Dongyue Lu
The RoboSense Challenge: Sense Anything, Navigate Anywhere, Adapt Across Platforms
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Autonomous systems are increasingly deployed in open and dynamic environments -- from city streets to aerial and indoor spaces -- where perception models must remain reliable under sensor noise, environmental variation, and platform shifts. However, even state-of-the-art methods often degrade under unseen conditions, highlighting the need for robust and generalizable robot sensing. The RoboSense 2025 Challenge is designed to advance robustness and adaptability in robot perception across diverse sensing scenarios. It unifies five complementary research tracks spanning language-grounded decision making, socially compliant navigation, sensor configuration generalization, cross-view and cross-modal correspondence, and cross-platform 3D perception. Together, these tasks form a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating real-world sensing reliability under domain shifts, sensor failures, and platform discrepancies. RoboSense 2025 provides standardized datasets, baseline models, and unified evaluation protocols, enabling large-scale and reproducible comparison of robust perception methods. The challenge attracted 143 teams from 85 institutions across 16 countries, reflecting broad community engagement. By consolidating insights from 23 winning solutions, this report highlights emerging methodological trends, shared design principles, and open challenges across all tracks, marking a step toward building robots that can sense reliably, act robustly, and adapt across platforms in real-world environments.
WorldLens: Full-Spectrum Evaluations of Driving World Models in Real World
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Generative world models are reshaping embodied AI, enabling agents to synthesize realistic 4D driving environments that look convincing but often fail physically or behaviorally. Despite rapid progress, the field still lacks a unified way to assess whether generated worlds preserve geometry, obey physics, or support reliable control. We introduce WorldLens, a full-spectrum benchmark evaluating how well a model builds, understands, and behaves within its generated world. It spans five aspects -- Generation, Reconstruction, Action-Following, Downstream Task, and Human Preference -- jointly covering visual realism, geometric consistency, physical plausibility, and functional reliability. Across these dimensions, no existing world model excels universally: those with strong textures often violate physics, while geometry-stable ones lack behavioral fidelity. To align objective metrics with human judgment, we further construct WorldLens-26K, a large-scale dataset of human-annotated videos with numerical scores and textual rationales, and develop WorldLens-Agent, an evaluation model distilled from these annotations to enable scalable, explainable scoring. Together, the benchmark, dataset, and agent form a unified ecosystem for measuring world fidelity -- standardizing how future models are judged not only by how real they look, but by how real they behave.
SEE4D: Pose-Free 4D Generation via Auto-Regressive Video Inpainting
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Immersive applications call for synthesizing spatiotemporal 4D content from casual videos without costly 3D supervision. Existing video-to-4D methods typically rely on manually annotated camera poses, which are labor-intensive and brittle for in-the-wild footage. Recent warp-then-inpaint approaches mitigate the need for pose labels by warping input frames along a novel camera trajectory and using an inpainting model to fill missing regions, thereby depicting the 4D scene from diverse viewpoints. However, this trajectory-to-trajectory formulation often entangles camera motion with scene dynamics and complicates both modeling and inference. We introduce SEE4D, a pose-free, trajectory-to-camera framework that replaces explicit trajectory prediction with rendering to a bank of fixed virtual cameras, thereby separating camera control from scene modeling. A view-conditional video inpainting model is trained to learn a robust geometry prior by denoising realistically synthesized warped images and to inpaint occluded or missing regions across virtual viewpoints, eliminating the need for explicit 3D annotations. Building on this inpainting core, we design a spatiotemporal autoregressive inference pipeline that traverses virtual-camera splines and extends videos with overlapping windows, enabling coherent generation at bounded per-step complexity. We validate See4D on cross-view video generation and sparse reconstruction benchmarks. Across quantitative metrics and qualitative assessments, our method achieves superior generalization and improved performance relative to pose- or trajectory-conditioned baselines, advancing practical 4D world modeling from casual videos.
Visual Grounding from Event Cameras
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Event cameras capture changes in brightness with microsecond precision and remain reliable under motion blur and challenging illumination, offering clear advantages for modeling highly dynamic scenes. Yet, their integration with natural language understanding has received little attention, leaving a gap in multimodal perception. To address this, we introduce Talk2Event, the first large-scale benchmark for language-driven object grounding using event data. Built on real-world driving scenarios, Talk2Event comprises 5,567 scenes, 13,458 annotated objects, and more than 30,000 carefully validated referring expressions. Each expression is enriched with four structured attributes -- appearance, status, relation to the viewer, and relation to surrounding objects -- that explicitly capture spatial, temporal, and relational cues. This attribute-centric design supports interpretable and compositional grounding, enabling analysis that moves beyond simple object recognition to contextual reasoning in dynamic environments. We envision Talk2Event as a foundation for advancing multimodal and temporally-aware perception, with applications spanning robotics, human-AI interaction, and so on.
Perspective-Invariant 3D Object Detection
Jul 23, 2025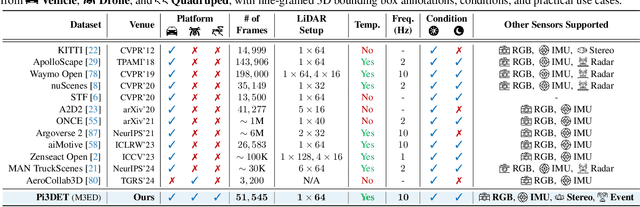
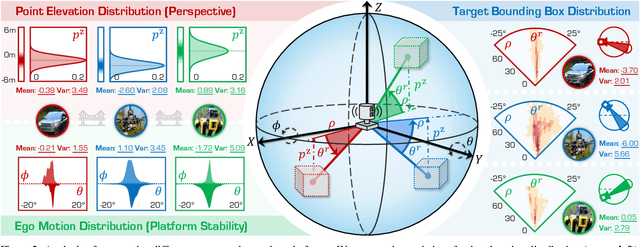
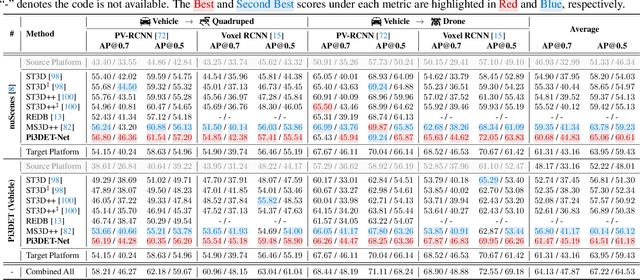
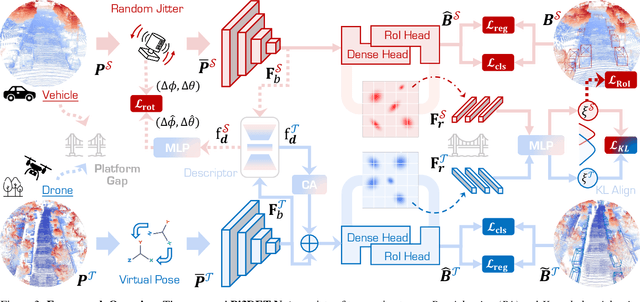
Abstract:With the rise of robotics, LiDAR-based 3D object detection has garnered significant attention in both academia and industry. However, existing datasets and methods predominantly focus on vehicle-mounted platforms, leaving other autonomous platforms underexplored. To bridge this gap, we introduce Pi3DET, the first benchmark featuring LiDAR data and 3D bounding box annotations collected from multiple platforms: vehicle, quadruped, and drone, thereby facilitating research in 3D object detection for non-vehicle platforms as well as cross-platform 3D detection. Based on Pi3DET, we propose a novel cross-platform adaptation framework that transfers knowledge from the well-studied vehicle platform to other platforms. This framework achieves perspective-invariant 3D detection through robust alignment at both geometric and feature levels. Additionally, we establish a benchmark to evaluate the resilience and robustness of current 3D detectors in cross-platform scenarios, providing valuable insights for developing adaptive 3D perception systems. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of our approach on challenging cross-platform tasks, demonstrating substantial gains over existing adaptation methods. We hope this work paves the way for generalizable and unified 3D perception systems across diverse and complex environments. Our Pi3DET dataset, cross-platform benchmark suite, and annotation toolkit have been made publicly available.
Talk2Event: Grounded Understanding of Dynamic Scenes from Event Cameras
Jul 23, 2025Abstract:Event cameras offer microsecond-level latency and robustness to motion blur, making them ideal for understanding dynamic environments. Yet, connecting these asynchronous streams to human language remains an open challenge. We introduce Talk2Event, the first large-scale benchmark for language-driven object grounding in event-based perception. Built from real-world driving data, we provide over 30,000 validated referring expressions, each enriched with four grounding attributes -- appearance, status, relation to viewer, and relation to other objects -- bridging spatial, temporal, and relational reasoning. To fully exploit these cues, we propose EventRefer, an attribute-aware grounding framework that dynamically fuses multi-attribute representations through a Mixture of Event-Attribute Experts (MoEE). Our method adapts to different modalities and scene dynamics, achieving consistent gains over state-of-the-art baselines in event-only, frame-only, and event-frame fusion settings. We hope our dataset and approach will establish a foundation for advancing multimodal, temporally-aware, and language-driven perception in real-world robotics and autonomy.
Reconstructing Close Human Interaction with Appearance and Proxemics Reasoning
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Due to visual ambiguities and inter-person occlusions, existing human pose estimation methods cannot recover plausible close interactions from in-the-wild videos. Even state-of-the-art large foundation models~(\eg, SAM) cannot accurately distinguish human semantics in such challenging scenarios. In this work, we find that human appearance can provide a straightforward cue to address these obstacles. Based on this observation, we propose a dual-branch optimization framework to reconstruct accurate interactive motions with plausible body contacts constrained by human appearances, social proxemics, and physical laws. Specifically, we first train a diffusion model to learn the human proxemic behavior and pose prior knowledge. The trained network and two optimizable tensors are then incorporated into a dual-branch optimization framework to reconstruct human motions and appearances. Several constraints based on 3D Gaussians, 2D keypoints, and mesh penetrations are also designed to assist the optimization. With the proxemics prior and diverse constraints, our method is capable of estimating accurate interactions from in-the-wild videos captured in complex environments. We further build a dataset with pseudo ground-truth interaction annotations, which may promote future research on pose estimation and human behavior understanding. Experimental results on several benchmarks demonstrate that our method outperforms existing approaches. The code and data are available at https://www.buzhenhuang.com/works/CloseApp.html.
SPIRAL: Semantic-Aware Progressive LiDAR Scene Generation
May 28, 2025Abstract:Leveraging recent diffusion models, LiDAR-based large-scale 3D scene generation has achieved great success. While recent voxel-based approaches can generate both geometric structures and semantic labels, existing range-view methods are limited to producing unlabeled LiDAR scenes. Relying on pretrained segmentation models to predict the semantic maps often results in suboptimal cross-modal consistency. To address this limitation while preserving the advantages of range-view representations, such as computational efficiency and simplified network design, we propose Spiral, a novel range-view LiDAR diffusion model that simultaneously generates depth, reflectance images, and semantic maps. Furthermore, we introduce novel semantic-aware metrics to evaluate the quality of the generated labeled range-view data. Experiments on the SemanticKITTI and nuScenes datasets demonstrate that Spiral achieves state-of-the-art performance with the smallest parameter size, outperforming two-step methods that combine the generative and segmentation models. Additionally, we validate that range images generated by Spiral can be effectively used for synthetic data augmentation in the downstream segmentation training, significantly reducing the labeling effort on LiDAR data.
EventFly: Event Camera Perception from Ground to the Sky
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Cross-platform adaptation in event-based dense perception is crucial for deploying event cameras across diverse settings, such as vehicles, drones, and quadrupeds, each with unique motion dynamics, viewpoints, and class distributions. In this work, we introduce EventFly, a framework for robust cross-platform adaptation in event camera perception. Our approach comprises three key components: i) Event Activation Prior (EAP), which identifies high-activation regions in the target domain to minimize prediction entropy, fostering confident, domain-adaptive predictions; ii) EventBlend, a data-mixing strategy that integrates source and target event voxel grids based on EAP-driven similarity and density maps, enhancing feature alignment; and iii) EventMatch, a dual-discriminator technique that aligns features from source, target, and blended domains for better domain-invariant learning. To holistically assess cross-platform adaptation abilities, we introduce EXPo, a large-scale benchmark with diverse samples across vehicle, drone, and quadruped platforms. Extensive experiments validate our effectiveness, demonstrating substantial gains over popular adaptation methods. We hope this work can pave the way for more adaptive, high-performing event perception across diverse and complex environments.
GEAL: Generalizable 3D Affordance Learning with Cross-Modal Consistency
Dec 12, 2024Abstract:Identifying affordance regions on 3D objects from semantic cues is essential for robotics and human-machine interaction. However, existing 3D affordance learning methods struggle with generalization and robustness due to limited annotated data and a reliance on 3D backbones focused on geometric encoding, which often lack resilience to real-world noise and data corruption. We propose GEAL, a novel framework designed to enhance the generalization and robustness of 3D affordance learning by leveraging large-scale pre-trained 2D models. We employ a dual-branch architecture with Gaussian splatting to establish consistent mappings between 3D point clouds and 2D representations, enabling realistic 2D renderings from sparse point clouds. A granularity-adaptive fusion module and a 2D-3D consistency alignment module further strengthen cross-modal alignment and knowledge transfer, allowing the 3D branch to benefit from the rich semantics and generalization capacity of 2D models. To holistically assess the robustness, we introduce two new corruption-based benchmarks: PIAD-C and LASO-C. Extensive experiments on public datasets and our benchmarks show that GEAL consistently outperforms existing methods across seen and novel object categories, as well as corrupted data, demonstrating robust and adaptable affordance prediction under diverse conditions. Code and corruption datasets have been made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge