Diego Saez-Trumper
Graph-Linguistic Fusion: Using Language Models for Wikidata Vandalism Detection
May 23, 2025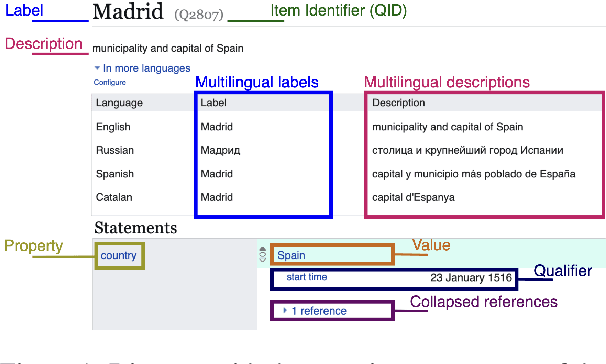
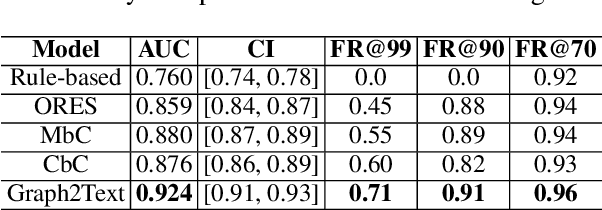

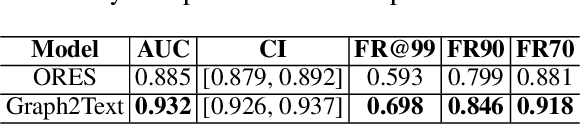
Abstract:We introduce a next-generation vandalism detection system for Wikidata, one of the largest open-source structured knowledge bases on the Web. Wikidata is highly complex: its items incorporate an ever-expanding universe of factual triples and multilingual texts. While edits can alter both structured and textual content, our approach converts all edits into a single space using a method we call Graph2Text. This allows for evaluating all content changes for potential vandalism using a single multilingual language model. This unified approach improves coverage and simplifies maintenance. Experiments demonstrate that our solution outperforms the current production system. Additionally, we are releasing the code under an open license along with a large dataset of various human-generated knowledge alterations, enabling further research.
Characterizing Knowledge Manipulation in a Russian Wikipedia Fork
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Wikipedia is powered by MediaWiki, a free and open-source software that is also the infrastructure for many other wiki-based online encyclopedias. These include the recently launched website Ruwiki, which has copied and modified the original Russian Wikipedia content to conform to Russian law. To identify practices and narratives that could be associated with different forms of knowledge manipulation, this article presents an in-depth analysis of this Russian Wikipedia fork. We propose a methodology to characterize the main changes with respect to the original version. The foundation of this study is a comprehensive comparative analysis of more than 1.9M articles from Russian Wikipedia and its fork. Using meta-information and geographical, temporal, categorical, and textual features, we explore the changes made by Ruwiki editors. Furthermore, we present a classification of the main topics of knowledge manipulation in this fork, including a numerical estimation of their scope. This research not only sheds light on significant changes within Ruwiki, but also provides a methodology that could be applied to analyze other Wikipedia forks and similar collaborative projects.
Fair multilingual vandalism detection system for Wikipedia
Jun 02, 2023



Abstract:This paper presents a novel design of the system aimed at supporting the Wikipedia community in addressing vandalism on the platform. To achieve this, we collected a massive dataset of 47 languages, and applied advanced filtering and feature engineering techniques, including multilingual masked language modeling to build the training dataset from human-generated data. The performance of the system was evaluated through comparison with the one used in production in Wikipedia, known as ORES. Our research results in a significant increase in the number of languages covered, making Wikipedia patrolling more efficient to a wider range of communities. Furthermore, our model outperforms ORES, ensuring that the results provided are not only more accurate but also less biased against certain groups of contributors.
WikiContradiction: Detecting Self-Contradiction Articles on Wikipedia
Nov 16, 2021

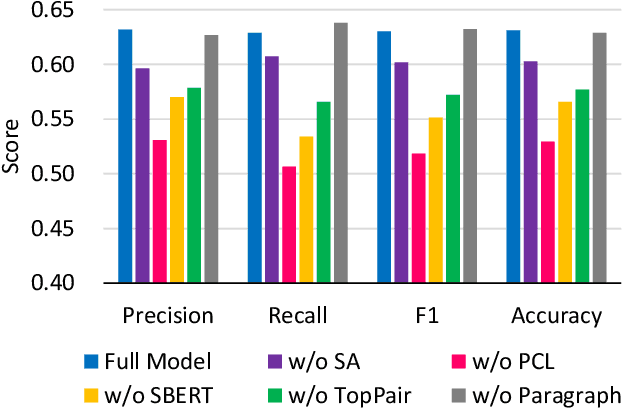
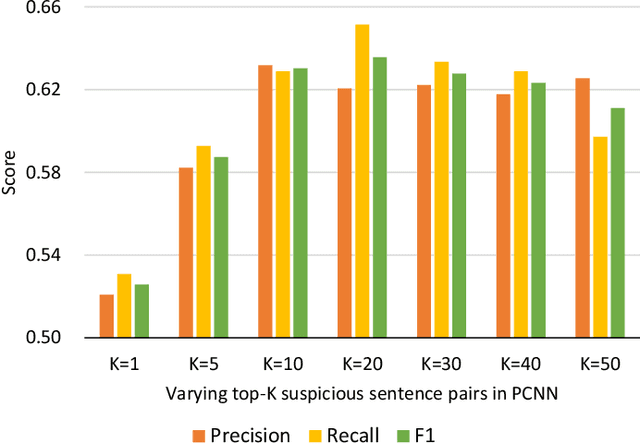
Abstract:While Wikipedia has been utilized for fact-checking and claim verification to debunk misinformation and disinformation, it is essential to either improve article quality and rule out noisy articles. Self-contradiction is one of the low-quality article types in Wikipedia. In this work, we propose a task of detecting self-contradiction articles in Wikipedia. Based on the "self-contradictory" template, we create a novel dataset for the self-contradiction detection task. Conventional contradiction detection focuses on comparing pairs of sentences or claims, but self-contradiction detection needs to further reason the semantics of an article and simultaneously learn the contradiction-aware comparison from all pairs of sentences. Therefore, we present the first model, Pairwise Contradiction Neural Network (PCNN), to not only effectively identify self-contradiction articles, but also highlight the most contradiction pairs of contradiction sentences. The main idea of PCNN is two-fold. First, to mitigate the effect of data scarcity on self-contradiction articles, we pre-train the module of pairwise contradiction learning using SNLI and MNLI benchmarks. Second, we select top-K sentence pairs with the highest contradiction probability values and model their correlation to determine whether the corresponding article belongs to self-contradiction. Experiments conducted on the proposed WikiContradiction dataset exhibit that PCNN can generate promising performance and comprehensively highlight the sentence pairs the contradiction locates.
Wiki-Reliability: A Large Scale Dataset for Content Reliability on Wikipedia
Jun 01, 2021
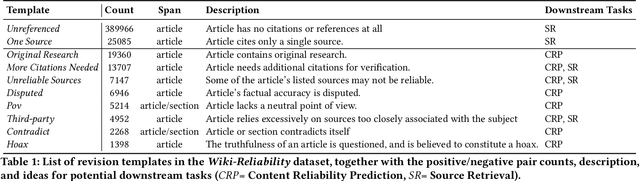
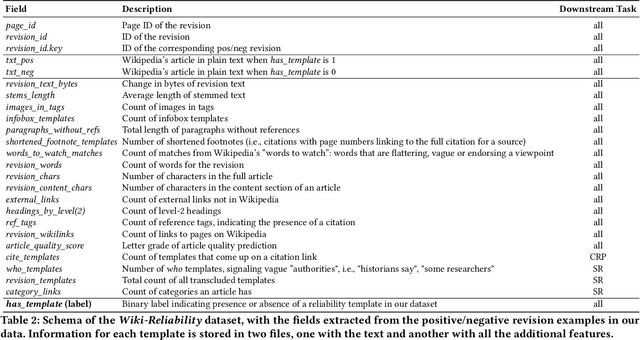
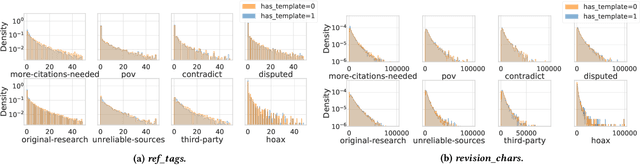
Abstract:Wikipedia is the largest online encyclopedia, used by algorithms and web users as a central hub of reliable information on the web. The quality and reliability of Wikipedia content is maintained by a community of volunteer editors. Machine learning and information retrieval algorithms could help scale up editors' manual efforts around Wikipedia content reliability. However, there is a lack of large-scale data to support the development of such research. To fill this gap, in this paper, we propose Wiki-Reliability, the first dataset of English Wikipedia articles annotated with a wide set of content reliability issues. To build this dataset, we rely on Wikipedia "templates". Templates are tags used by expert Wikipedia editors to indicate content issues, such as the presence of "non-neutral point of view" or "contradictory articles", and serve as a strong signal for detecting reliability issues in a revision. We select the 10 most popular reliability-related templates on Wikipedia, and propose an effective method to label almost 1M samples of Wikipedia article revisions as positive or negative with respect to each template. Each positive/negative example in the dataset comes with the full article text and 20 features from the revision's metadata. We provide an overview of the possible downstream tasks enabled by such data, and show that Wiki-Reliability can be used to train large-scale models for content reliability prediction. We release all data and code for public use.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge