Ehsan Degan
Chain-of-Descriptions: Improving Code LLMs for VHDL Code Generation and Summarization
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have become widely used across diverse NLP tasks and domains, demonstrating their adaptability and effectiveness. In the realm of Electronic Design Automation (EDA), LLMs show promise for tasks like Register-Transfer Level (RTL) code generation and summarization. However, despite the proliferation of LLMs for general code-related tasks, there's a dearth of research focused on evaluating and refining these models for hardware description languages (HDLs), notably VHDL. In this study, we evaluate the performance of existing code LLMs for VHDL code generation and summarization using various metrics and two datasets -- VHDL-Eval and VHDL-Xform. The latter, an in-house dataset, aims to gauge LLMs' understanding of functionally equivalent code. Our findings reveal consistent underperformance of these models across different metrics, underscoring a significant gap in their suitability for this domain. To address this challenge, we propose Chain-of-Descriptions (CoDes), a novel approach to enhance the performance of LLMs for VHDL code generation and summarization tasks. CoDes involves generating a series of intermediate descriptive steps based on: (i) the problem statement for code generation, and (ii) the VHDL code for summarization. These steps are then integrated with the original input prompt (problem statement or code) and provided as input to the LLMs to generate the final output. Our experiments demonstrate that the CoDes approach significantly surpasses the standard prompting strategy across various metrics on both datasets. This method not only improves the quality of VHDL code generation and summarization but also serves as a framework for future research aimed at enhancing code LLMs for VHDL.
DECASTE: Unveiling Caste Stereotypes in Large Language Models through Multi-Dimensional Bias Analysis
May 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing (NLP) and expanded their applications across diverse domains. However, despite their impressive capabilities, LLMs have been shown to reflect and perpetuate harmful societal biases, including those based on ethnicity, gender, and religion. A critical and underexplored issue is the reinforcement of caste-based biases, particularly towards India's marginalized caste groups such as Dalits and Shudras. In this paper, we address this gap by proposing DECASTE, a novel, multi-dimensional framework designed to detect and assess both implicit and explicit caste biases in LLMs. Our approach evaluates caste fairness across four dimensions: socio-cultural, economic, educational, and political, using a range of customized prompting strategies. By benchmarking several state-of-the-art LLMs, we reveal that these models systematically reinforce caste biases, with significant disparities observed in the treatment of oppressed versus dominant caste groups. For example, bias scores are notably elevated when comparing Dalits and Shudras with dominant caste groups, reflecting societal prejudices that persist in model outputs. These results expose the subtle yet pervasive caste biases in LLMs and emphasize the need for more comprehensive and inclusive bias evaluation methodologies that assess the potential risks of deploying such models in real-world contexts.
Self-Regulated Data-Free Knowledge Amalgamation for Text Classification
Jun 16, 2024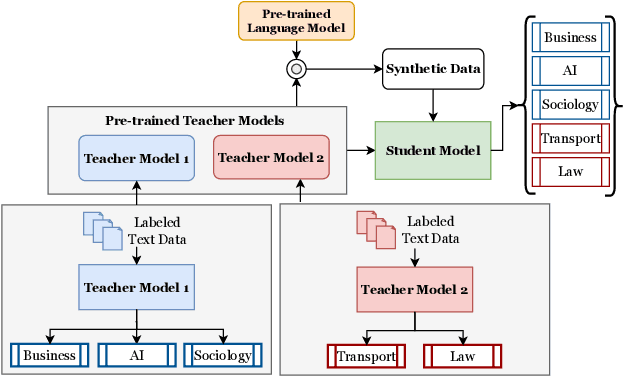
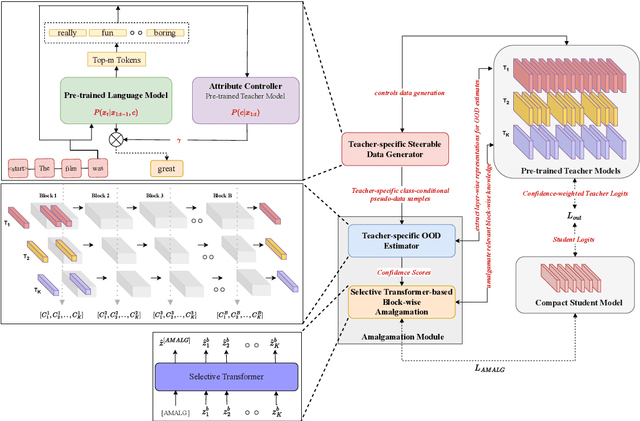
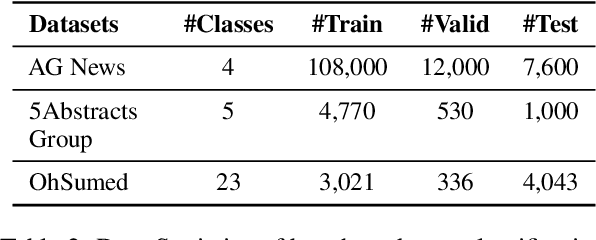
Abstract:Recently, there has been a growing availability of pre-trained text models on various model repositories. These models greatly reduce the cost of training new models from scratch as they can be fine-tuned for specific tasks or trained on large datasets. However, these datasets may not be publicly accessible due to the privacy, security, or intellectual property issues. In this paper, we aim to develop a lightweight student network that can learn from multiple teacher models without accessing their original training data. Hence, we investigate Data-Free Knowledge Amalgamation (DFKA), a knowledge-transfer task that combines insights from multiple pre-trained teacher models and transfers them effectively to a compact student network. To accomplish this, we propose STRATANET, a modeling framework comprising: (a) a steerable data generator that produces text data tailored to each teacher and (b) an amalgamation module that implements a self-regulative strategy using confidence estimates from the teachers' different layers to selectively integrate their knowledge and train a versatile student. We evaluate our method on three benchmark text classification datasets with varying labels or domains. Empirically, we demonstrate that the student model learned using our STRATANET outperforms several baselines significantly under data-driven and data-free constraints.
VHDL-Eval: A Framework for Evaluating Large Language Models in VHDL Code Generation
Jun 06, 2024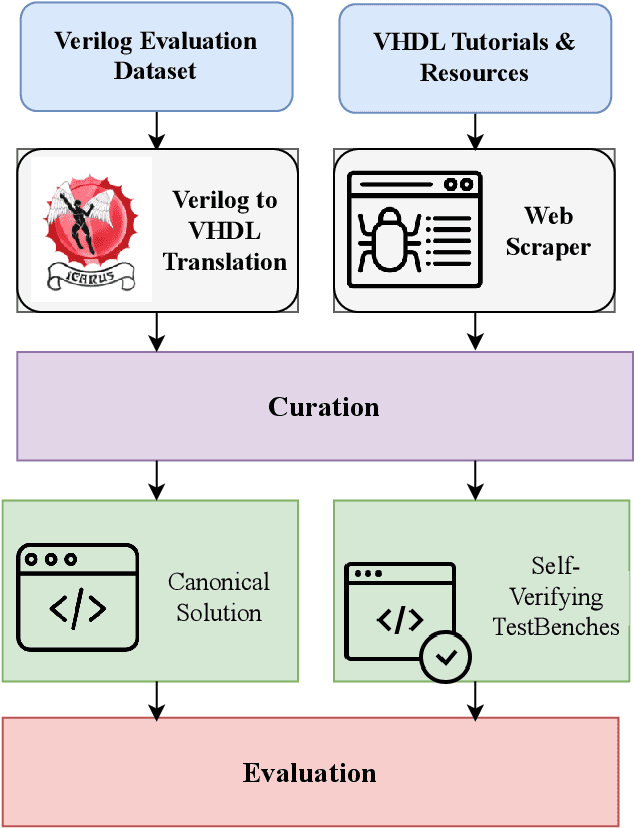

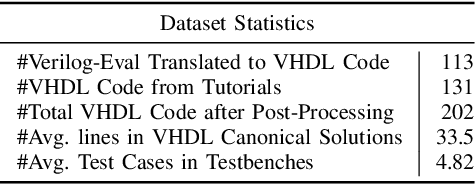
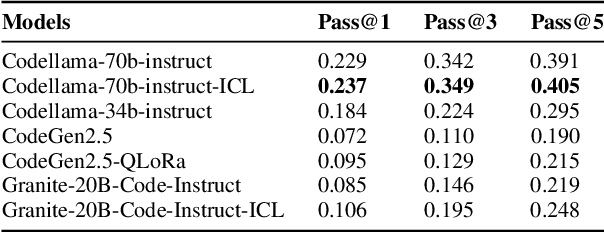
Abstract:With the unprecedented advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), their application domains have expanded to include code generation tasks across various programming languages. While significant progress has been made in enhancing LLMs for popular programming languages, there exists a notable gap in comprehensive evaluation frameworks tailored for Hardware Description Languages (HDLs), particularly VHDL. This paper addresses this gap by introducing a comprehensive evaluation framework designed specifically for assessing LLM performance in VHDL code generation task. We construct a dataset for evaluating LLMs on VHDL code generation task. This dataset is constructed by translating a collection of Verilog evaluation problems to VHDL and aggregating publicly available VHDL problems, resulting in a total of 202 problems. To assess the functional correctness of the generated VHDL code, we utilize a curated set of self-verifying testbenches specifically designed for those aggregated VHDL problem set. We conduct an initial evaluation of different LLMs and their variants, including zero-shot code generation, in-context learning (ICL), and Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods. Our findings underscore the considerable challenges faced by existing LLMs in VHDL code generation, revealing significant scope for improvement. This study emphasizes the necessity of supervised fine-tuning code generation models specifically for VHDL, offering potential benefits to VHDL designers seeking efficient code generation solutions.
PROMINET: Prototype-based Multi-View Network for Interpretable Email Response Prediction
Oct 25, 2023
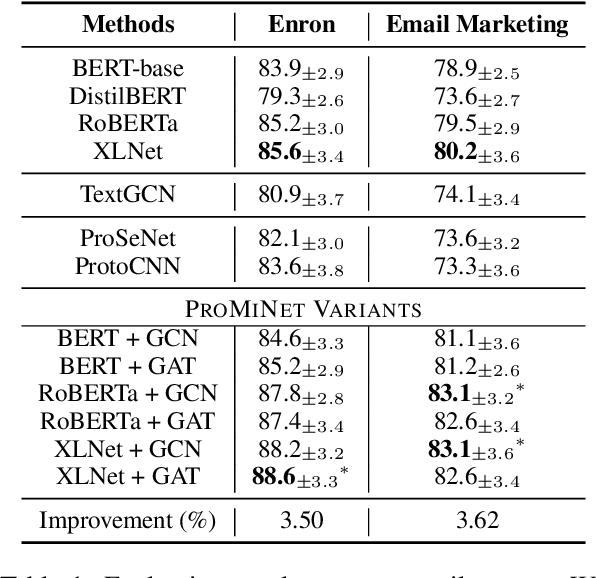
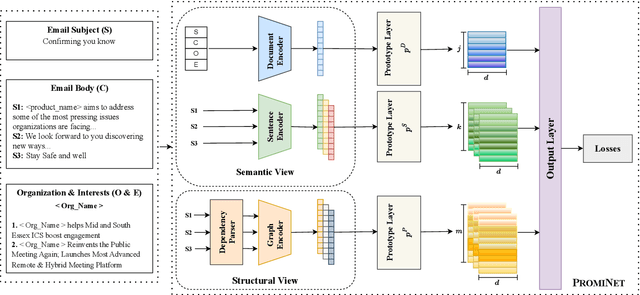
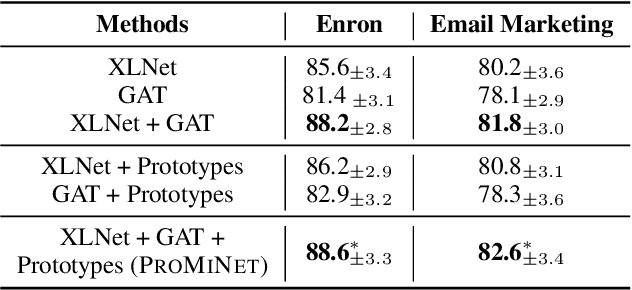
Abstract:Email is a widely used tool for business communication, and email marketing has emerged as a cost-effective strategy for enterprises. While previous studies have examined factors affecting email marketing performance, limited research has focused on understanding email response behavior by considering email content and metadata. This study proposes a Prototype-based Multi-view Network (PROMINET) that incorporates semantic and structural information from email data. By utilizing prototype learning, the PROMINET model generates latent exemplars, enabling interpretable email response prediction. The model maps learned semantic and structural exemplars to observed samples in the training data at different levels of granularity, such as document, sentence, or phrase. The approach is evaluated on two real-world email datasets: the Enron corpus and an in-house Email Marketing corpus. Experimental results demonstrate that the PROMINET model outperforms baseline models, achieving a ~3% improvement in F1 score on both datasets. Additionally, the model provides interpretability through prototypes at different granularity levels while maintaining comparable performance to non-interpretable models. The learned prototypes also show potential for generating suggestions to enhance email text editing and improve the likelihood of effective email responses. This research contributes to enhancing sender-receiver communication and customer engagement in email interactions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge