Martin Böckling
Walk&Retrieve: Simple Yet Effective Zero-shot Retrieval-Augmented Generation via Knowledge Graph Walks
May 22, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have showcased impressive reasoning abilities, but often suffer from hallucinations or outdated knowledge. Knowledge Graph (KG)-based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) remedies these shortcomings by grounding LLM responses in structured external information from a knowledge base. However, many KG-based RAG approaches struggle with (i) aligning KG and textual representations, (ii) balancing retrieval accuracy and efficiency, and (iii) adapting to dynamically updated KGs. In this work, we introduce Walk&Retrieve, a simple yet effective KG-based framework that leverages walk-based graph traversal and knowledge verbalization for corpus generation for zero-shot RAG. Built around efficient KG walks, our method does not require fine-tuning on domain-specific data, enabling seamless adaptation to KG updates, reducing computational overhead, and allowing integration with any off-the-shelf backbone LLM. Despite its simplicity, Walk&Retrieve performs competitively, often outperforming existing RAG systems in response accuracy and hallucination reduction. Moreover, it demonstrates lower query latency and robust scalability to large KGs, highlighting the potential of lightweight retrieval strategies as strong baselines for future RAG research.
Semantic Web and Creative AI -- A Technical Report from ISWS 2023
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:The International Semantic Web Research School (ISWS) is a week-long intensive program designed to immerse participants in the field. This document reports a collaborative effort performed by ten teams of students, each guided by a senior researcher as their mentor, attending ISWS 2023. Each team provided a different perspective to the topic of creative AI, substantiated by a set of research questions as the main subject of their investigation. The 2023 edition of ISWS focuses on the intersection of Semantic Web technologies and Creative AI. ISWS 2023 explored various intersections between Semantic Web technologies and creative AI. A key area of focus was the potential of LLMs as support tools for knowledge engineering. Participants also delved into the multifaceted applications of LLMs, including legal aspects of creative content production, humans in the loop, decentralised approaches to multimodal generative AI models, nanopublications and AI for personal scientific knowledge graphs, commonsense knowledge in automatic story and narrative completion, generative AI for art critique, prompt engineering, automatic music composition, commonsense prototyping and conceptual blending, and elicitation of tacit knowledge. As Large Language Models and semantic technologies continue to evolve, new exciting prospects are emerging: a future where the boundaries between creative expression and factual knowledge become increasingly permeable and porous, leading to a world of knowledge that is both informative and inspiring.
A Planet Scale Spatial-Temporal Knowledge Graph Based On OpenStreetMap And H3 Grid
May 24, 2024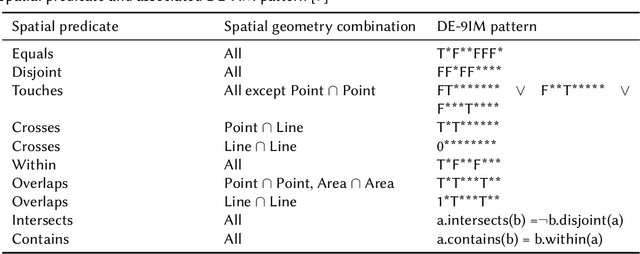



Abstract:Geospatial data plays a central role in modeling our world, for which OpenStreetMap (OSM) provides a rich source of such data. While often spatial data is represented in a tabular format, a graph based representation provides the possibility to interconnect entities which would have been separated in a tabular representation. We propose in our paper a framework which supports a planet scale transformation of OpenStreetMap data into a Spatial Temporal Knowledge Graph. In addition to OpenStreetMap data, we align the different OpenStreetMap geometries on individual h3 grid cells. We compare our constructed spatial knowledge graph to other spatial knowledge graphs and outline our contribution in this paper. As a basis for our computation, we use Apache Sedona as a computational framework for our Spatial Temporal Knowledge Graph construction
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge