David Peng
FOLIO: Natural Language Reasoning with First-Order Logic
Sep 02, 2022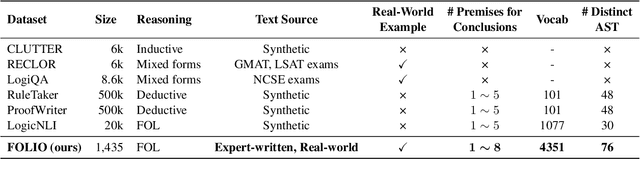
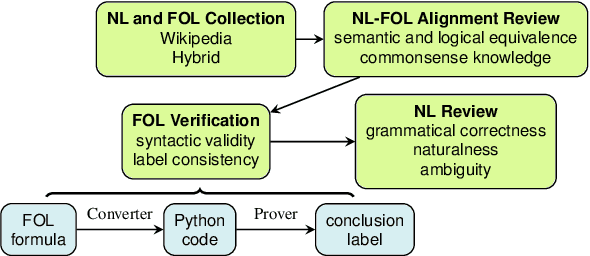
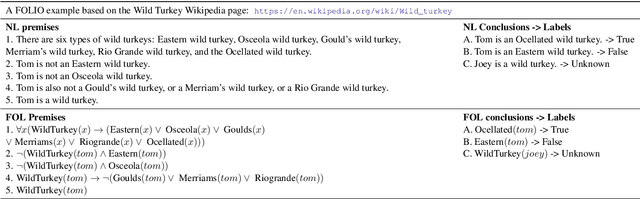
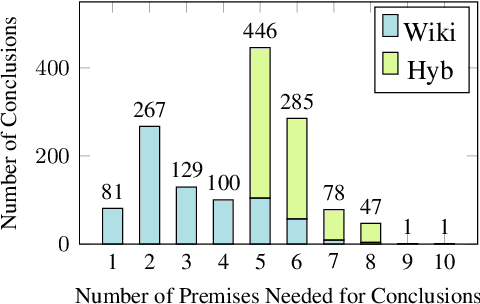
Abstract:We present FOLIO, a human-annotated, open-domain, and logically complex and diverse dataset for reasoning in natural language (NL), equipped with first order logic (FOL) annotations. FOLIO consists of 1,435 examples (unique conclusions), each paired with one of 487 sets of premises which serve as rules to be used to deductively reason for the validity of each conclusion. The logical correctness of premises and conclusions is ensured by their parallel FOL annotations, which are automatically verified by our FOL inference engine. In addition to the main NL reasoning task, NL-FOL pairs in FOLIO automatically constitute a new NL-FOL translation dataset using FOL as the logical form. Our experiments on FOLIO systematically evaluate the FOL reasoning ability of supervised fine-tuning on medium-sized language models (BERT, RoBERTa) and few-shot prompting on large language models (GPT-NeoX, OPT, GPT-3, Codex). For NL-FOL translation, we experiment with GPT-3 and Codex. Our results show that one of the most capable Large Language Model (LLM) publicly available, GPT-3 davinci, achieves only slightly better than random results with few-shot prompting on a subset of FOLIO, and the model is especially bad at predicting the correct truth values for False and Unknown conclusions. Our dataset and code are available at https://github.com/Yale-LILY/FOLIO.
Exploring the Sensory Spaces of English Perceptual Verbs in Natural Language Data
Oct 19, 2021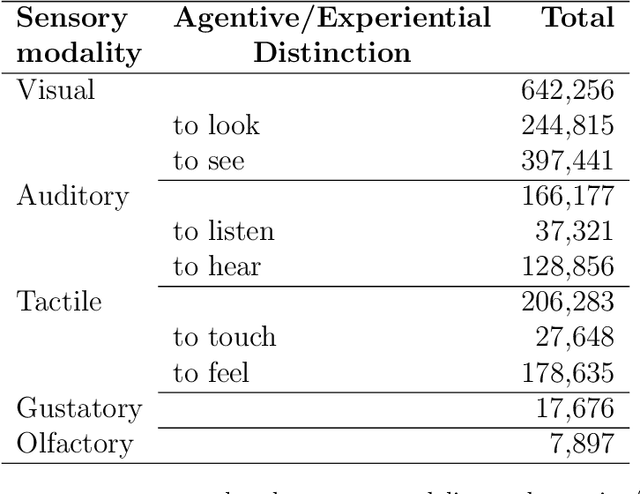

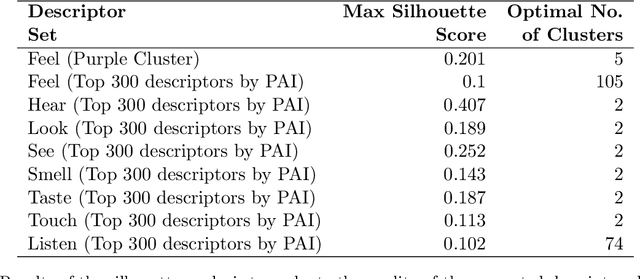
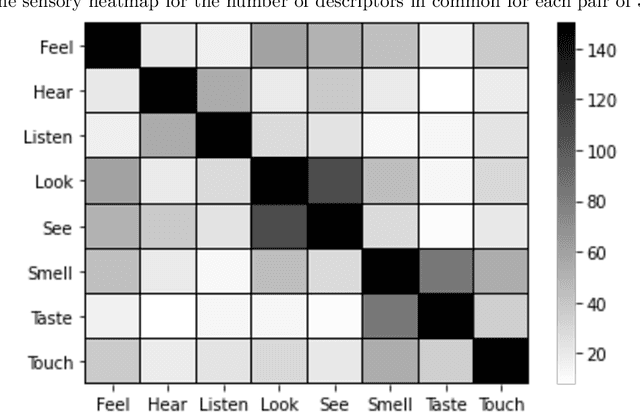
Abstract:In this study, we explore how language captures the meaning of words, in particular meaning related to sensory experiences learned from statistical distributions across texts. We focus on the most frequent perception verbs of English analyzed from an and Agentive vs. Experiential distinction across the five basic sensory modalities: Visual (to look vs. to see), Auditory (to listen vs. to hear), Tactile (to touch vs. to feel), Olfactory (to smell), and Gustatory (to taste). In this study we report on a data-driven approach based on distributional-semantic word embeddings and clustering models to identify and uncover the descriptor sensory spaces of the perception verbs. In the analysis, we identified differences and similarities of the generated descriptors based on qualitative and quantitative differences of the perceptual experience they denote. For instance, our results show that while the perceptual spaces of the experiential verbs like to see, to hear show a more detached, logical way of knowing and learning, their agentive counterparts (to look, listen) provide a more intentional as well as more intimate and intuitive way of discovering and interacting with the world around us. We believe that such an approach has a high potential to expand our understanding and the applicability of such sensory spaces to different fields of social and cultural analysis. Research on the semantic organization of sensory spaces for various applications might benefit from an the Agentive/Experiential account to address the complexity of multiple senses wired with each other in still unexplored ways.
* 19 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge