Ekta Vats
Exploiting the Asymmetric Uncertainty Structure of Pre-trained VLMs on the Unit Hypersphere
May 16, 2025Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) as foundation models have significantly enhanced performance across a wide range of visual and textual tasks, without requiring large-scale training from scratch for downstream tasks. However, these deterministic VLMs fail to capture the inherent ambiguity and uncertainty in natural language and visual data. Recent probabilistic post-hoc adaptation methods address this by mapping deterministic embeddings onto probability distributions; however, existing approaches do not account for the asymmetric uncertainty structure of the modalities, and the constraint that meaningful deterministic embeddings reside on a unit hypersphere, potentially leading to suboptimal performance. In this paper, we address the asymmetric uncertainty structure inherent in textual and visual data, and propose AsymVLM to build probabilistic embeddings from pre-trained VLMs on the unit hypersphere, enabling uncertainty quantification. We validate the effectiveness of the probabilistic embeddings on established benchmarks, and present comprehensive ablation studies demonstrating the inherent nature of asymmetry in the uncertainty structure of textual and visual data.
Cutup and Detect: Human Fall Detection on Cutup Untrimmed Videos Using a Large Foundational Video Understanding Model
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:This work explores the performance of a large video understanding foundation model on the downstream task of human fall detection on untrimmed video and leverages a pretrained vision transformer for multi-class action detection, with classes: "Fall", "Lying" and "Other/Activities of daily living (ADL)". A method for temporal action localization that relies on a simple cutup of untrimmed videos is demonstrated. The methodology includes a preprocessing pipeline that converts datasets with timestamp action annotations into labeled datasets of short action clips. Simple and effective clip-sampling strategies are introduced. The effectiveness of the proposed method has been empirically evaluated on the publicly available High-Quality Fall Simulation Dataset (HQFSD). The experimental results validate the performance of the proposed pipeline. The results are promising for real-time application, and the falls are detected on video level with a state-of-the-art 0.96 F1 score on the HQFSD dataset under the given experimental settings. The source code will be made available on GitHub.
Marginalia and machine learning: Handwritten text recognition for Marginalia Collections
Mar 10, 2023



Abstract:The pressing need for digitization of historical document collections has led to a strong interest in designing computerised image processing methods for automatic handwritten text recognition (HTR). Handwritten text possesses high variability due to different writing styles, languages and scripts. Training an accurate and robust HTR system calls for data-efficient approaches due to the unavailability of sufficient amounts of annotated multi-writer text. A case study on an ongoing project ``Marginalia and Machine Learning" is presented here that focuses on automatic detection and recognition of handwritten marginalia texts i.e., text written in margins or handwritten notes. Faster R-CNN network is used for detection of marginalia and AttentionHTR is used for word recognition. The data comes from early book collections (printed) found in the Uppsala University Library, with handwritten marginalia texts. Source code and pretrained models are available at https://github.com/ektavats/Project-Marginalia.
Paired Image to Image Translation for Strikethrough Removal From Handwritten Words
Jan 24, 2022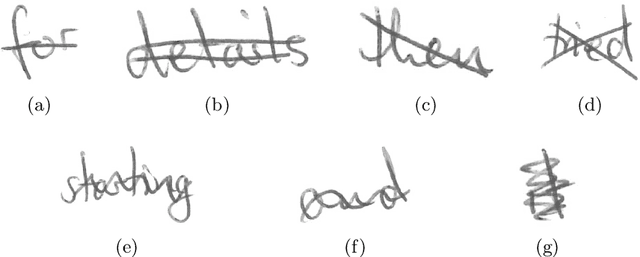
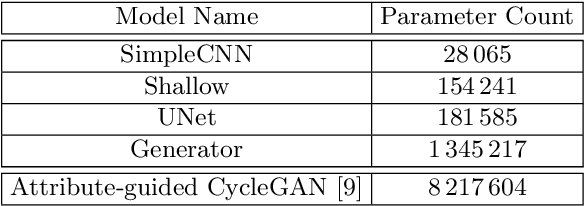
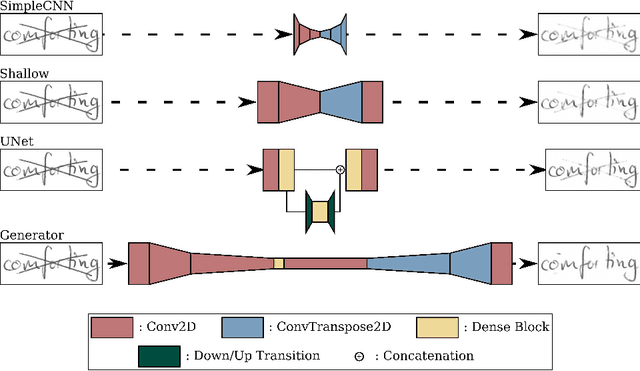

Abstract:Transcribing struck-through, handwritten words, for example for the purpose of genetic criticism, can pose a challenge to both humans and machines, due to the obstructive properties of the superimposed strokes. This paper investigates the use of paired image to image translation approaches to remove strikethrough strokes from handwritten words. Four different neural network architectures are examined, ranging from a few simple convolutional layers to deeper ones, employing Dense blocks. Experimental results, obtained from one synthetic and one genuine paired strikethrough dataset, confirm that the proposed paired models outperform the CycleGAN-based state of the art, while using less than a sixth of the trainable parameters.
AttentionHTR: Handwritten Text Recognition Based on Attention Encoder-Decoder Networks
Jan 23, 2022


Abstract:This work proposes an attention-based sequence-to-sequence model for handwritten word recognition and explores transfer learning for data-efficient training of HTR systems. To overcome training data scarcity, this work leverages models pre-trained on scene text images as a starting point towards tailoring the handwriting recognition models. ResNet feature extraction and bidirectional LSTM-based sequence modeling stages together form an encoder. The prediction stage consists of a decoder and a content-based attention mechanism. The effectiveness of the proposed end-to-end HTR system has been empirically evaluated on a novel multi-writer dataset Imgur5K and the IAM dataset. The experimental results evaluate the performance of the HTR framework, further supported by an in-depth analysis of the error cases. Source code and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/dmitrijsk/AttentionHTR.
Radial Line Fourier Descriptor for Historical Handwritten Text Representation
Mar 20, 2018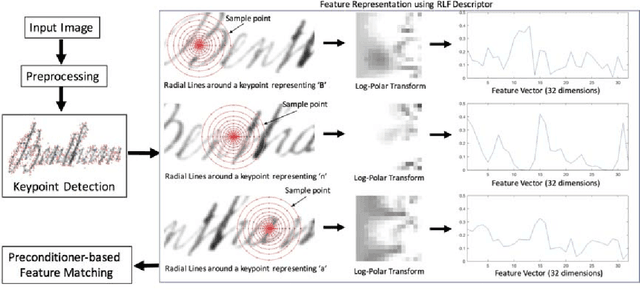



Abstract:Automatic recognition of historical handwritten manuscripts is a daunting task due to paper degradation over time. Recognition-free retrieval or word spotting is popularly used for information retrieval and digitization of the historical handwritten documents. However, the performance of word spotting algorithms depends heavily on feature detection and representation methods. Although there exist popular feature descriptors such as Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) and Speeded Up Robust Features (SURF), the invariant properties of these descriptors amplify the noise in the degraded document images, rendering them more sensitive to noise and complex characteristics of historical manuscripts. Therefore, an efficient and relaxed feature descriptor is required as handwritten words across different documents are indeed similar, but not identical. This paper introduces a Radial Line Fourier (RLF) descriptor for handwritten word representation, with a short feature vector of 32 dimensions. A segmentation-free and training-free handwritten word spotting method is studied herein that relies on the proposed RLF descriptor, takes into account different keypoint representations and uses a simple preconditioner-based feature matching algorithm. The effectiveness of the RLF descriptor for segmentation-free handwritten word spotting is empirically evaluated on well-known historical handwritten datasets using standard evaluation measures.
Learning Surrogate Models of Document Image Quality Metrics for Automated Document Image Processing
Dec 11, 2017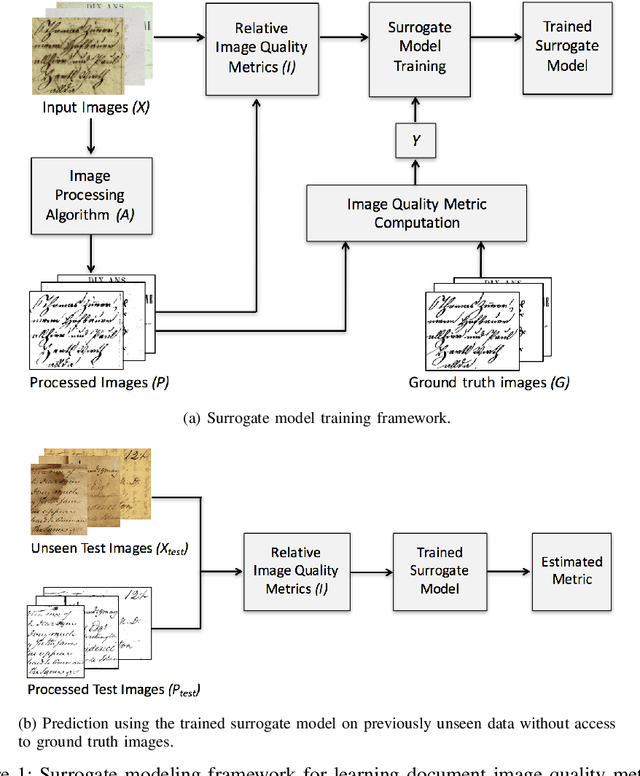



Abstract:Computation of document image quality metrics often depends upon the availability of a ground truth image corresponding to the document. This limits the applicability of quality metrics in applications such as hyperparameter optimization of image processing algorithms that operate on-the-fly on unseen documents. This work proposes the use of surrogate models to learn the behavior of a given document quality metric on existing datasets where ground truth images are available. The trained surrogate model can later be used to predict the metric value on previously unseen document images without requiring access to ground truth images. The surrogate model is empirically evaluated on the Document Image Binarization Competition (DIBCO) and the Handwritten Document Image Binarization Competition (H-DIBCO) datasets.
TexT - Text Extractor Tool for Handwritten Document Transcription and Annotation
Nov 22, 2017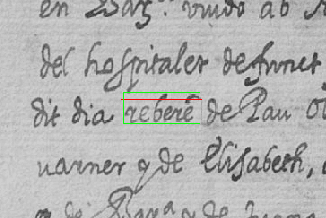


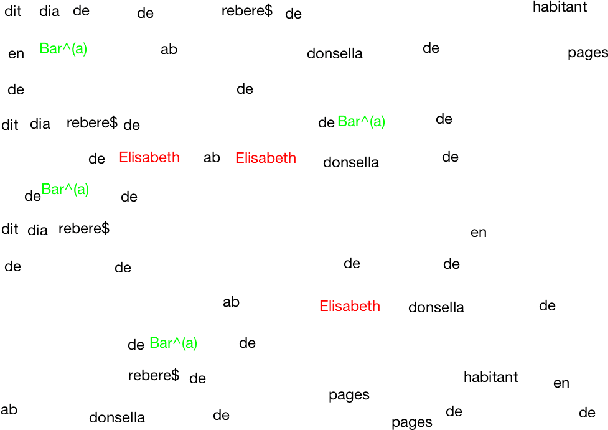
Abstract:This paper presents a framework for semi-automatic transcription of large-scale historical handwritten documents and proposes a simple user-friendly text extractor tool, TexT for transcription. The proposed approach provides a quick and easy transcription of text using computer assisted interactive technique. The algorithm finds multiple occurrences of the marked text on-the-fly using a word spotting system. TexT is also capable of performing on-the-fly annotation of handwritten text with automatic generation of ground truth labels, and dynamic adjustment and correction of user generated bounding box annotations with the word being perfectly encapsulated. The user can view the document and the found words in the original form or with background noise removed for easier visualization of transcription results. The effectiveness of TexT is demonstrated on an archival manuscript collection from well-known publicly available dataset.
Automatic Document Image Binarization using Bayesian Optimization
Oct 21, 2017



Abstract:Document image binarization is often a challenging task due to various forms of degradation. Although there exist several binarization techniques in literature, the binarized image is typically sensitive to control parameter settings of the employed technique. This paper presents an automatic document image binarization algorithm to segment the text from heavily degraded document images. The proposed technique uses a two band-pass filtering approach for background noise removal, and Bayesian optimization for automatic hyperparameter selection for optimal results. The effectiveness of the proposed binarization technique is empirically demonstrated on the Document Image Binarization Competition (DIBCO) and the Handwritten Document Image Binarization Competition (H-DIBCO) datasets.
Fuzzy human motion analysis: A review
Dec 02, 2014

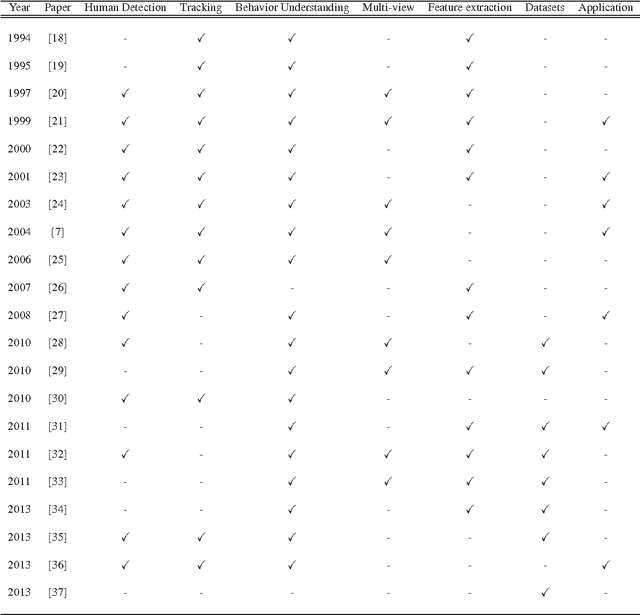

Abstract:Human Motion Analysis (HMA) is currently one of the most popularly active research domains as such significant research interests are motivated by a number of real world applications such as video surveillance, sports analysis, healthcare monitoring and so on. However, most of these real world applications face high levels of uncertainties that can affect the operations of such applications. Hence, the fuzzy set theory has been applied and showed great success in the recent past. In this paper, we aim at reviewing the fuzzy set oriented approaches for HMA, individuating how the fuzzy set may improve the HMA, envisaging and delineating the future perspectives. To the best of our knowledge, there is not found a single survey in the current literature that has discussed and reviewed fuzzy approaches towards the HMA. For ease of understanding, we conceptually classify the human motion into three broad levels: Low-Level (LoL), Mid-Level (MiL), and High-Level (HiL) HMA.
* Accepted in Pattern Recognition, first survey paper that discusses and reviews fuzzy approaches towards HMA
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge