Emily Scherer
Arges: Spatio-Temporal Transformer for Ulcerative Colitis Severity Assessment in Endoscopy Videos
Oct 01, 2024Abstract:Accurate assessment of disease severity from endoscopy videos in ulcerative colitis (UC) is crucial for evaluating drug efficacy in clinical trials. Severity is often measured by the Mayo Endoscopic Subscore (MES) and Ulcerative Colitis Endoscopic Index of Severity (UCEIS) score. However, expert MES/UCEIS annotation is time-consuming and susceptible to inter-rater variability, factors addressable by automation. Automation attempts with frame-level labels face challenges in fully-supervised solutions due to the prevalence of video-level labels in clinical trials. CNN-based weakly-supervised models (WSL) with end-to-end (e2e) training lack generalization to new disease scores and ignore spatio-temporal information crucial for accurate scoring. To address these limitations, we propose "Arges", a deep learning framework that utilizes a transformer with positional encoding to incorporate spatio-temporal information from frame features to estimate disease severity scores in endoscopy video. Extracted features are derived from a foundation model (ArgesFM), pre-trained on a large diverse dataset from multiple clinical trials (61M frames, 3927 videos). We evaluate four UC disease severity scores, including MES and three UCEIS component scores. Test set evaluation indicates significant improvements, with F1 scores increasing by 4.1% for MES and 18.8%, 6.6%, 3.8% for the three UCEIS component scores compared to state-of-the-art methods. Prospective validation on previously unseen clinical trial data further demonstrates the model's successful generalization.
Patient-independent Schizophrenia Relapse Prediction Using Mobile Sensor based Daily Behavioral Rhythm Changes
Jun 25, 2021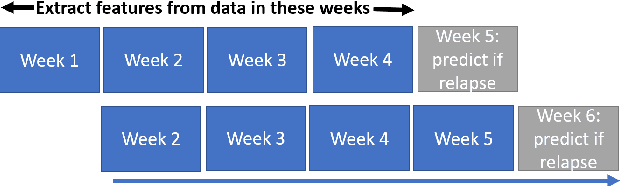
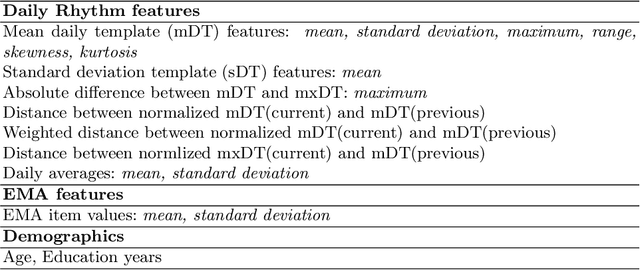
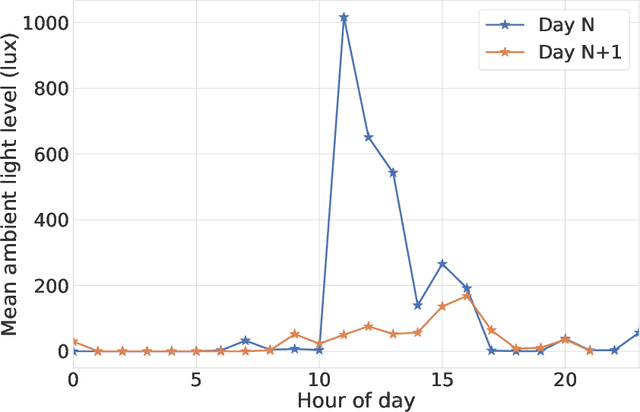
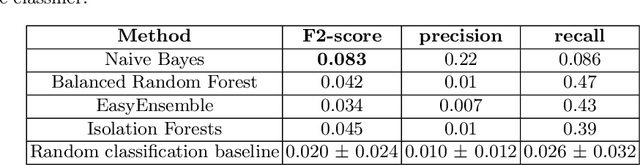
Abstract:A schizophrenia relapse has severe consequences for a patient's health, work, and sometimes even life safety. If an oncoming relapse can be predicted on time, for example by detecting early behavioral changes in patients, then interventions could be provided to prevent the relapse. In this work, we investigated a machine learning based schizophrenia relapse prediction model using mobile sensing data to characterize behavioral features. A patient-independent model providing sequential predictions, closely representing the clinical deployment scenario for relapse prediction, was evaluated. The model uses the mobile sensing data from the recent four weeks to predict an oncoming relapse in the next week. We used the behavioral rhythm features extracted from daily templates of mobile sensing data, self-reported symptoms collected via EMA (Ecological Momentary Assessment), and demographics to compare different classifiers for the relapse prediction. Naive Bayes based model gave the best results with an F2 score of 0.083 when evaluated in a dataset consisting of 63 schizophrenia patients, each monitored for up to a year. The obtained F2 score, though low, is better than the baseline performance of random classification (F2 score of 0.02 $\pm$ 0.024). Thus, mobile sensing has predictive value for detecting an oncoming relapse and needs further investigation to improve the current performance. Towards that end, further feature engineering and model personalization based on the behavioral idiosyncrasies of a patient could be helpful.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge