Elena Gal
Domain Generalization with Small Data
Feb 09, 2024



Abstract:In this work, we propose to tackle the problem of domain generalization in the context of \textit{insufficient samples}. Instead of extracting latent feature embeddings based on deterministic models, we propose to learn a domain-invariant representation based on the probabilistic framework by mapping each data point into probabilistic embeddings. Specifically, we first extend empirical maximum mean discrepancy (MMD) to a novel probabilistic MMD that can measure the discrepancy between mixture distributions (i.e., source domains) consisting of a series of latent distributions rather than latent points. Moreover, instead of imposing the contrastive semantic alignment (CSA) loss based on pairs of latent points, a novel probabilistic CSA loss encourages positive probabilistic embedding pairs to be closer while pulling other negative ones apart. Benefiting from the learned representation captured by probabilistic models, our proposed method can marriage the measurement on the \textit{distribution over distributions} (i.e., the global perspective alignment) and the distribution-based contrastive semantic alignment (i.e., the local perspective alignment). Extensive experimental results on three challenging medical datasets show the effectiveness of our proposed method in the context of insufficient data compared with state-of-the-art methods.
Unbiased Decisions Reduce Regret: Adversarial Domain Adaptation for the Bank Loan Problem
Aug 15, 2023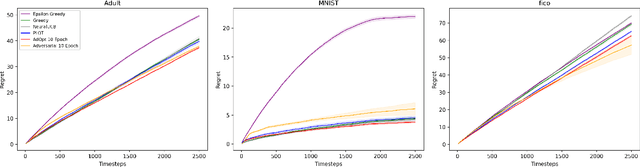
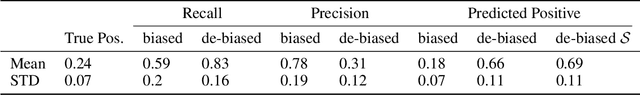
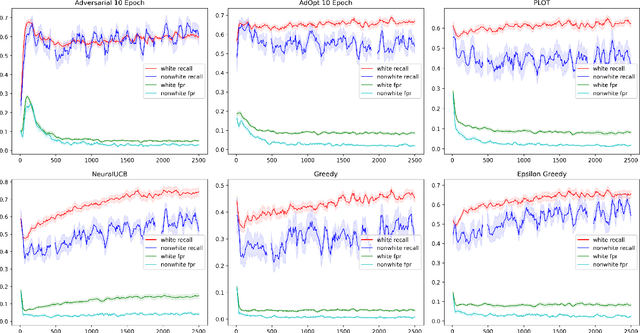

Abstract:In many real world settings binary classification decisions are made based on limited data in near real-time, e.g. when assessing a loan application. We focus on a class of these problems that share a common feature: the true label is only observed when a data point is assigned a positive label by the principal, e.g. we only find out whether an applicant defaults if we accepted their loan application. As a consequence, the false rejections become self-reinforcing and cause the labelled training set, that is being continuously updated by the model decisions, to accumulate bias. Prior work mitigates this effect by injecting optimism into the model, however this comes at the cost of increased false acceptance rate. We introduce adversarial optimism (AdOpt) to directly address bias in the training set using adversarial domain adaptation. The goal of AdOpt is to learn an unbiased but informative representation of past data, by reducing the distributional shift between the set of accepted data points and all data points seen thus far. AdOpt significantly exceeds state-of-the-art performance on a set of challenging benchmark problems. Our experiments also provide initial evidence that the introduction of adversarial domain adaptation improves fairness in this setting.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge