David J Wu
Mastering the Game of No-Press Diplomacy via Human-Regularized Reinforcement Learning and Planning
Oct 11, 2022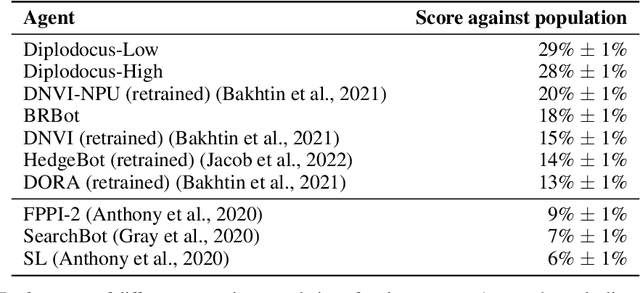
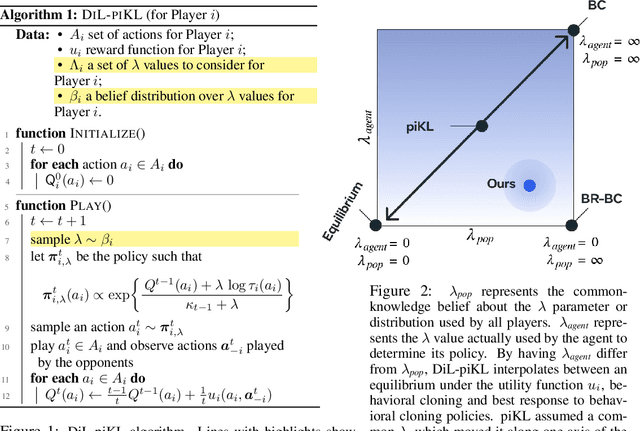
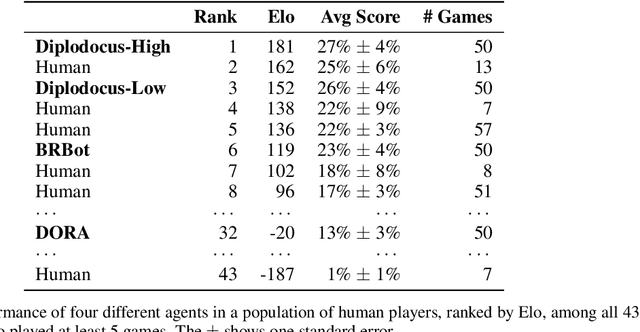
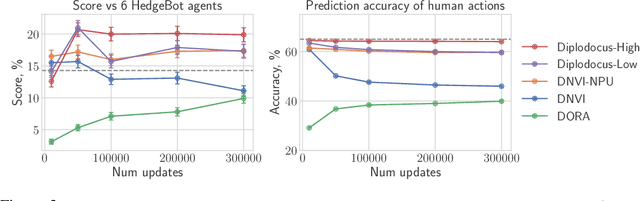
Abstract:No-press Diplomacy is a complex strategy game involving both cooperation and competition that has served as a benchmark for multi-agent AI research. While self-play reinforcement learning has resulted in numerous successes in purely adversarial games like chess, Go, and poker, self-play alone is insufficient for achieving optimal performance in domains involving cooperation with humans. We address this shortcoming by first introducing a planning algorithm we call DiL-piKL that regularizes a reward-maximizing policy toward a human imitation-learned policy. We prove that this is a no-regret learning algorithm under a modified utility function. We then show that DiL-piKL can be extended into a self-play reinforcement learning algorithm we call RL-DiL-piKL that provides a model of human play while simultaneously training an agent that responds well to this human model. We used RL-DiL-piKL to train an agent we name Diplodocus. In a 200-game no-press Diplomacy tournament involving 62 human participants spanning skill levels from beginner to expert, two Diplodocus agents both achieved a higher average score than all other participants who played more than two games, and ranked first and third according to an Elo ratings model.
Human-AI Coordination via Human-Regularized Search and Learning
Oct 11, 2022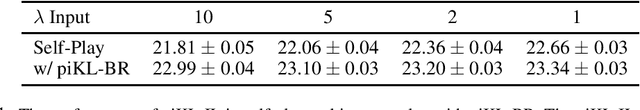
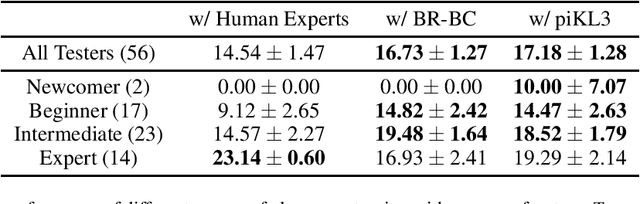
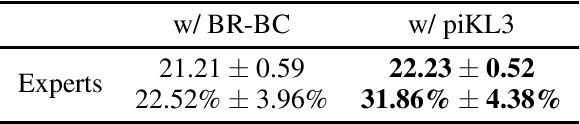
Abstract:We consider the problem of making AI agents that collaborate well with humans in partially observable fully cooperative environments given datasets of human behavior. Inspired by piKL, a human-data-regularized search method that improves upon a behavioral cloning policy without diverging far away from it, we develop a three-step algorithm that achieve strong performance in coordinating with real humans in the Hanabi benchmark. We first use a regularized search algorithm and behavioral cloning to produce a better human model that captures diverse skill levels. Then, we integrate the policy regularization idea into reinforcement learning to train a human-like best response to the human model. Finally, we apply regularized search on top of the best response policy at test time to handle out-of-distribution challenges when playing with humans. We evaluate our method in two large scale experiments with humans. First, we show that our method outperforms experts when playing with a group of diverse human players in ad-hoc teams. Second, we show that our method beats a vanilla best response to behavioral cloning baseline by having experts play repeatedly with the two agents.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge