Dilek Hakkani-tur
Just Ask:An Interactive Learning Framework for Vision and Language Navigation
Dec 02, 2019
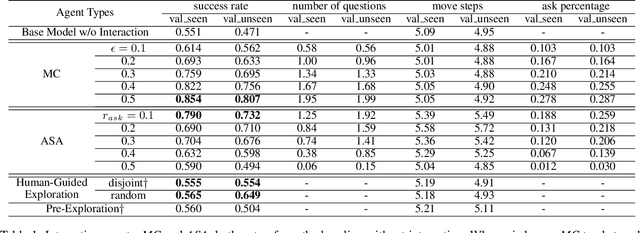
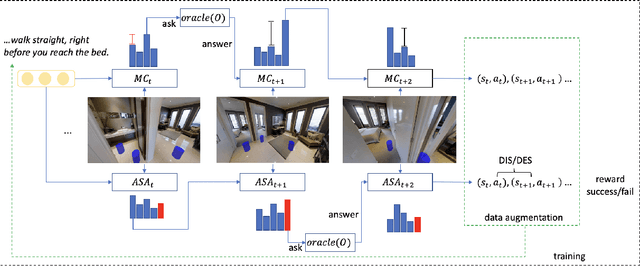

Abstract:In the vision and language navigation task, the agent may encounter ambiguous situations that are hard to interpret by just relying on visual information and natural language instructions. We propose an interactive learning framework to endow the agent with the ability to ask for users' help in such situations. As part of this framework, we investigate multiple learning approaches for the agent with different levels of complexity. The simplest model-confusion-based method lets the agent ask questions based on its confusion, relying on the predefined confidence threshold of a next action prediction model. To build on this confusion-based method, the agent is expected to demonstrate more sophisticated reasoning such that it discovers the timing and locations to interact with a human. We achieve this goal using reinforcement learning (RL) with a proposed reward shaping term, which enables the agent to ask questions only when necessary. The success rate can be boosted by at least 15% with only one question asked on average during the navigation. Furthermore, we show that the RL agent is capable of adjusting dynamically to noisy human responses. Finally, we design a continual learning strategy, which can be viewed as a data augmentation method, for the agent to improve further utilizing its interaction history with a human. We demonstrate the proposed strategy is substantially more realistic and data-efficient compared to previously proposed pre-exploration techniques.
MMM: Multi-stage Multi-task Learning for Multi-choice Reading Comprehension
Oct 01, 2019
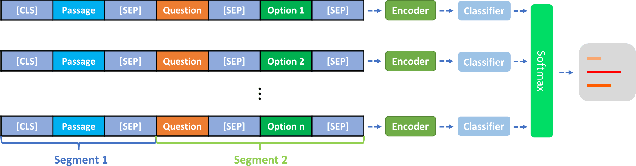
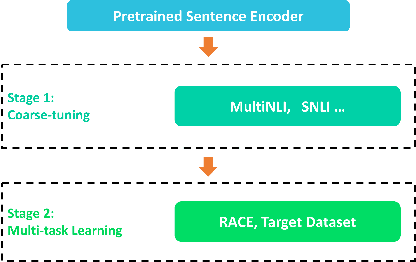
Abstract:Machine Reading Comprehension (MRC) for question answering (QA), which aims to answer a question given the relevant context passages, is an important way to test the ability of intelligence systems to understand human language. Multiple-Choice QA (MCQA) is one of the most difficult tasks in MRC because it often requires more advanced reading comprehension skills such as logical reasoning, summarization, and arithmetic operations, compared to the extractive counterpart where answers are usually spans of text within given passages. Moreover, most existing MCQA datasets are small in size, making the learning task even harder. We introduce MMM, a Multi-stage Multi-task learning framework for Multi-choice reading comprehension. Our method involves two sequential stages: coarse-tuning stage using out-of-domain datasets and multi-task learning stage using a larger in-domain dataset to help model generalize better with limited data. Furthermore, we propose a novel multi-step attention network (MAN) as the top-level classifier for this task. We demonstrate MMM significantly advances the state-of-the-art on four representative MCQA datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge