David Blondheim
High frame-rate cardiac ultrasound imaging with deep learning
Aug 23, 2018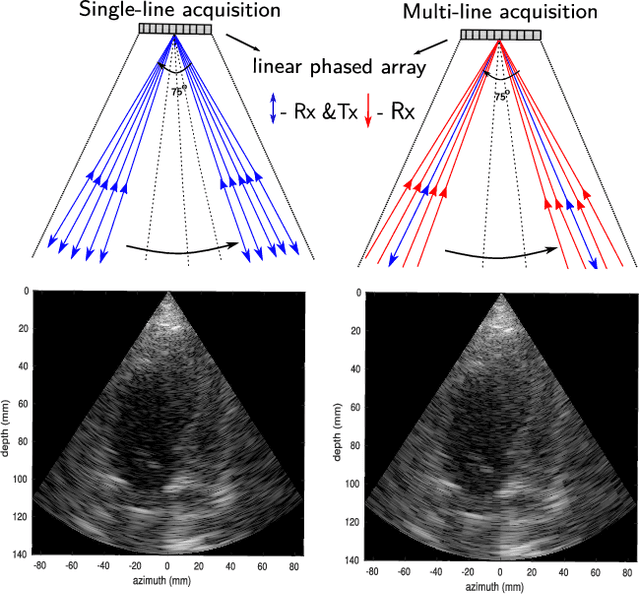

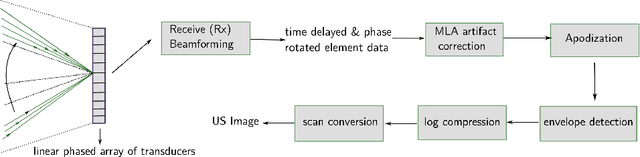

Abstract:Cardiac ultrasound imaging requires a high frame rate in order to capture rapid motion. This can be achieved by multi-line acquisition (MLA), where several narrow-focused received lines are obtained from each wide-focused transmitted line. This shortens the acquisition time at the expense of introducing block artifacts. In this paper, we propose a data-driven learning-based approach to improve the MLA image quality. We train an end-to-end convolutional neural network on pairs of real ultrasound cardiac data, acquired through MLA and the corresponding single-line acquisition (SLA). The network achieves a significant improvement in image quality for both $5-$ and $7-$line MLA resulting in a decorrelation measure similar to that of SLA while having the frame rate of MLA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge