Daniil Dobriy
Semantic Web and Creative AI -- A Technical Report from ISWS 2023
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:The International Semantic Web Research School (ISWS) is a week-long intensive program designed to immerse participants in the field. This document reports a collaborative effort performed by ten teams of students, each guided by a senior researcher as their mentor, attending ISWS 2023. Each team provided a different perspective to the topic of creative AI, substantiated by a set of research questions as the main subject of their investigation. The 2023 edition of ISWS focuses on the intersection of Semantic Web technologies and Creative AI. ISWS 2023 explored various intersections between Semantic Web technologies and creative AI. A key area of focus was the potential of LLMs as support tools for knowledge engineering. Participants also delved into the multifaceted applications of LLMs, including legal aspects of creative content production, humans in the loop, decentralised approaches to multimodal generative AI models, nanopublications and AI for personal scientific knowledge graphs, commonsense knowledge in automatic story and narrative completion, generative AI for art critique, prompt engineering, automatic music composition, commonsense prototyping and conceptual blending, and elicitation of tacit knowledge. As Large Language Models and semantic technologies continue to evolve, new exciting prospects are emerging: a future where the boundaries between creative expression and factual knowledge become increasingly permeable and porous, leading to a world of knowledge that is both informative and inspiring.
Scholarly Wikidata: Population and Exploration of Conference Data in Wikidata using LLMs
Nov 13, 2024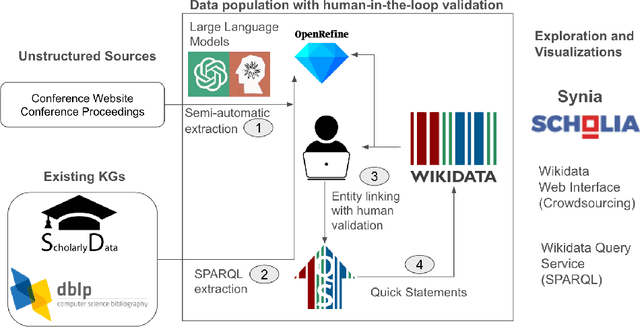
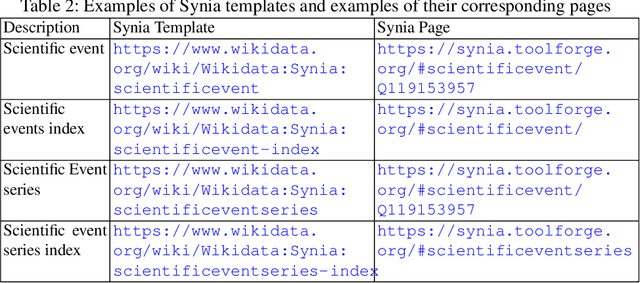
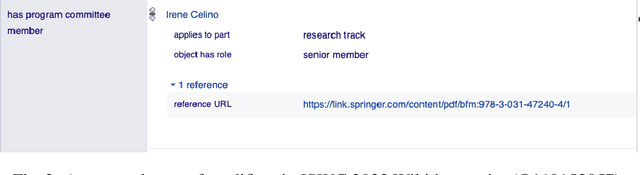

Abstract:Several initiatives have been undertaken to conceptually model the domain of scholarly data using ontologies and to create respective Knowledge Graphs. Yet, the full potential seems unleashed, as automated means for automatic population of said ontologies are lacking, and respective initiatives from the Semantic Web community are not necessarily connected: we propose to make scholarly data more sustainably accessible by leveraging Wikidata's infrastructure and automating its population in a sustainable manner through LLMs by tapping into unstructured sources like conference Web sites and proceedings texts as well as already existing structured conference datasets. While an initial analysis shows that Semantic Web conferences are only minimally represented in Wikidata, we argue that our methodology can help to populate, evolve and maintain scholarly data as a community within Wikidata. Our main contributions include (a) an analysis of ontologies for representing scholarly data to identify gaps and relevant entities/properties in Wikidata, (b) semi-automated extraction -- requiring (minimal) manual validation -- of conference metadata (e.g., acceptance rates, organizer roles, programme committee members, best paper awards, keynotes, and sponsors) from websites and proceedings texts using LLMs. Finally, we discuss (c) extensions to visualization tools in the Wikidata context for data exploration of the generated scholarly data. Our study focuses on data from 105 Semantic Web-related conferences and extends/adds more than 6000 entities in Wikidata. It is important to note that the method can be more generally applicable beyond Semantic Web-related conferences for enhancing Wikidata's utility as a comprehensive scholarly resource. Source Repository: https://github.com/scholarly-wikidata/ DOI: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10989709 License: Creative Commons CC0 (Data), MIT (Code)
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge