DongGeon Lee
COMPASS: A Framework for Evaluating Organization-Specific Policy Alignment in LLMs
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:As large language models are deployed in high-stakes enterprise applications, from healthcare to finance, ensuring adherence to organization-specific policies has become essential. Yet existing safety evaluations focus exclusively on universal harms. We present COMPASS (Company/Organization Policy Alignment Assessment), the first systematic framework for evaluating whether LLMs comply with organizational allowlist and denylist policies. We apply COMPASS to eight diverse industry scenarios, generating and validating 5,920 queries that test both routine compliance and adversarial robustness through strategically designed edge cases. Evaluating seven state-of-the-art models, we uncover a fundamental asymmetry: models reliably handle legitimate requests (>95% accuracy) but catastrophically fail at enforcing prohibitions, refusing only 13-40% of adversarial denylist violations. These results demonstrate that current LLMs lack the robustness required for policy-critical deployments, establishing COMPASS as an essential evaluation framework for organizational AI safety.
Are Vision-Language Models Safe in the Wild? A Meme-Based Benchmark Study
May 21, 2025Abstract:Rapid deployment of vision-language models (VLMs) magnifies safety risks, yet most evaluations rely on artificial images. This study asks: How safe are current VLMs when confronted with meme images that ordinary users share? To investigate this question, we introduce MemeSafetyBench, a 50,430-instance benchmark pairing real meme images with both harmful and benign instructions. Using a comprehensive safety taxonomy and LLM-based instruction generation, we assess multiple VLMs across single and multi-turn interactions. We investigate how real-world memes influence harmful outputs, the mitigating effects of conversational context, and the relationship between model scale and safety metrics. Our findings demonstrate that VLMs show greater vulnerability to meme-based harmful prompts than to synthetic or typographic images. Memes significantly increase harmful responses and decrease refusals compared to text-only inputs. Though multi-turn interactions provide partial mitigation, elevated vulnerability persists. These results highlight the need for ecologically valid evaluations and stronger safety mechanisms.
Typed-RAG: Type-aware Multi-Aspect Decomposition for Non-Factoid Question Answering
Mar 21, 2025



Abstract:Non-factoid question-answering (NFQA) poses a significant challenge due to its open-ended nature, diverse intents, and the need for multi-aspect reasoning, which renders conventional factoid QA approaches, including retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), inadequate. Unlike factoid questions, non-factoid questions (NFQs) lack definitive answers and require synthesizing information from multiple sources across various reasoning dimensions. To address these limitations, we introduce Typed-RAG, a type-aware multi-aspect decomposition framework within the RAG paradigm for NFQA. Typed-RAG classifies NFQs into distinct types -- such as debate, experience, and comparison -- and applies aspect-based decomposition to refine retrieval and generation strategies. By decomposing multi-aspect NFQs into single-aspect sub-queries and aggregating the results, Typed-RAG generates more informative and contextually relevant responses. To evaluate Typed-RAG, we introduce Wiki-NFQA, a benchmark dataset covering diverse NFQ types. Experimental results demonstrate that Typed-RAG outperforms baselines, thereby highlighting the importance of type-aware decomposition for effective retrieval and generation in NFQA. Our code and dataset are available at https://github.com/TeamNLP/Typed-RAG.
REFIND: Retrieval-Augmented Factuality Hallucination Detection in Large Language Models
Feb 19, 2025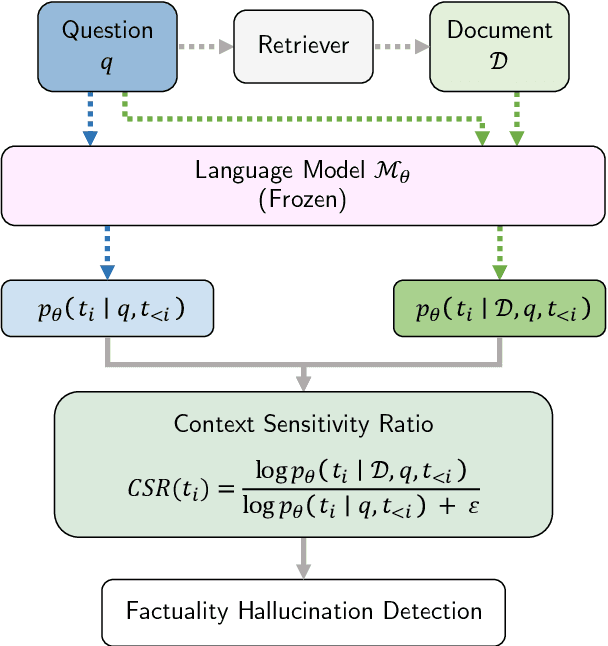
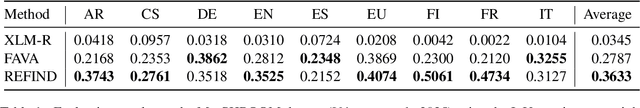

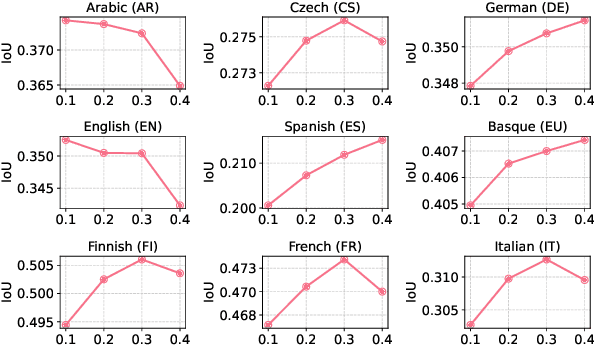
Abstract:Hallucinations in large language model (LLM) outputs severely limit their reliability in knowledge-intensive tasks such as question answering. To address this challenge, we introduce REFIND (Retrieval-augmented Factuality hallucINation Detection), a novel framework that detects hallucinated spans within LLM outputs by directly leveraging retrieved documents. As part of the REFIND, we propose the Context Sensitivity Ratio (CSR), a novel metric that quantifies the sensitivity of LLM outputs to retrieved evidence. This innovative approach enables REFIND to efficiently and accurately detect hallucinations, setting it apart from existing methods. In the evaluation, REFIND demonstrated robustness across nine languages, including low-resource settings, and significantly outperformed baseline models, achieving superior IoU scores in identifying hallucinated spans. This work highlights the effectiveness of quantifying context sensitivity for hallucination detection, thereby paving the way for more reliable and trustworthy LLM applications across diverse languages.
Tabular-TX: Theme-Explanation Structure-based Table Summarization via In-Context Learning
Jan 17, 2025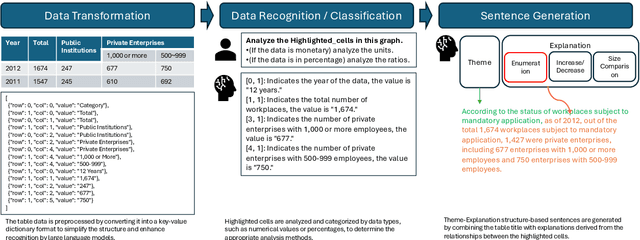
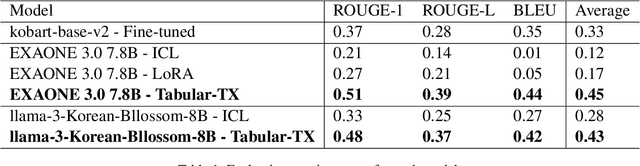

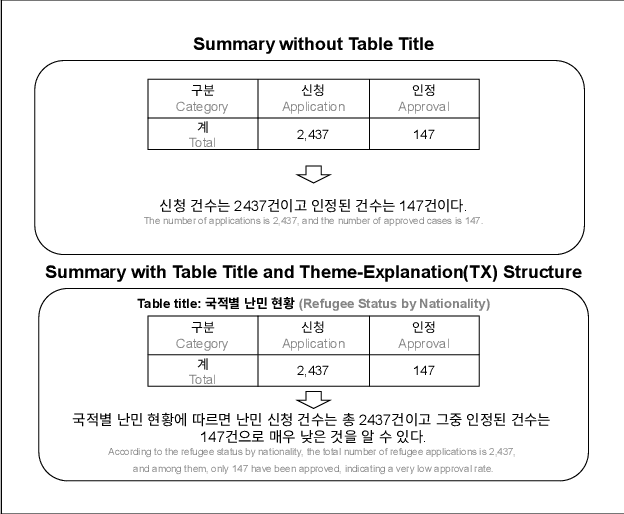
Abstract:This paper proposes a Theme-Explanation Structure-based Table Summarization (Tabular-TX) pipeline designed to efficiently process table data. Tabular-TX preprocesses table data by focusing on highlighted cells and then generates summary sentences structured with a Theme Part in the form of adverbial phrases followed by an Explanation Part in the form of clauses. In this process, customized analysis is performed by considering the structural characteristics and comparability of the table. Additionally, by utilizing In-Context Learning, Tabular-TX optimizes the analytical capabilities of large language models (LLMs) without the need for fine-tuning, effectively handling the structural complexity of table data. Results from applying the proposed Tabular-TX to generate table-based summaries demonstrated superior performance compared to existing fine-tuning-based methods, despite limitations in dataset size. Experimental results confirmed that Tabular-TX can process complex table data more effectively and established it as a new alternative for table-based question answering and summarization tasks, particularly in resource-constrained environments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge