Dominique Stutzmann
HORAE: an annotated dataset of books of hours
Dec 01, 2020



Abstract:We introduce in this paper a new dataset of annotated pages from books of hours, a type of handwritten prayer books owned and used by rich lay people in the late middle ages. The dataset was created for conducting historical research on the evolution of the religious mindset in Europe at this period since the book of hours represent one of the major sources of information thanks both to their rich illustrations and the different types of religious sources they contain. We first describe how the corpus was collected and manually annotated then present the evaluation of a state-of-the-art system for text line detection and for zone detection and typing. The corpus is freely available for research.
ICFHR 2020 Competition on Image Retrieval for Historical Handwritten Fragments
Oct 20, 2020
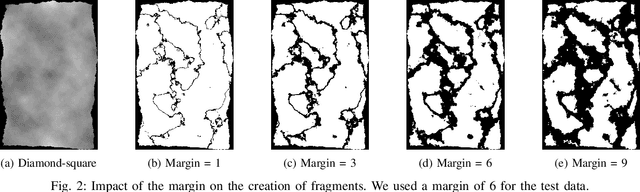


Abstract:This competition succeeds upon a line of competitions for writer and style analysis of historical document images. In particular, we investigate the performance of large-scale retrieval of historical document fragments in terms of style and writer identification. The analysis of historic fragments is a difficult challenge commonly solved by trained humanists. In comparison to previous competitions, we make the results more meaningful by addressing the issue of sample granularity and moving from writer to page fragment retrieval. The two approaches, style and author identification, provide information on what kind of information each method makes better use of and indirectly contribute to the interpretability of the participating method. Therefore, we created a large dataset consisting of more than 120 000 fragments. Although the most teams submitted methods based on convolutional neural networks, the winning entry achieves an mAP below 40%.
ICDAR 2019 Competition on Image Retrieval for Historical Handwritten Documents
Dec 08, 2019



Abstract:This competition investigates the performance of large-scale retrieval of historical document images based on writing style. Based on large image data sets provided by cultural heritage institutions and digital libraries, providing a total of 20 000 document images representing about 10 000 writers, divided in three types: writers of (i) manuscript books, (ii) letters, (iii) charters and legal documents. We focus on the task of automatic image retrieval to simulate common scenarios of humanities research, such as writer retrieval. The most teams submitted traditional methods not using deep learning techniques. The competition results show that a combination of methods is outperforming single methods. Furthermore, letters are much more difficult to retrieve than manuscripts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge