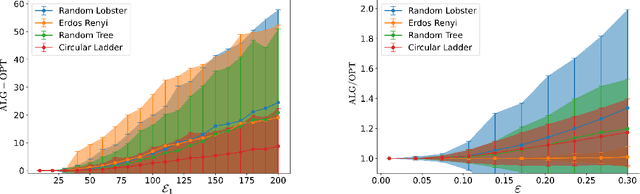

Abstract:We consider the problem of graph searching with prediction recently introduced by Banerjee et al. (2022). In this problem, an agent, starting at some vertex $r$ has to traverse a (potentially unknown) graph $G$ to find a hidden goal node $g$ while minimizing the total distance travelled. We study a setting in which at any node $v$, the agent receives a noisy estimate of the distance from $v$ to $g$. We design algorithms for this search task on unknown graphs. We establish the first formal guarantees on unknown weighted graphs and provide lower bounds showing that the algorithms we propose have optimal or nearly-optimal dependence on the prediction error. Further, we perform numerical experiments demonstrating that in addition to being robust to adversarial error, our algorithms perform well in typical instances in which the error is stochastic. Finally, we provide alternative simpler performance bounds on the algorithms of Banerjee et al. (2022) for the case of searching on a known graph, and establish new lower bounds for this setting.
Error-Tolerant Exact Query Learning of Finite Set Partitions with Same-Cluster Oracle
May 22, 2023

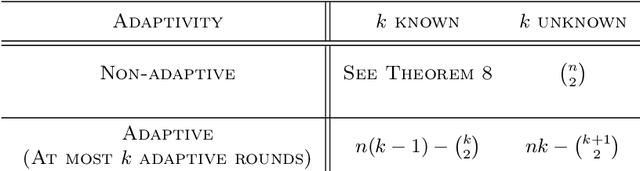

Abstract:This paper initiates the study of active learning for exact recovery of partitions exclusively through access to a same-cluster oracle in the presence of bounded adversarial error. We first highlight a novel connection between learning partitions and correlation clustering. Then we use this connection to build a R\'enyi-Ulam style analytical framework for this problem, and prove upper and lower bounds on its worst-case query complexity. Further, we bound the expected performance of a relevant randomized algorithm. Finally, we study the relationship between adaptivity and query complexity for this problem and related variants.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge