Emily Öhman
Affect as a proxy for literary mood
Apr 06, 2023



Abstract:We propose to use affect as a proxy for mood in literary texts. In this study, we explore the differences in computationally detecting tone versus detecting mood. Methodologically we utilize affective word embeddings to look at the affective distribution in different text segments. We also present a simple yet efficient and effective method of enhancing emotion lexicons to take both semantic shift and the domain of the text into account producing real-world congruent results closely matching both contemporary and modern qualitative analyses.
Hate speech, Censorship, and Freedom of Speech: The Changing Policies of Reddit
Mar 18, 2022



Abstract:This paper examines the shift in focus on content policies and user attitudes on the social media platform Reddit. We do this by focusing on comments from general Reddit users from five posts made by admins (moderators) on updates to Reddit Content Policy. All five concern the nature of what kind of content is allowed to be posted on Reddit, and which measures will be taken against content that violates these policies. We use topic modeling to probe how the general discourse for Redditors has changed around limitations on content, and later, limitations on hate speech, or speech that incites violence against a particular group. We show that there is a clear shift in both the contents and the user attitudes that can be linked to contemporary societal upheaval as well as newly passed laws and regulations, and contribute to the wider discussion on hate speech moderation.
SELF & FEIL: Emotion and Intensity Lexicons for Finnish
Apr 28, 2021



Abstract:This paper introduces a Sentiment and Emotion Lexicon for Finnish (SELF) and a Finnish Emotion Intensity Lexicon (FEIL). We describe the lexicon creation process and evaluate the lexicon using some commonly available tools. The lexicon uses annotations projected from the NRC Emotion Lexicon with carefully edited translations. To our knowledge, this is the first comprehensive sentiment and emotion lexicon for Finnish.
XED: A Multilingual Dataset for Sentiment Analysis and Emotion Detection
Nov 06, 2020



Abstract:We introduce XED, a multilingual fine-grained emotion dataset. The dataset consists of human-annotated Finnish (25k) and English sentences (30k), as well as projected annotations for 30 additional languages, providing new resources for many low-resource languages. We use Plutchik's core emotions to annotate the dataset with the addition of neutral to create a multilabel multiclass dataset. The dataset is carefully evaluated using language-specific BERT models and SVMs to show that XED performs on par with other similar datasets and is therefore a useful tool for sentiment analysis and emotion detection.
LT@Helsinki at SemEval-2020 Task 12: Multilingual or language-specific BERT?
Aug 03, 2020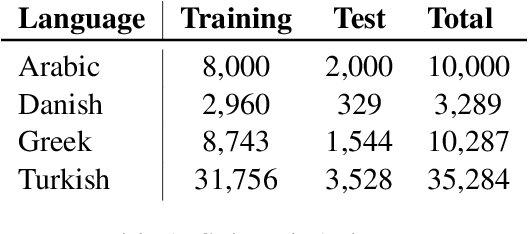

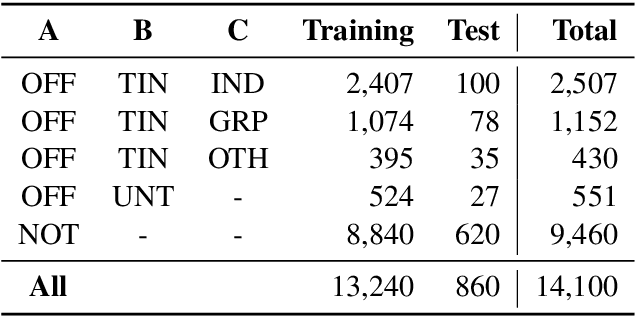

Abstract:This paper presents the different models submitted by the LT@Helsinki team for the SemEval 2020 Shared Task 12. Our team participated in sub-tasks A and C; titled offensive language identification and offense target identification, respectively. In both cases we used the so-called Bidirectional Encoder Representation from Transformer (BERT), a model pre-trained by Google and fine-tuned by us on the OLID and SOLID datasets. The results show that offensive tweet classification is one of several language-based tasks where BERT can achieve state-of-the-art results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge