Davide Zappetti
Seeking Quality Diversity in Evolutionary Co-design of Morphology and Control of Soft Tensegrity Modular Robots
Apr 25, 2021
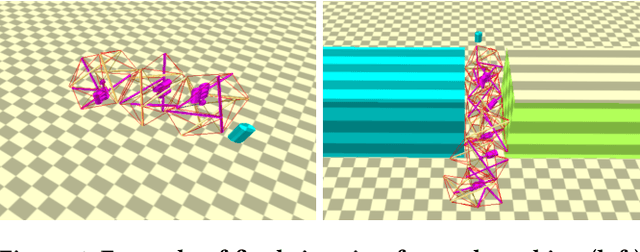
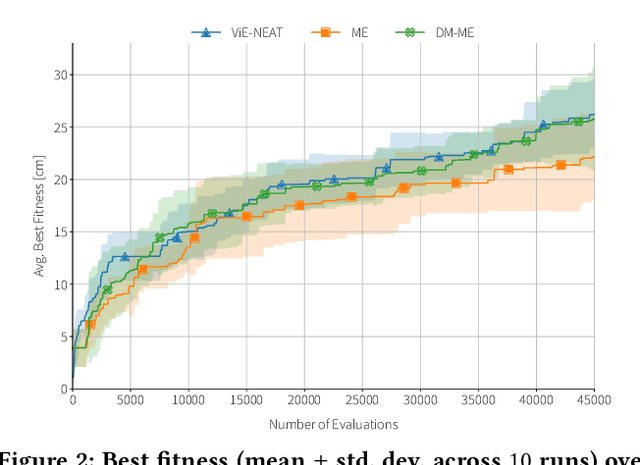
Abstract:Designing optimal soft modular robots is difficult, due to non-trivial interactions between morphology and controller. Evolutionary algorithms (EAs), combined with physical simulators, represent a valid tool to overcome this issue. In this work, we investigate algorithmic solutions to improve the Quality Diversity of co-evolved designs of Tensegrity Soft Modular Robots (TSMRs) for two robotic tasks, namely goal reaching and squeezing trough a narrow passage. To this aim, we use three different EAs, i.e., MAP-Elites and two custom algorithms: one based on Viability Evolution (ViE) and NEAT (ViE-NEAT), the other named Double Map MAP-Elites (DM-ME) and devised to seek diversity while co-evolving robot morphologies and neural network (NN)-based controllers. In detail, DM-ME extends MAP-Elites in that it uses two distinct feature maps, referring to morphologies and controllers respectively, and integrates a mechanism to automatically define the NN-related feature descriptor. Considering the fitness, in the goal-reaching task ViE-NEAT outperforms MAP-Elites and results equivalent to DM-ME. Instead, when considering diversity in terms of "illumination" of the feature space, DM-ME outperforms the other two algorithms on both tasks, providing a richer pool of possible robotic designs, whereas ViE-NEAT shows comparable performance to MAP-Elites on goal reaching, although it does not exploit any map.
Evolutionary Co-Design of Morphology and Control of Soft Tensegrity Modular Robots with Programmable Stiffness
Jan 28, 2021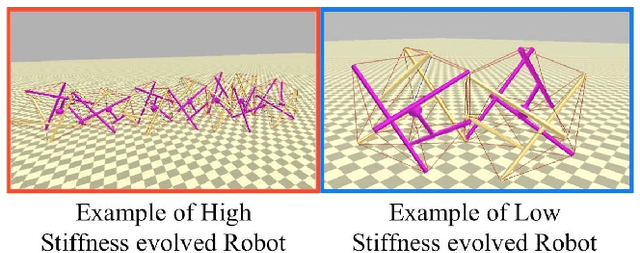
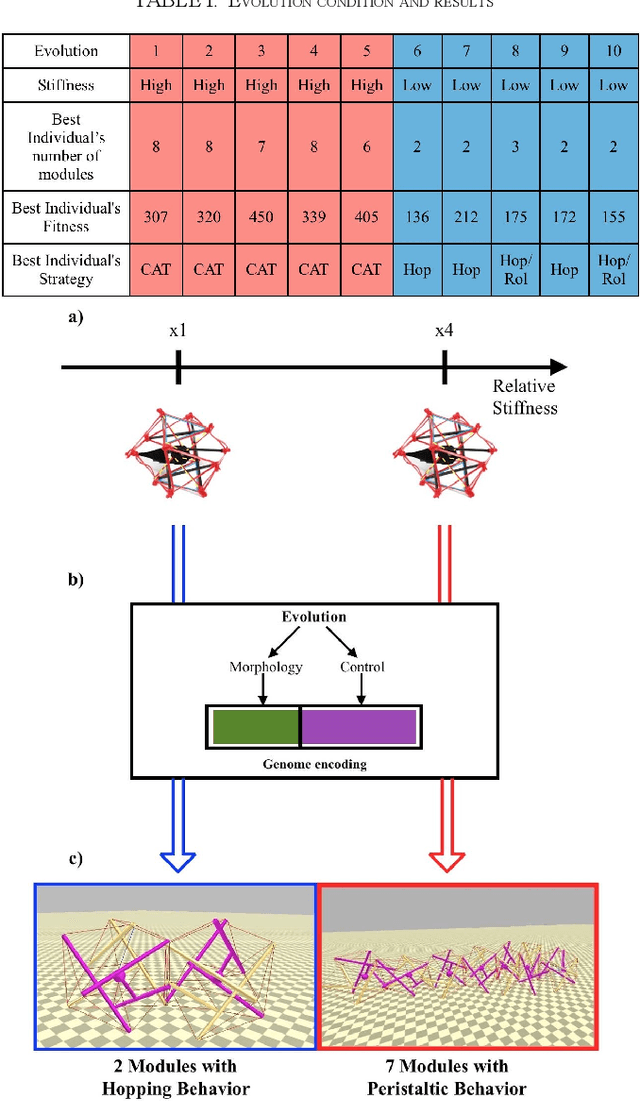
Abstract:Tensegrity structures are lightweight, can undergo large deformations, and have outstanding robustness capabilities. These unique properties inspired roboticists to investigate their use. However, the morphological design, control, assembly, and actuation of tensegrity robots are still difficult tasks. Moreover, the stiffness of tensegrity robots is still an underestimated design parameter. In this article, we propose to use easy to assemble, actuated tensegrity modules and body-brain co-evolution to design soft tensegrity modular robots. Moreover, we prove the importance of tensegrity robots stiffness showing how the evolution suggests a different morphology, control, and locomotion strategy according to the modules stiffness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge