Dongming Li
Silhouette Score Efficient Radio Frequency Fingerprint Feature Extraction
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Radio frequency fingerprint (RFF) identification technology, which exploits relatively stable hardware imperfections, is highly susceptible to constantly changing channel effects. Although various channel-robust RFF feature extraction methods have been proposed, they predominantly rely on experimental comparisons rather than theoretical analyses. This limitation hinders the progress of channel-robust RFF feature extraction and impedes the establishment of theoretical guidance for its design. In this paper, we establish a unified theoretical performance analysis framework for different RFF feature extraction methods using the silhouette score as an evaluation metric, and propose a precoding-based channel-robust RFF feature extraction method that enhances the silhouette score without requiring channel estimation. First, we employ the silhouette score as an evaluation metric and obtain the theoretical performance of various RFF feature extraction methods using the Taylor series expansion. Next, we mitigate channel effects by computing the reciprocal of the received signal in the frequency domain at the device under authentication. We then compare these methods across three different scenarios: the deterministic channel scenario, the independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.) stochastic channel scenario, and the non-i.i.d. stochastic channel scenario. Finally, simulation and experimental results demonstrate that the silhouette score is an efficient metric to evaluate classification accuracy. Furthermore, the results indicate that the proposed precoding-based channel-robust RFF feature extraction method achieves the highest silhouette score and classification accuracy under channel variations.
Division-based Receiver-agnostic RFF Identification in WiFi Systems
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:In physical-layer security schemes, radio frequency fingerprint (RFF) identification of WiFi devices is susceptible to receiver differences, which can significantly degrade classification performance when a model is trained on one receiver but tested on another. In this paper, we propose a division-based receiver-agnostic RFF extraction method for WiFi systems, which removes the receivers' effects by dividing different preambles in the frequency domain. The proposed method requires only a single receiver for training and does not rely on additional calibration or stacking processes. First, for flat fading channel scenarios, the legacy short training field (L-STF) and legacy long training field (L-LTF) of the unknown device are divided by those of the reference device in the frequency domain. The receiver-dependent effects can be eliminated with the requirement of only a single receiver for training, and the higher-dimensional RFF features can be extracted. Second, for frequency-selective fading channel scenarios, the high-throughput long training field (HT-LTF) is divided by the L-LTF in the frequency domain. Only a single receiver is required for training and the higher-dimensional RFF features that are both channel-invariant and receiver-agnostic are extracted. Finally, simulation and experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method effectively mitigate the impacts of channel variations and receiver differences. The classification results show that, even when training on a single receiver and testing on a different one, the proposed method achieves classification accuracy improvements of 15.5% and 28.45% over the state-of-the-art approach in flat fading and frequency-selective fading channel scenarios, respectively.
Methodological Explainability Evaluation of an Interpretable Deep Learning Model for Post-Hepatectomy Liver Failure Prediction Incorporating Counterfactual Explanations and Layerwise Relevance Propagation: A Prospective In Silico Trial
Aug 07, 2024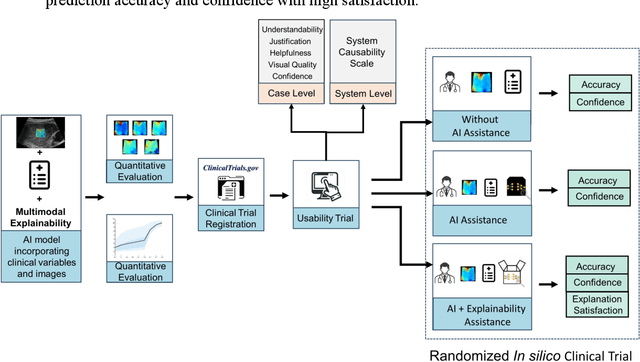
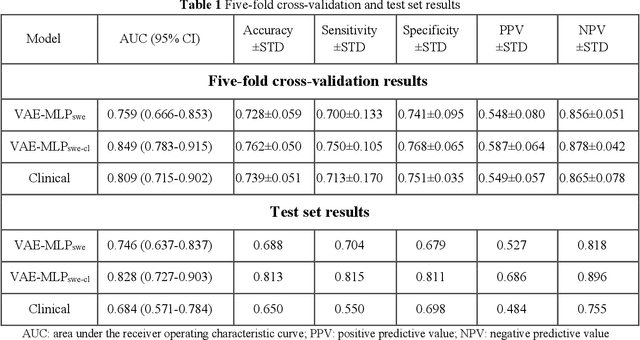
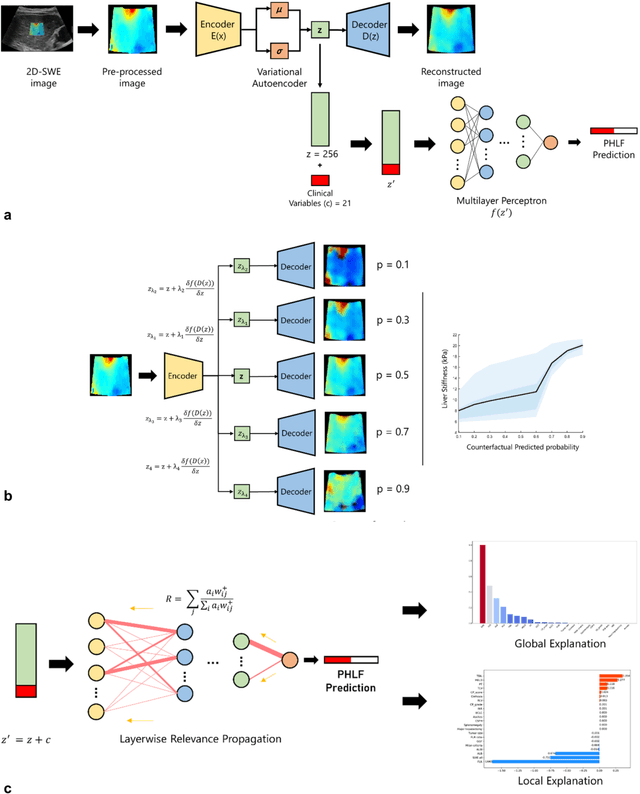
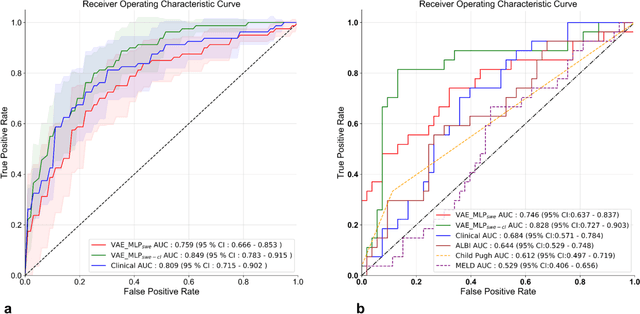
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI)-based decision support systems have demonstrated value in predicting post-hepatectomy liver failure (PHLF) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, they often lack transparency, and the impact of model explanations on clinicians' decisions has not been thoroughly evaluated. Building on prior research, we developed a variational autoencoder-multilayer perceptron (VAE-MLP) model for preoperative PHLF prediction. This model integrated counterfactuals and layerwise relevance propagation (LRP) to provide insights into its decision-making mechanism. Additionally, we proposed a methodological framework for evaluating the explainability of AI systems. This framework includes qualitative and quantitative assessments of explanations against recognized biomarkers, usability evaluations, and an in silico clinical trial. Our evaluations demonstrated that the model's explanation correlated with established biomarkers and exhibited high usability at both the case and system levels. Furthermore, results from the three-track in silico clinical trial showed that clinicians' prediction accuracy and confidence increased when AI explanations were provided.
Insight from NLP Analysis: COVID-19 Vaccines Sentiments on Social Media
Jun 08, 2021



Abstract:Social media is an appropriate source for analyzing public attitudes towards the COVID-19 vaccine and various brands. Nevertheless, there are few relevant studies. In the research, we collected tweet posts by the UK and US residents from the Twitter API during the pandemic and designed experiments to answer three main questions concerning vaccination. To get the dominant sentiment of the civics, we performed sentiment analysis by VADER and proposed a new method that can count the individual's influence. This allows us to go a step further in sentiment analysis and explain some of the fluctuations in the data changing. The results indicated that celebrities could lead the opinion shift on social media in vaccination progress. Moreover, at the peak, nearly 40\% of the population in both countries have a negative attitude towards COVID-19 vaccines. Besides, we investigated how people's opinions toward different vaccine brands are. We found that the Pfizer vaccine enjoys the most popular among people. By applying the sentiment analysis tool, we discovered most people hold positive views toward the COVID-19 vaccine manufactured by most brands. In the end, we carried out topic modelling by using the LDA model. We found residents in the two countries are willing to share their views and feelings concerning the vaccine. Several death cases have occurred after vaccination. Due to these negative events, US residents are more worried about the side effects and safety of the vaccine.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge