Ebrahim Bagheri
Toronto Metropolitan University, Canada
exHarmony: Authorship and Citations for Benchmarking the Reviewer Assignment Problem
Feb 11, 2025



Abstract:The peer review process is crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of scholarly work, yet assigning suitable reviewers remains a significant challenge. Traditional manual methods are labor-intensive and often ineffective, leading to nonconstructive or biased reviews. This paper introduces the exHarmony (eHarmony but for connecting experts to manuscripts) benchmark, designed to address these challenges by re-imagining the Reviewer Assignment Problem (RAP) as a retrieval task. Utilizing the extensive data from OpenAlex, we propose a novel approach that considers a host of signals from the authors, most similar experts, and the citation relations as potential indicators for a suitable reviewer for a manuscript. This approach allows us to develop a standard benchmark dataset for evaluating the reviewer assignment problem without needing explicit labels. We benchmark various methods, including traditional lexical matching, static neural embeddings, and contextualized neural embeddings, and introduce evaluation metrics that assess both relevance and diversity in the context of RAP. Our results indicate that while traditional methods perform reasonably well, contextualized embeddings trained on scholarly literature show the best performance. The findings underscore the importance of further research to enhance the diversity and effectiveness of reviewer assignments.
Benchmarking Prompt Sensitivity in Large Language Models
Feb 09, 2025
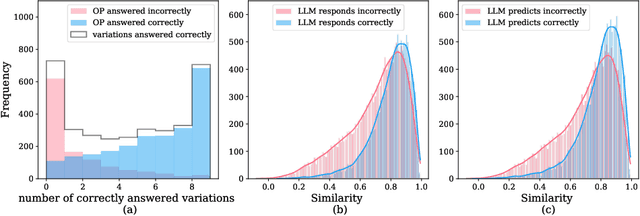
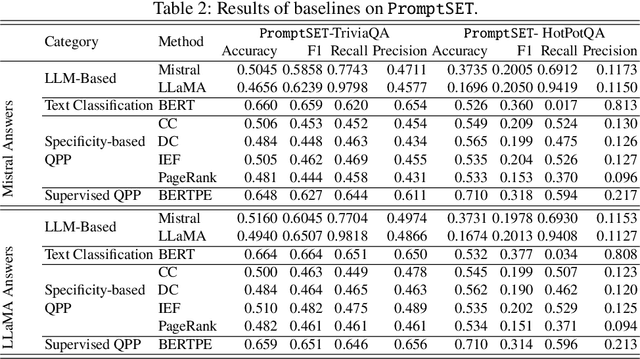
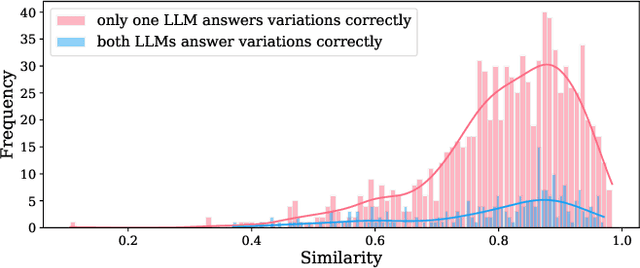
Abstract:Large language Models (LLMs) are highly sensitive to variations in prompt formulation, which can significantly impact their ability to generate accurate responses. In this paper, we introduce a new task, Prompt Sensitivity Prediction, and a dataset PromptSET designed to investigate the effects of slight prompt variations on LLM performance. Using TriviaQA and HotpotQA datasets as the foundation of our work, we generate prompt variations and evaluate their effectiveness across multiple LLMs. We benchmark the prompt sensitivity prediction task employing state-of-the-art methods from related tasks, including LLM-based self-evaluation, text classification, and query performance prediction techniques. Our findings reveal that existing methods struggle to effectively address prompt sensitivity prediction, underscoring the need to understand how information needs should be phrased for accurate LLM responses.
EMPRA: Embedding Perturbation Rank Attack against Neural Ranking Models
Dec 20, 2024



Abstract:Recent research has shown that neural information retrieval techniques may be susceptible to adversarial attacks. Adversarial attacks seek to manipulate the ranking of documents, with the intention of exposing users to targeted content. In this paper, we introduce the Embedding Perturbation Rank Attack (EMPRA) method, a novel approach designed to perform adversarial attacks on black-box Neural Ranking Models (NRMs). EMPRA manipulates sentence-level embeddings, guiding them towards pertinent context related to the query while preserving semantic integrity. This process generates adversarial texts that seamlessly integrate with the original content and remain imperceptible to humans. Our extensive evaluation conducted on the widely-used MS MARCO V1 passage collection demonstrate the effectiveness of EMPRA against a wide range of state-of-the-art baselines in promoting a specific set of target documents within a given ranked results. Specifically, EMPRA successfully achieves a re-ranking of almost 96% of target documents originally ranked between 51-100 to rank within the top 10. Furthermore, EMPRA does not depend on surrogate models for adversarial text generation, enhancing its robustness against different NRMs in realistic settings.
Reviewer assignment problem: A scoping review
May 13, 2023



Abstract:Peer review is an integral component of scientific research. The quality of peer review, and consequently the published research, depends to a large extent on the ability to recruit adequate reviewers for submitted papers. However, finding such reviewers is an increasingly difficult task due to several factors, such as the continuous increase both in the production of scientific papers and the workload of scholars. To mitigate these challenges, solutions for automated association of papers with "well matching" reviewers - the task often referred to as reviewer assignment problem (RAP) - have been the subject of research for thirty years now. Even though numerous solutions have been suggested, to our knowledge, a recent systematic synthesis of the RAP-related literature is missing. To fill this gap and support further RAP-related research, in this paper, we present a scoping review of computational approaches for addressing RAP. Following the latest methodological guidance for scoping reviews, we have collected recent literature on RAP from three databases (Scopus, Google Scholar, DBLP) and, after applying the eligibility criteria, retained 26 studies for extracting and synthesising data on several aspects of RAP research including: i) the overall framing of and approach to RAP; ii) the criteria for reviewer selection; iii) the modelling of candidate reviewers and submissions; iv) the computational methods for matching reviewers and submissions; and v) the methods for evaluating the performance of the proposed solutions. The paper summarises and discusses the findings for each of the aforementioned aspects of RAP research and suggests future research directions.
Open Information Extraction
Jul 10, 2016



Abstract:Open Information Extraction (Open IE) systems aim to obtain relation tuples with highly scalable extraction in portable across domain by identifying a variety of relation phrases and their arguments in arbitrary sentences. The first generation of Open IE learns linear chain models based on unlexicalized features such as Part-of-Speech (POS) or shallow tags to label the intermediate words between pair of potential arguments for identifying extractable relations. Open IE currently is developed in the second generation that is able to extract instances of the most frequently observed relation types such as Verb, Noun and Prep, Verb and Prep, and Infinitive with deep linguistic analysis. They expose simple yet principled ways in which verbs express relationships in linguistics such as verb phrase-based extraction or clause-based extraction. They obtain a significantly higher performance over previous systems in the first generation. In this paper, we describe an overview of two Open IE generations including strengths, weaknesses and application areas.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge