Deliang Wang
Using Vision Language Models to Detect Students' Academic Emotion through Facial Expressions
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Students' academic emotions significantly influence their social behavior and learning performance. Traditional approaches to automatically and accurately analyze these emotions have predominantly relied on supervised machine learning algorithms. However, these models often struggle to generalize across different contexts, necessitating repeated cycles of data collection, annotation, and training. The emergence of Vision-Language Models (VLMs) offers a promising alternative, enabling generalization across visual recognition tasks through zero-shot prompting without requiring fine-tuning. This study investigates the potential of VLMs to analyze students' academic emotions via facial expressions in an online learning environment. We employed two VLMs, Llama-3.2-11B-Vision-Instruct and Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct, to analyze 5,000 images depicting confused, distracted, happy, neutral, and tired expressions using zero-shot prompting. Preliminary results indicate that both models demonstrate moderate performance in academic facial expression recognition, with Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct outperforming Llama-3.2-11B-Vision-Instruct. Notably, both models excel in identifying students' happy emotions but fail to detect distracted behavior. Additionally, Qwen2.5-VL-7B-Instruct exhibits relatively high performance in recognizing students' confused expressions, highlighting its potential for practical applications in identifying content that causes student confusion.
IKUN: Initialization to Keep snn training and generalization great with sUrrogate-stable variaNce
Nov 27, 2024



Abstract:Weight initialization significantly impacts the convergence and performance of neural networks. While traditional methods like Xavier and Kaiming initialization are widely used, they often fall short for spiking neural networks (SNNs), which have distinct requirements compared to artificial neural networks (ANNs). To address this, we introduce \textbf{IKUN}, a variance-stabilizing initialization method integrated with surrogate gradient functions, specifically designed for SNNs. \textbf{IKUN} stabilizes signal propagation, accelerates convergence, and enhances generalization. Experiments show \textbf{IKUN} improves training efficiency by up to \textbf{50\%}, achieving \textbf{95\%} training accuracy and \textbf{91\%} generalization accuracy. Hessian analysis reveals that \textbf{IKUN}-trained models converge to flatter minima, characterized by Hessian eigenvalues near zero on the positive side, promoting better generalization. The method is open-sourced for further exploration: \href{https://github.com/MaeChd/SurrogateVarStabe}{https://github.com/MaeChd/SurrogateVarStabe}.
Interpreting Deep Knowledge Tracing Model on EdNet Dataset
Oct 31, 2021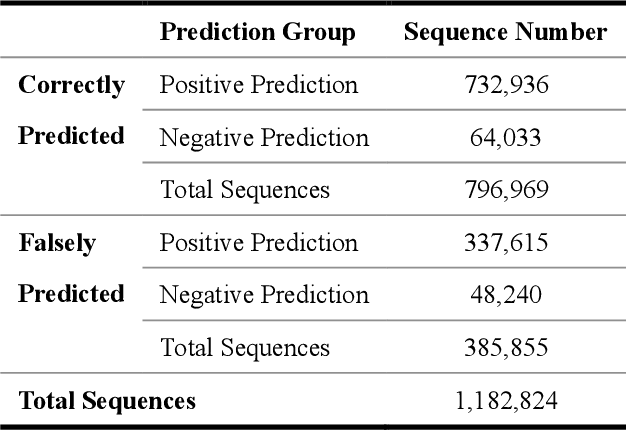
Abstract:With more deep learning techniques being introduced into the knowledge tracing domain, the interpretability issue of the knowledge tracing models has aroused researchers' attention. Our previous study(Lu et al. 2020) on building and interpreting the KT model mainly adopts the ASSISTment dataset(Feng, Heffernan, and Koedinger 2009),, whose size is relatively small. In this work, we perform the similar tasks but on a large and newly available dataset, called EdNet(Choi et al. 2020). The preliminary experiment results show the effectiveness of the interpreting techniques, while more questions and tasks are worthy to be further explored and accomplished.
Towards Interpretable Deep Learning Models for Knowledge Tracing
May 13, 2020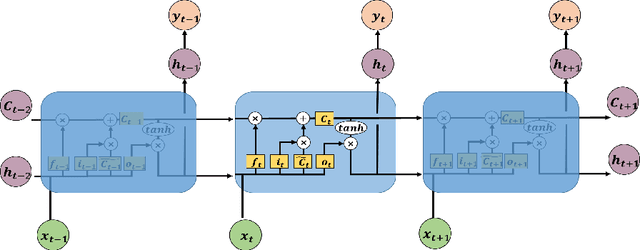
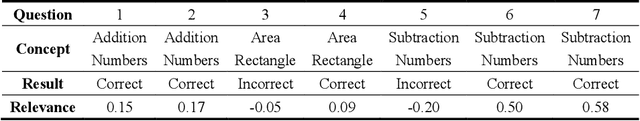
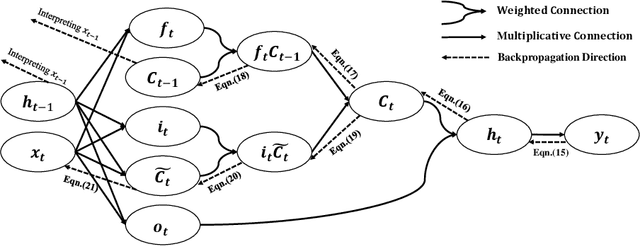
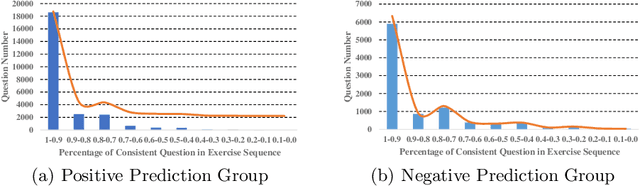
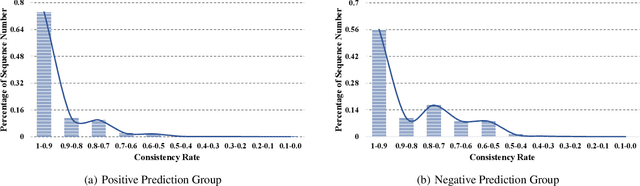
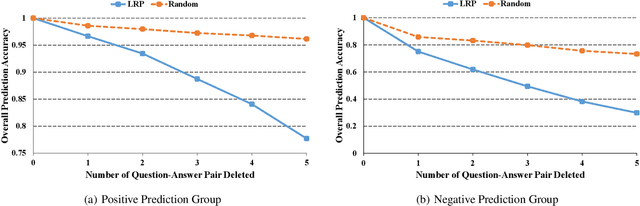
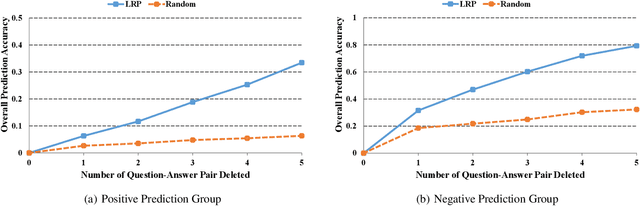
Abstract:As an important technique for modeling the knowledge states of learners, the traditional knowledge tracing (KT) models have been widely used to support intelligent tutoring systems and MOOC platforms. Driven by the fast advancements of deep learning techniques, deep neural network has been recently adopted to design new KT models for achieving better prediction performance. However, the lack of interpretability of these models has painfully impeded their practical applications, as their outputs and working mechanisms suffer from the intransparent decision process and complex inner structures. We thus propose to adopt the post-hoc method to tackle the interpretability issue for deep learning based knowledge tracing (DLKT) models. Specifically, we focus on applying the layer-wise relevance propagation (LRP) method to interpret RNN-based DLKT model by backpropagating the relevance from the model's output layer to its input layer. The experiment results show the feasibility using the LRP method for interpreting the DLKT model's predictions, and partially validate the computed relevance scores from both question level and concept level. We believe it can be a solid step towards fully interpreting the DLKT models and promote their practical applications in the education domain.
Incorporating Language Level Information into Acoustic Models
Dec 14, 2016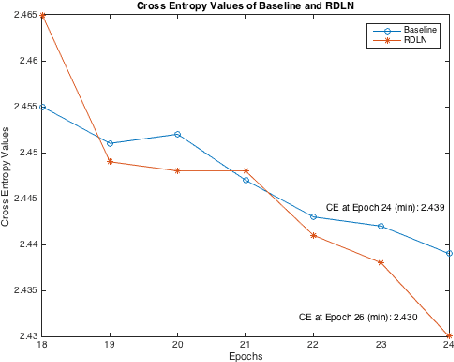
Abstract:This paper proposed a class of novel Deep Recurrent Neural Networks which can incorporate language-level information into acoustic models. For simplicity, we named these networks Recurrent Deep Language Networks (RDLNs). Multiple variants of RDLNs were considered, including two kinds of context information, two methods to process the context, and two methods to incorporate the language-level information. RDLNs provided possible methods to fine-tune the whole Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) system in the acoustic modeling process.
Recurrent Deep Stacking Networks for Speech Recognition
Dec 14, 2016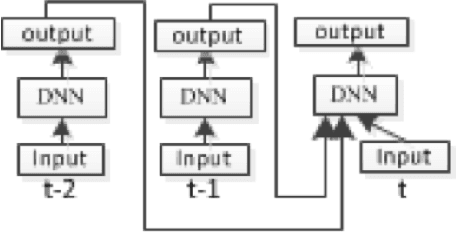
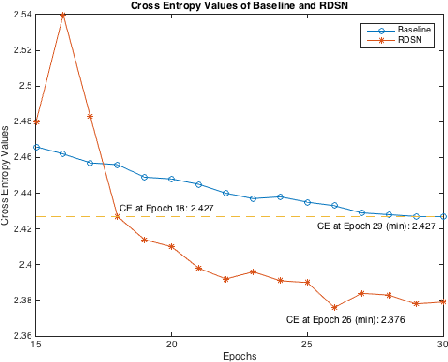
Abstract:This paper presented our work on applying Recurrent Deep Stacking Networks (RDSNs) to Robust Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) tasks. In the paper, we also proposed a more efficient yet comparable substitute to RDSN, Bi- Pass Stacking Network (BPSN). The main idea of these two models is to add phoneme-level information into acoustic models, transforming an acoustic model to the combination of an acoustic model and a phoneme-level N-gram model. Experiments showed that RDSN and BPsn can substantially improve the performances over conventional DNNs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge