Dechun Cong
BiCANet: Bi-directional Contextual Aggregating Network for Image Semantic Segmentation
Mar 21, 2020
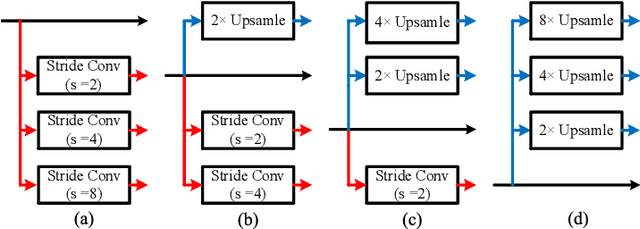
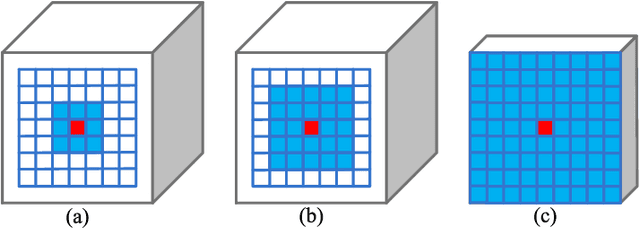

Abstract:Exploring contextual information in convolution neural networks (CNNs) has gained substantial attention in recent years for semantic segmentation. This paper introduces a Bi-directional Contextual Aggregating Network, called BiCANet, for semantic segmentation. Unlike previous approaches that encode context in feature space, BiCANet aggregates contextual cues from a categorical perspective, which is mainly consist of three parts: contextual condensed projection block (CCPB), bi-directional context interaction block (BCIB), and muti-scale contextual fusion block (MCFB). More specifically, CCPB learns a category-based mapping through a split-transform-merge architecture, which condenses contextual cues with different receptive fields from intermediate layer. BCIB, on the other hand, employs dense skipped-connections to enhance the class-level context exchanging. Finally, MCFB integrates multi-scale contextual cues by investigating short- and long-ranged spatial dependencies. To evaluate BiCANet, we have conducted extensive experiments on three semantic segmentation datasets: PASCAL VOC 2012, Cityscapes, and ADE20K. The experimental results demonstrate that BiCANet outperforms recent state-of-the-art networks without any postprocess techniques. Particularly, BiCANet achieves the mIoU score of 86.7%, 82.4% and 38.66% on PASCAL VOC 2012, Cityscapes and ADE20K testset, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge