Debajit Chakraborty
When expertise gone missing: Uncovering the loss of prolific contributors in Wikipedia
Sep 21, 2021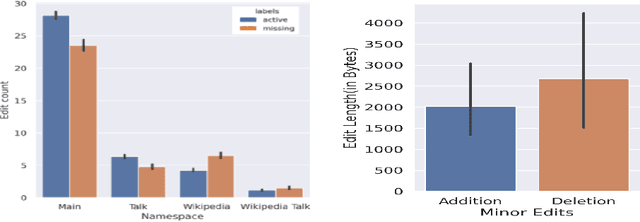
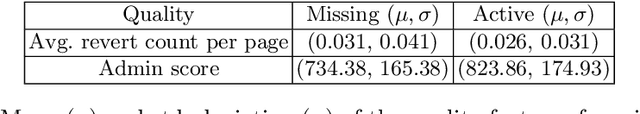
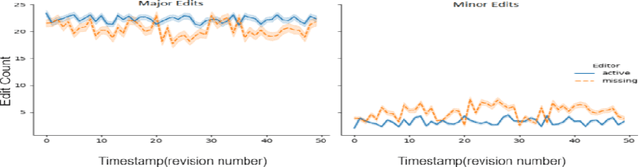

Abstract:Success of planetary-scale online collaborative platforms such as Wikipedia is hinged on active and continued participation of its voluntary contributors. The phenomenal success of Wikipedia as a valued multilingual source of information is a testament to the possibilities of collective intelligence. Specifically, the sustained and prudent contributions by the experienced prolific editors play a crucial role to operate the platform smoothly for decades. However, it has been brought to light that growth of Wikipedia is stagnating in terms of the number of editors that faces steady decline over time. This decreasing productivity and ever increasing attrition rate in both newcomer and experienced editors is a major concern for not only the future of this platform but also for several industry-scale information retrieval systems such as Siri, Alexa which depend on Wikipedia as knowledge store. In this paper, we have studied the ongoing crisis in which experienced and prolific editors withdraw. We performed extensive analysis of the editor activities and their language usage to identify features that can forecast prolific Wikipedians, who are at risk of ceasing voluntary services. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work which proposes a scalable prediction pipeline, towards detecting the prolific Wikipedians, who might be at a risk of retiring from the platform and, thereby, can potentially enable moderators to launch appropriate incentive mechanisms to retain such `would-be missing' valued Wikipedians.
Hate-Alert@DravidianLangTech-EACL2021: Ensembling strategies for Transformer-based Offensive language Detection
Feb 19, 2021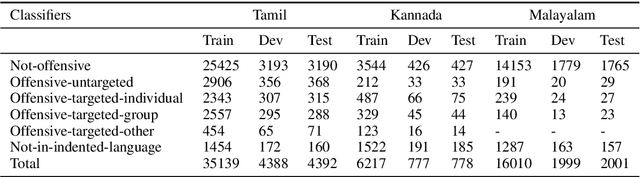
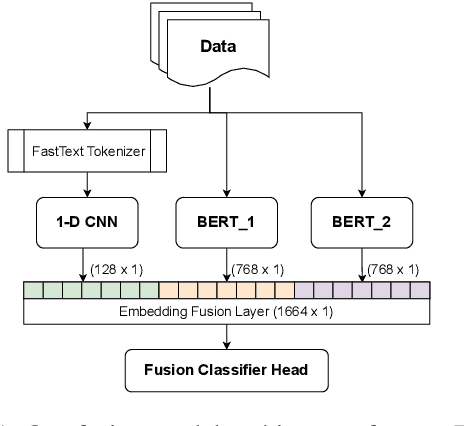
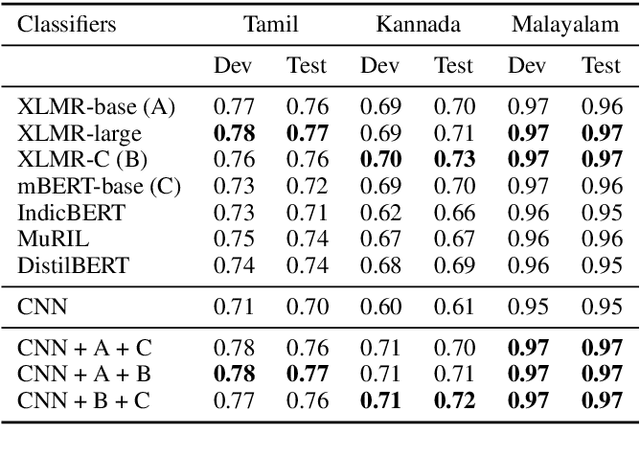
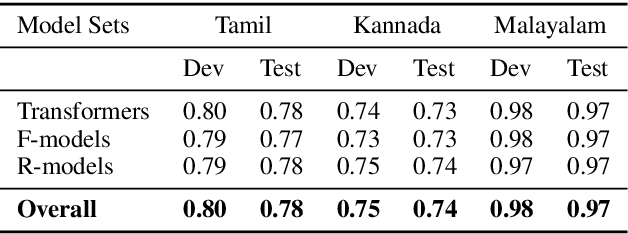
Abstract:Social media often acts as breeding grounds for different forms of offensive content. For low resource languages like Tamil, the situation is more complex due to the poor performance of multilingual or language-specific models and lack of proper benchmark datasets. Based on this shared task, Offensive Language Identification in Dravidian Languages at EACL 2021, we present an exhaustive exploration of different transformer models, We also provide a genetic algorithm technique for ensembling different models. Our ensembled models trained separately for each language secured the first position in Tamil, the second position in Kannada, and the first position in Malayalam sub-tasks. The models and codes are provided.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge