Davinia Hernandez-Leo
Understanding Learner-LLM Chatbot Interactions and the Impact of Prompting Guidelines
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have transformed human-computer interaction by enabling natural language-based communication with AI-powered chatbots. These models are designed to be intuitive and user-friendly, allowing users to articulate requests with minimal effort. However, despite their accessibility, studies reveal that users often struggle with effective prompting, resulting in inefficient responses. Existing research has highlighted both the limitations of LLMs in interpreting vague or poorly structured prompts and the difficulties users face in crafting precise queries. This study investigates learner-AI interactions through an educational experiment in which participants receive structured guidance on effective prompting. We introduce and compare three types of prompting guidelines: a task-specific framework developed through a structured methodology and two baseline approaches. To assess user behavior and prompting efficacy, we analyze a dataset of 642 interactions from 107 users. Using Von NeuMidas, an extended pragmatic annotation schema for LLM interaction analysis, we categorize common prompting errors and identify recurring behavioral patterns. We then evaluate the impact of different guidelines by examining changes in user behavior, adherence to prompting strategies, and the overall quality of AI-generated responses. Our findings provide a deeper understanding of how users engage with LLMs and the role of structured prompting guidance in enhancing AI-assisted communication. By comparing different instructional frameworks, we offer insights into more effective approaches for improving user competency in AI interactions, with implications for AI literacy, chatbot usability, and the design of more responsive AI systems.
Use Me Wisely: AI-Driven Assessment for LLM Prompting Skills Development
Mar 04, 2025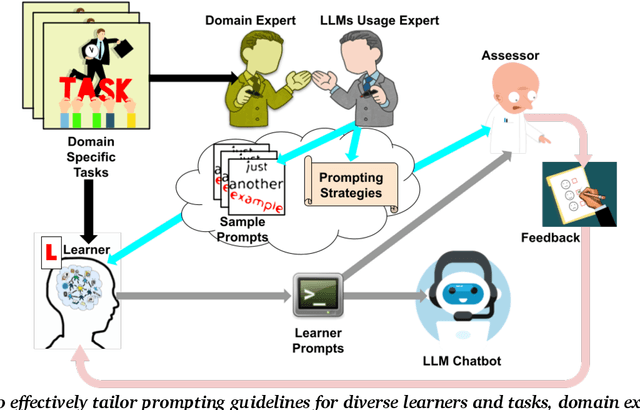
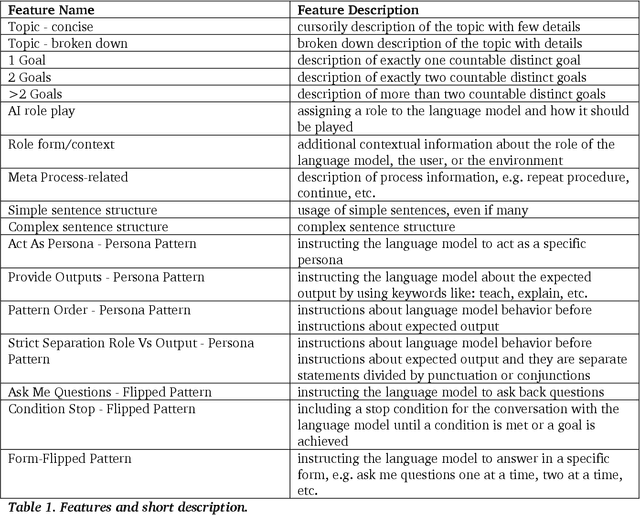
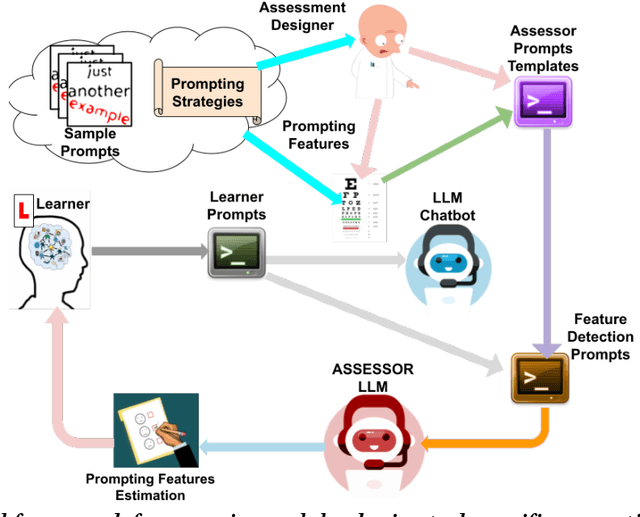
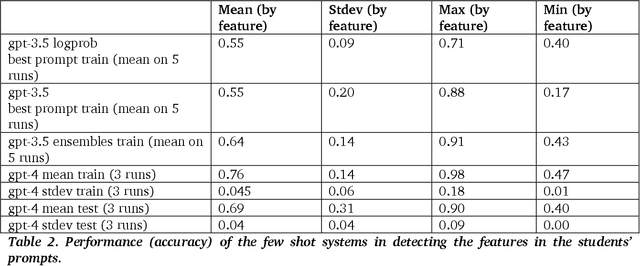
Abstract:The use of large language model (LLM)-powered chatbots, such as ChatGPT, has become popular across various domains, supporting a range of tasks and processes. However, due to the intrinsic complexity of LLMs, effective prompting is more challenging than it may seem. This highlights the need for innovative educational and support strategies that are both widely accessible and seamlessly integrated into task workflows. Yet, LLM prompting is highly task- and domain-dependent, limiting the effectiveness of generic approaches. In this study, we explore whether LLM-based methods can facilitate learning assessments by using ad-hoc guidelines and a minimal number of annotated prompt samples. Our framework transforms these guidelines into features that can be identified within learners' prompts. Using these feature descriptions and annotated examples, we create few-shot learning detectors. We then evaluate different configurations of these detectors, testing three state-of-the-art LLMs and ensembles. We run experiments with cross-validation on a sample of original prompts, as well as tests on prompts collected from task-naive learners. Our results show how LLMs perform on feature detection. Notably, GPT- 4 demonstrates strong performance on most features, while closely related models, such as GPT-3 and GPT-3.5 Turbo (Instruct), show inconsistent behaviors in feature classification. These differences highlight the need for further research into how design choices impact feature selection and prompt detection. Our findings contribute to the fields of generative AI literacy and computer-supported learning assessment, offering valuable insights for both researchers and practitioners.
Learning to Prompt in the Classroom to Understand AI Limits: A pilot study
Jul 04, 2023Abstract:Artificial intelligence's progress holds great promise in assisting society in addressing pressing societal issues. In particular Large Language Models (LLM) and the derived chatbots, like ChatGPT, have highly improved the natural language processing capabilities of AI systems allowing them to process an unprecedented amount of unstructured data. The consequent hype has also backfired, raising negative sentiment even after novel AI methods' surprising contributions. One of the causes, but also an important issue per se, is the rising and misleading feeling of being able to access and process any form of knowledge to solve problems in any domain with no effort or previous expertise in AI or problem domain, disregarding current LLMs limits, such as hallucinations and reasoning limits. Acknowledging AI fallibility is crucial to address the impact of dogmatic overconfidence in possibly erroneous suggestions generated by LLMs. At the same time, it can reduce fear and other negative attitudes toward AI. AI literacy interventions are necessary that allow the public to understand such LLM limits and learn how to use them in a more effective manner, i.e. learning to "prompt". With this aim, a pilot educational intervention was performed in a high school with 30 students. It involved (i) presenting high-level concepts about intelligence, AI, and LLM, (ii) an initial naive practice with ChatGPT in a non-trivial task, and finally (iii) applying currently-accepted prompting strategies. Encouraging preliminary results have been collected such as students reporting a) high appreciation of the activity, b) improved quality of the interaction with the LLM during the educational activity, c) decreased negative sentiments toward AI, d) increased understanding of limitations and specifically We aim to study factors that impact AI acceptance and to refine and repeat this activity in more controlled settings.
Developing Effective Educational Chatbots with ChatGPT prompts: Insights from Preliminary Tests in a Case Study on Social Media Literacy
Jun 18, 2023

Abstract:Educational chatbots come with a promise of interactive and personalized learning experiences, yet their development has been limited by the restricted free interaction capabilities of available platforms and the difficulty of encoding knowledge in a suitable format. Recent advances in language learning models with zero-shot learning capabilities, such as ChatGPT, suggest a new possibility for developing educational chatbots using a prompt-based approach. We present a case study with a simple system that enables mixed-turn chatbot interactions and we discuss the insights and preliminary guidelines obtained from initial tests. We examine ChatGPT's ability to pursue multiple interconnected learning objectives, adapt the educational activity to users' characteristics, such as culture, age, and level of education, and its ability to use diverse educational strategies and conversational styles. Although the results are encouraging, challenges are posed by the limited history maintained for the conversation and the highly structured form of responses by ChatGPT, as well as their variability, which can lead to an unexpected switch of the chatbot's role from a teacher to a therapist. We provide some initial guidelines to address these issues and to facilitate the development of effective educational chatbots.
Predicting Early Dropout: Calibration and Algorithmic Fairness Considerations
Mar 16, 2021

Abstract:In this work, the problem of predicting dropout risk in undergraduate studies is addressed from a perspective of algorithmic fairness. We develop a machine learning method to predict the risks of university dropout and underperformance. The objective is to understand if such a system can identify students at risk while avoiding potential discriminatory biases. When modeling both risks, we obtain prediction models with an Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC) of 0.77-0.78 based on the data available at the enrollment time, before the first year of studies starts. This data includes the students' demographics, the high school they attended, and their admission (average) grade. Our models are calibrated: they produce estimated probabilities for each risk, not mere scores. We analyze if this method leads to discriminatory outcomes for some sensitive groups in terms of prediction accuracy (AUC) and error rates (Generalized False Positive Rate, GFPR, or Generalized False Negative Rate, GFNR). The models exhibit some equity in terms of AUC and GFNR along groups. The similar GFNR means a similar probability of failing to detect risk for students who drop out. The disparities in GFPR are addressed through a mitigation process that does not affect the calibration of the model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge