Devansh Saxena
Measurement as Bricolage: Examining How Data Scientists Construct Target Variables for Predictive Modeling Tasks
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:Data scientists often formulate predictive modeling tasks involving fuzzy, hard-to-define concepts, such as the "authenticity" of student writing or the "healthcare need" of a patient. Yet the process by which data scientists translate fuzzy concepts into a concrete, proxy target variable remains poorly understood. We interview fifteen data scientists in education (N=8) and healthcare (N=7) to understand how they construct target variables for predictive modeling tasks. Our findings suggest that data scientists construct target variables through a bricolage process, involving iterative negotiation between high-level measurement objectives and low-level practical constraints. Data scientists attempt to satisfy five major criteria for a target variable through bricolage: validity, simplicity, predictability, portability, and resource requirements. To achieve this, data scientists adaptively use problem (re)formulation strategies, such as swapping out one candidate target variable for another when the first fails to meet certain criteria (e.g., predictability), or composing multiple outcomes into a single target variable to capture a more holistic set of modeling objectives. Based on our findings, we present opportunities for future HCI, CSCW, and ML research to better support the art and science of target variable construction.
AI Mismatches: Identifying Potential Algorithmic Harms Before AI Development
Feb 25, 2025
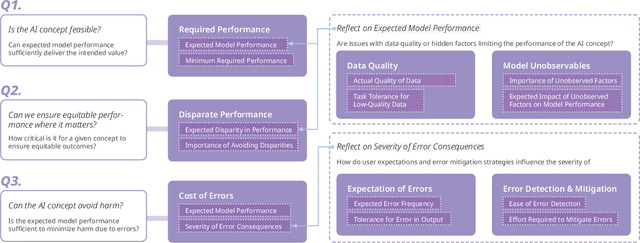
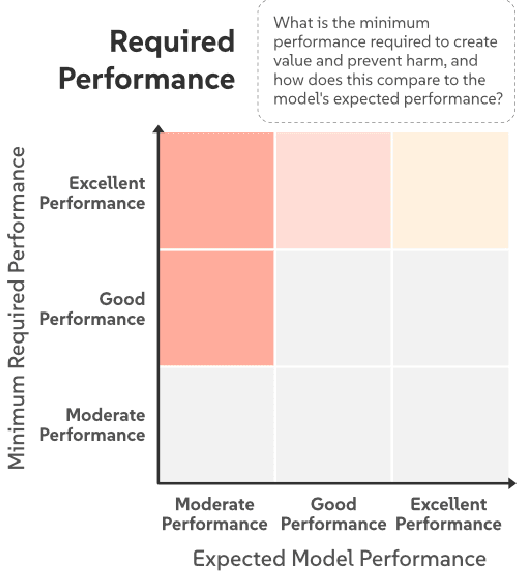
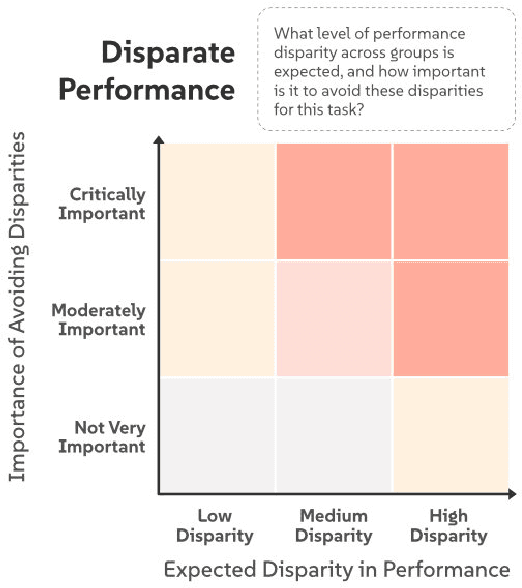
Abstract:AI systems are often introduced with high expectations, yet many fail to deliver, resulting in unintended harm and missed opportunities for benefit. We frequently observe significant "AI Mismatches", where the system's actual performance falls short of what is needed to ensure safety and co-create value. These mismatches are particularly difficult to address once development is underway, highlighting the need for early-stage intervention. Navigating complex, multi-dimensional risk factors that contribute to AI Mismatches is a persistent challenge. To address it, we propose an AI Mismatch approach to anticipate and mitigate risks early on, focusing on the gap between realistic model performance and required task performance. Through an analysis of 774 AI cases, we extracted a set of critical factors, which informed the development of seven matrices that map the relationships between these factors and highlight high-risk areas. Through case studies, we demonstrate how our approach can help reduce risks in AI development.
Beyond Predictive Algorithms in Child Welfare
Feb 26, 2024


Abstract:Caseworkers in the child welfare (CW) sector use predictive decision-making algorithms built on risk assessment (RA) data to guide and support CW decisions. Researchers have highlighted that RAs can contain biased signals which flatten CW case complexities and that the algorithms may benefit from incorporating contextually rich case narratives, i.e. - casenotes written by caseworkers. To investigate this hypothesized improvement, we quantitatively deconstructed two commonly used RAs from a United States CW agency. We trained classifier models to compare the predictive validity of RAs with and without casenote narratives and applied computational text analysis on casenotes to highlight topics uncovered in the casenotes. Our study finds that common risk metrics used to assess families and build CWS predictive risk models (PRMs) are unable to predict discharge outcomes for children who are not reunified with their birth parent(s). We also find that although casenotes cannot predict discharge outcomes, they contain contextual case signals. Given the lack of predictive validity of RA scores and casenotes, we propose moving beyond quantitative risk assessments for public sector algorithms and towards using contextual sources of information such as narratives to study public sociotechnical systems.
A Human-Centered Review of the Algorithms used within the U.S. Child Welfare System
Mar 07, 2020
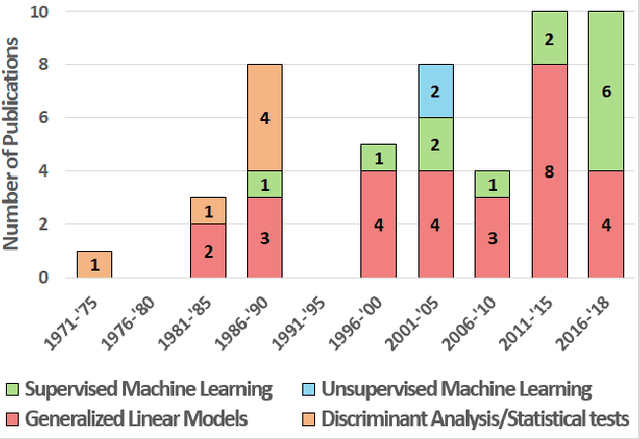
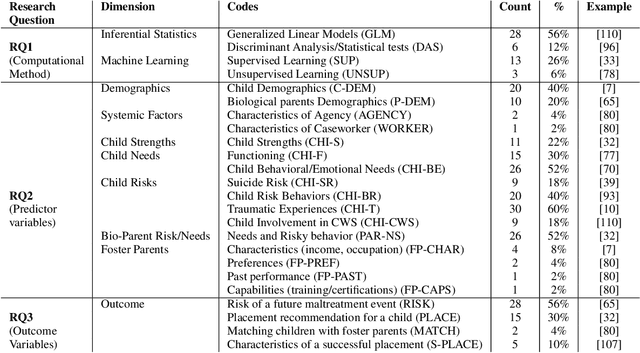
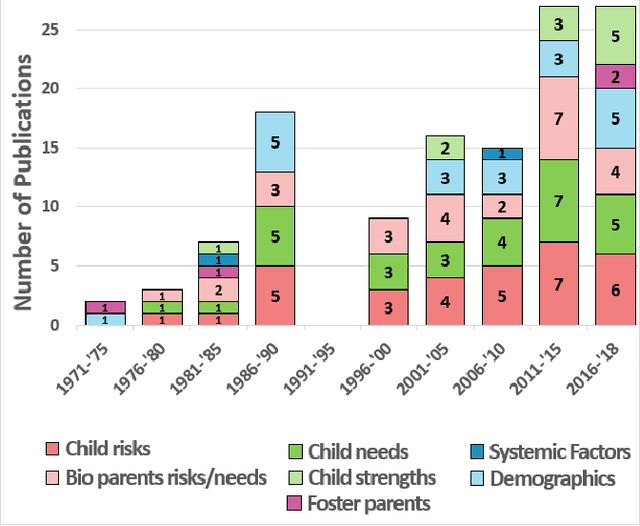
Abstract:The U.S. Child Welfare System (CWS) is charged with improving outcomes for foster youth; yet, they are overburdened and underfunded. To overcome this limitation, several states have turned towards algorithmic decision-making systems to reduce costs and determine better processes for improving CWS outcomes. Using a human-centered algorithmic design approach, we synthesize 50 peer-reviewed publications on computational systems used in CWS to assess how they were being developed, common characteristics of predictors used, as well as the target outcomes. We found that most of the literature has focused on risk assessment models but does not consider theoretical approaches (e.g., child-foster parent matching) nor the perspectives of caseworkers (e.g., case notes). Therefore, future algorithms should strive to be context-aware and theoretically robust by incorporating salient factors identified by past research. We provide the HCI community with research avenues for developing human-centered algorithms that redirect attention towards more equitable outcomes for CWS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge