Dong Sun Park
Adaptive Label Smoothing for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Oct 08, 2024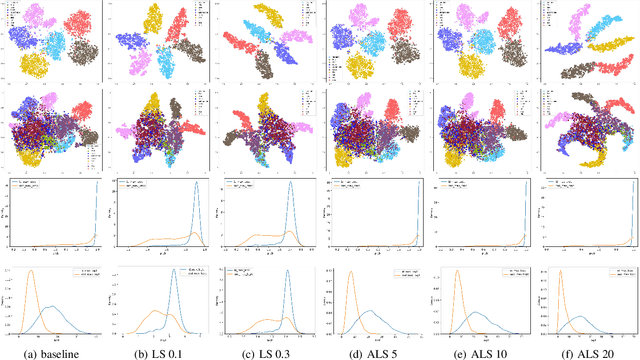
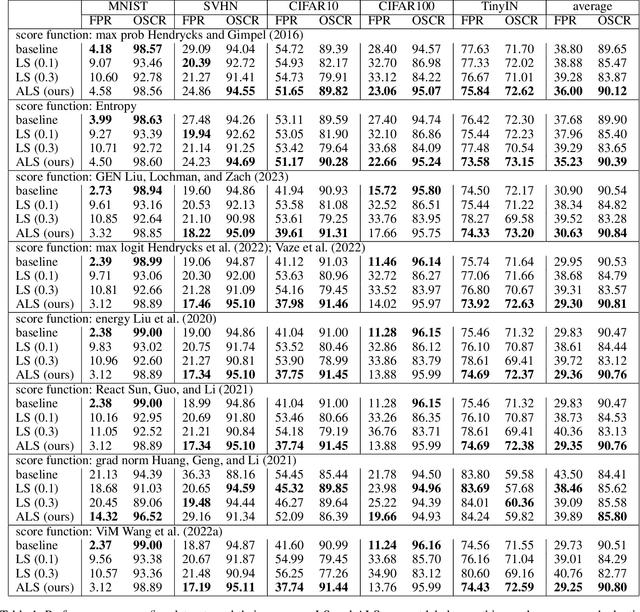
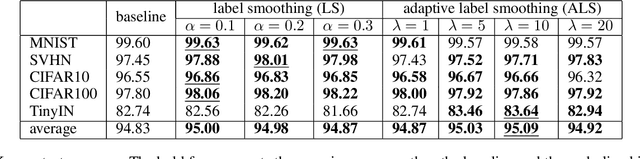
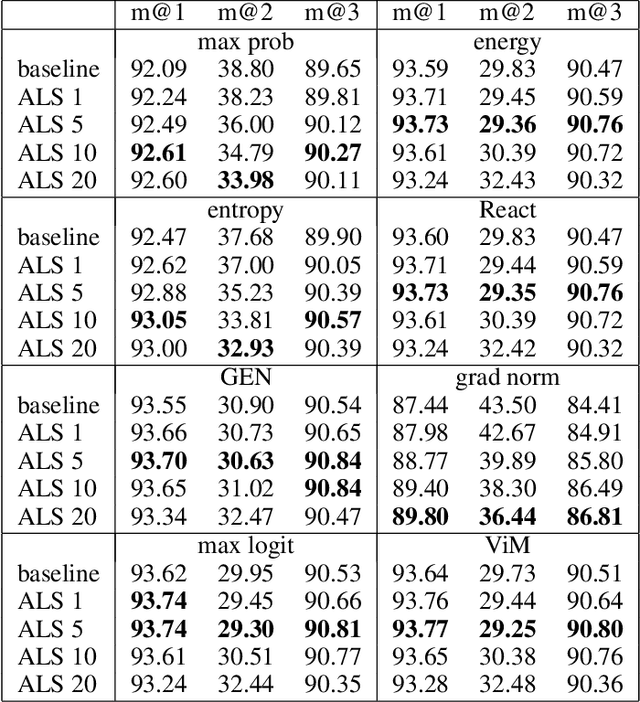
Abstract:Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection, which aims to distinguish unknown classes from known classes, has received increasing attention recently. A main challenge within is the unavailable of samples from the unknown classes in the training process, and an effective strategy is to improve the performance for known classes. Using beneficial strategies such as data augmentation and longer training is thus a way to improve OOD detection. However, label smoothing, an effective method for classifying known classes, degrades the performance of OOD detection, and this phenomenon is under exploration. In this paper, we first analyze that the limited and predefined learning target in label smoothing results in the smaller maximal probability and logit, which further leads to worse OOD detection performance. To mitigate this issue, we then propose a novel regularization method, called adaptive label smoothing (ALS), and the core is to push the non-true classes to have same probabilities whereas the maximal probability is neither fixed nor limited. Extensive experimental results in six datasets with two backbones suggest that ALS contributes to classifying known samples and discerning unknown samples with clear margins. Our code will be available to the public.
Embracing Limited and Imperfect Data: A Review on Plant Stress Recognition Using Deep Learning
May 19, 2023Abstract:Plant stress recognition has witnessed significant improvements in recent years with the advent of deep learning. A large-scale and annotated training dataset is required to achieve decent performance; however, collecting it is frequently difficult and expensive. Therefore, deploying current deep learning-based methods in real-world applications may suffer primarily from limited and imperfect data. Embracing them is a promising strategy that has not received sufficient attention. From this perspective, a systematic survey was conducted in this study, with the ultimate objective of monitoring plant growth by implementing deep learning, which frees humans and potentially reduces the resultant losses from plant stress. We believe that our paper has highlighted the importance of embracing this limited and imperfect data and enhanced its relevant understanding.
Variation-Aware Semantic Image Synthesis
Jan 25, 2023Abstract:Semantic image synthesis (SIS) aims to produce photorealistic images aligning to given conditional semantic layout and has witnessed a significant improvement in recent years. Although the diversity in image-level has been discussed heavily, class-level mode collapse widely exists in current algorithms. Therefore, we declare a new requirement for SIS to achieve more photorealistic images, variation-aware, which consists of inter- and intra-class variation. The inter-class variation is the diversity between different semantic classes while the intra-class variation stresses the diversity inside one class. Through analysis, we find that current algorithms elusively embrace the inter-class variation but the intra-class variation is still not enough. Further, we introduce two simple methods to achieve variation-aware semantic image synthesis (VASIS) with a higher intra-class variation, semantic noise and position code. We combine our method with several state-of-the-art algorithms and the experimental result shows that our models generate more natural images and achieves slightly better FIDs and/or mIoUs than the counterparts. Our codes and models will be publicly available.
A Comprehensive Survey of Image Augmentation Techniques for Deep Learning
May 03, 2022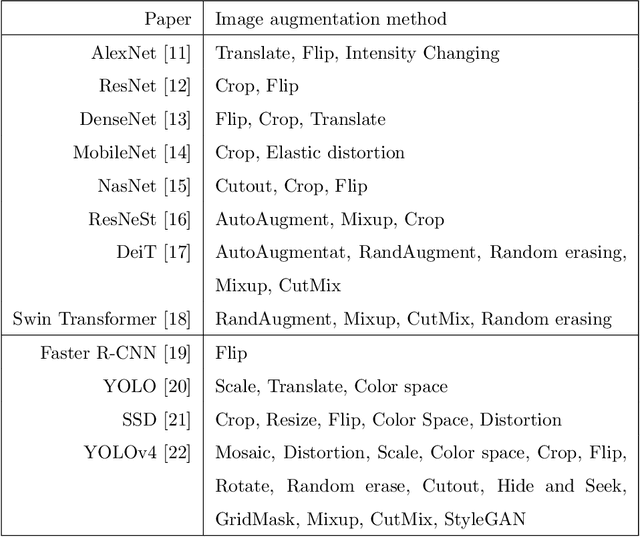
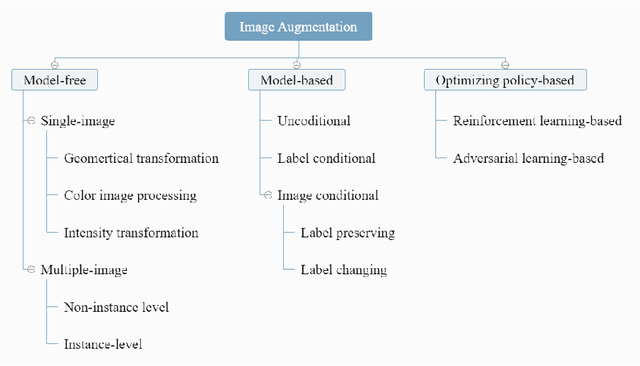
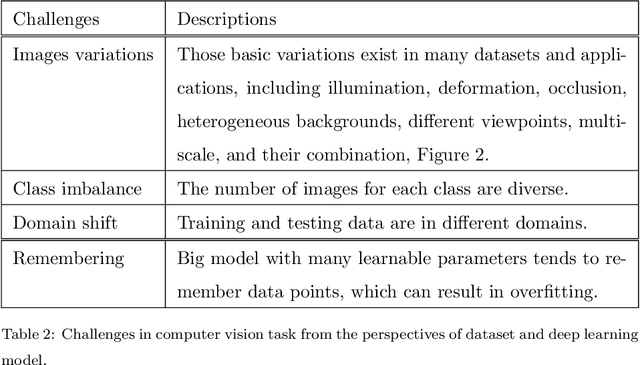
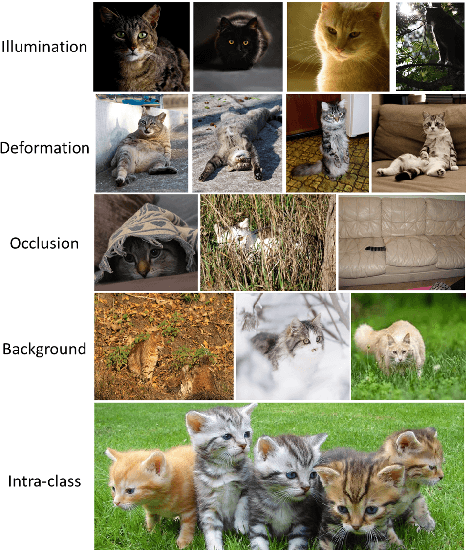
Abstract:Deep learning has been achieving decent performance in computer vision requiring a large volume of images, however, collecting images is expensive and difficult in many scenarios. To alleviate this issue, many image augmentation algorithms have been proposed as effective and efficient strategies. Understanding current algorithms is essential to find suitable methods or develop novel techniques for given tasks. In this paper, we perform a comprehensive survey on image augmentation for deep learning with a novel informative taxonomy. To get the basic idea why we need image augmentation, we introduce the challenges in computer vision tasks and vicinity distribution. Then, the algorithms are split into three categories; model-free, model-based, and optimizing policy-based. The model-free category employs image processing methods while the model-based method leverages trainable image generation models. In contrast, the optimizing policy-based approach aims to find the optimal operations or their combinations. Furthermore, we discuss the current trend of common applications with two more active topics, leveraging different ways to understand image augmentation, such as group and kernel theory, and deploying image augmentation for unsupervised learning. Based on the analysis, we believe that our survey gives a better understanding helpful to choose suitable methods or design novel algorithms for practical applications.
Unsupervised Image Translation using Adversarial Networks for Improved Plant Disease Recognition
Sep 26, 2019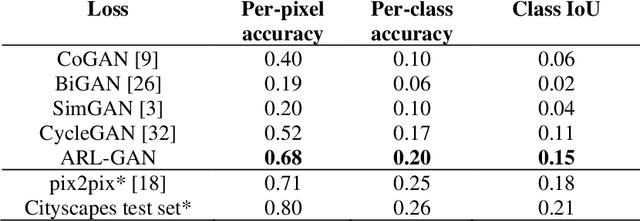
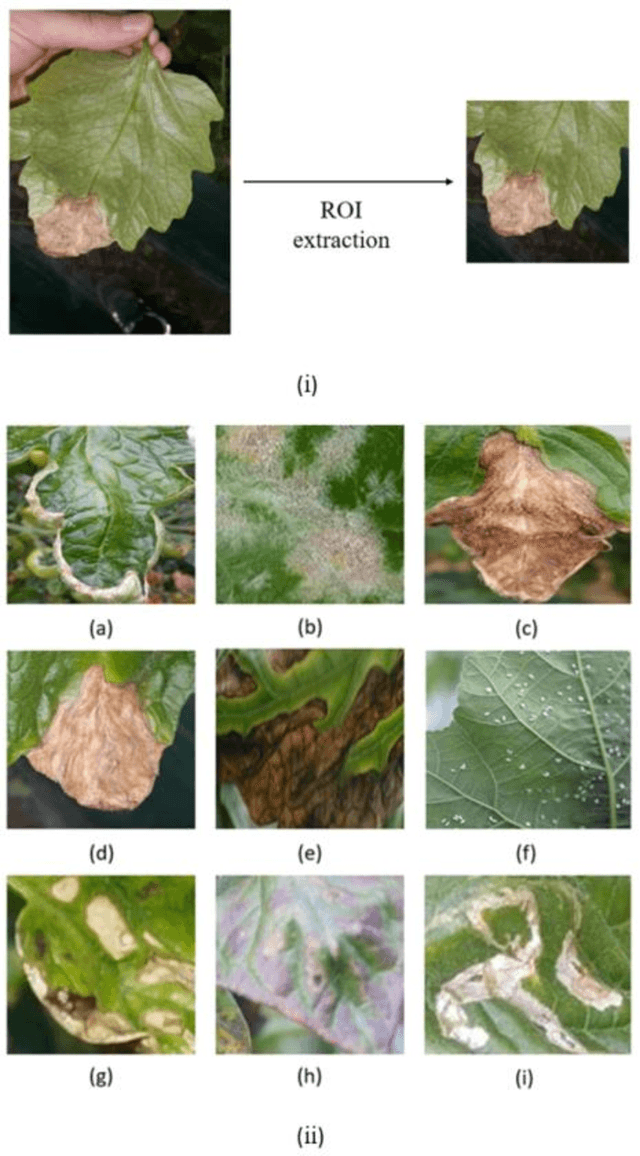
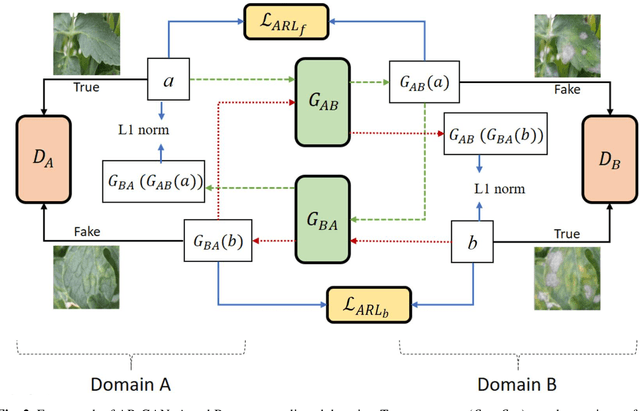
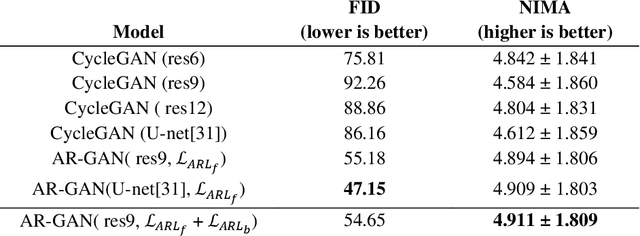

Abstract:Acquisition of data in task-specific applications of machine learning like plant disease recognition is a costly endeavor owing to the requirements of professional human diligence and time constraints. In this paper, we present a simple pipeline that uses GANs in an unsupervised image translation environment to improve learning with respect to the data distribution in a plant disease dataset, reducing the partiality introduced by acute class imbalance and hence shifting the classification decision boundary towards better performance. The empirical analysis of our method is demonstrated on a limited dataset of 2789 tomato plant disease images, highly corrupted with an imbalance in the 9 disease categories. First, we extend the state of the art for the GAN-based image-to-image translation method by enhancing the perceptual quality of the generated images and preserving the semantics. We introduce AR-GAN, where in addition to the adversarial loss, our synthetic image generator optimizes on Activation Reconstruction loss (ARL) function that optimizes feature activations against the natural image. We present visually more compelling synthetic images in comparison to most prominent existing models and evaluate the performance of our GAN framework in terms of various datasets and metrics. Second, we evaluate the performance of a baseline convolutional neural network classifier for improved recognition using the resulting synthetic samples to augment our training set and compare it with the classical data augmentation scheme. We observe a significant improvement in classification accuracy (+5.2%) using generated synthetic samples as compared to (+0.8%) increase using classic augmentation in an equal class distribution environment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge