Enkhbayar Erdenee
Meet Your Favorite Character: Open-domain Chatbot Mimicking Fictional Characters with only a Few Utterances
Apr 22, 2022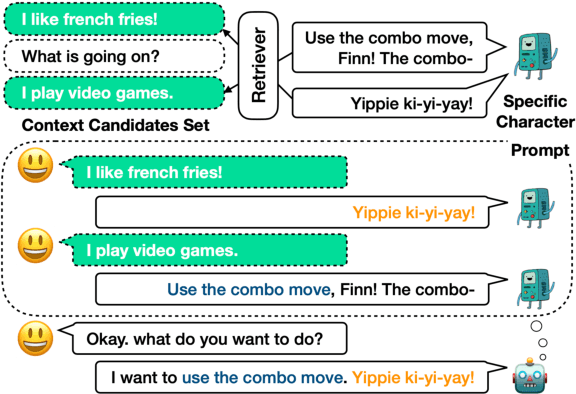
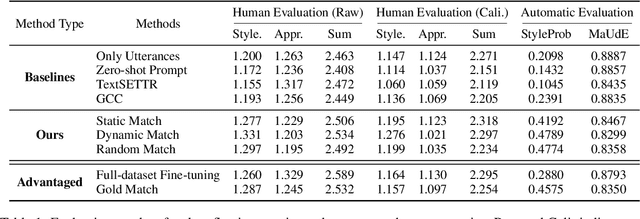

Abstract:In this paper, we consider mimicking fictional characters as a promising direction for building engaging conversation models. To this end, we present a new practical task where only a few utterances of each fictional character are available to generate responses mimicking them. Furthermore, we propose a new method named Pseudo Dialog Prompting (PDP) that generates responses by leveraging the power of large-scale language models with prompts containing the target character's utterances. To better reflect the style of the character, PDP builds the prompts in the form of dialog that includes the character's utterances as dialog history. Since only utterances of the characters are available in the proposed task, PDP matches each utterance with an appropriate pseudo-context from a predefined set of context candidates using a retrieval model. Through human and automatic evaluation, we show that PDP generates responses that better reflect the style of fictional characters than baseline methods.
Understanding and Improving the Exemplar-based Generation for Open-domain Conversation
Dec 13, 2021


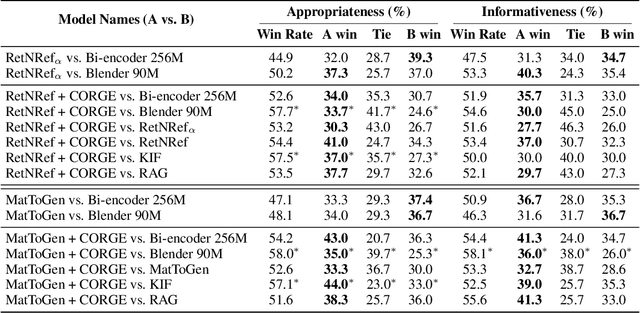
Abstract:Exemplar-based generative models for open-domain conversation produce responses based on the exemplars provided by the retriever, taking advantage of generative models and retrieval models. However, they often ignore the retrieved exemplars while generating responses or produce responses over-fitted to the retrieved exemplars. In this paper, we argue that these drawbacks are derived from the one-to-many problem of the open-domain conversation. When the retrieved exemplar is relevant to the given context yet significantly different from the gold response, the exemplar-based generative models are trained to ignore the exemplar since the exemplar is not helpful for generating the gold response. On the other hand, when the retrieved exemplar is lexically similar to the gold response, the generative models are trained to rely on the exemplar highly. Therefore, we propose a training method selecting exemplars that are semantically relevant to the gold response but lexically distanced from the gold response to mitigate the above disadvantages. In the training phase, our proposed training method first uses the gold response instead of dialogue context as a query to select exemplars that are semantically relevant to the gold response. And then, it eliminates the exemplars that lexically resemble the gold responses to alleviate the dependency of the generative models on that exemplars. The remaining exemplars could be irrelevant to the given context since they are searched depending on the gold response. Thus, our proposed training method further utilizes the relevance scores between the given context and the exemplars to penalize the irrelevant exemplars. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed training method alleviates the drawbacks of the existing exemplar-based generative models and significantly improves the performance in terms of appropriateness and informativeness.
Distilling the Knowledge of Large-scale Generative Models into Retrieval Models for Efficient Open-domain Conversation
Aug 31, 2021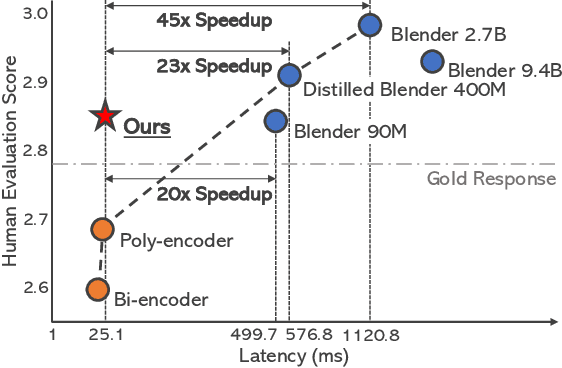
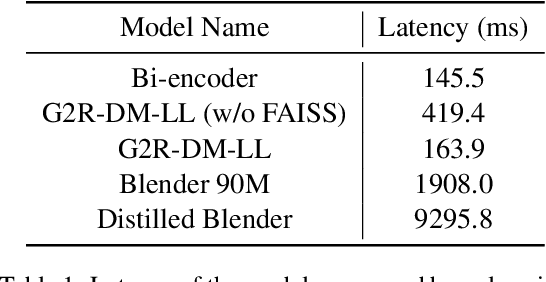
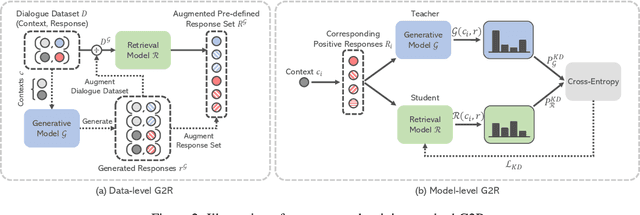
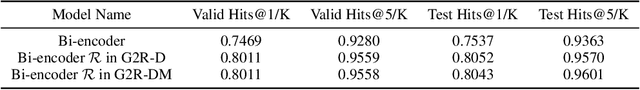
Abstract:Despite the remarkable performance of large-scale generative models in open-domain conversation, they are known to be less practical for building real-time conversation systems due to high latency. On the other hand, retrieval models could return responses with much lower latency but show inferior performance to the large-scale generative models since the conversation quality is bounded by the pre-defined response set. To take advantage of both approaches, we propose a new training method called G2R (Generative-to-Retrieval distillation) that preserves the efficiency of a retrieval model while leveraging the conversational ability of a large-scale generative model by infusing the knowledge of the generative model into the retrieval model. G2R consists of two distinct techniques of distillation: the data-level G2R augments the dialogue dataset with additional responses generated by the large-scale generative model, and the model-level G2R transfers the response quality score assessed by the generative model to the score of the retrieval model by the knowledge distillation loss. Through extensive experiments including human evaluation, we demonstrate that our retrieval-based conversation system trained with G2R shows a substantially improved performance compared to the baseline retrieval model while showing significantly lower inference latency than the large-scale generative models.
Multi-Class Multi-Object Tracking using Changing Point Detection
Aug 30, 2016



Abstract:This paper presents a robust multi-class multi-object tracking (MCMOT) formulated by a Bayesian filtering framework. Multi-object tracking for unlimited object classes is conducted by combining detection responses and changing point detection (CPD) algorithm. The CPD model is used to observe abrupt or abnormal changes due to a drift and an occlusion based spatiotemporal characteristics of track states. The ensemble of convolutional neural network (CNN) based object detector and Lucas-Kanede Tracker (KLT) based motion detector is employed to compute the likelihoods of foreground regions as the detection responses of different object classes. Extensive experiments are performed using lately introduced challenging benchmark videos; ImageNet VID and MOT benchmark dataset. The comparison to state-of-the-art video tracking techniques shows very encouraging results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge