Daniele Gambetta
A linguistic analysis of undesirable outcomes in the era of generative AI
Oct 16, 2024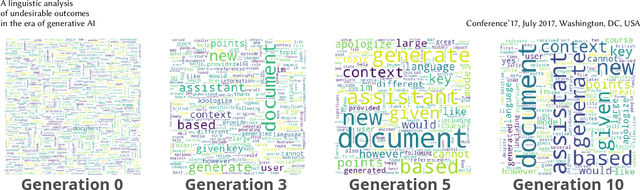
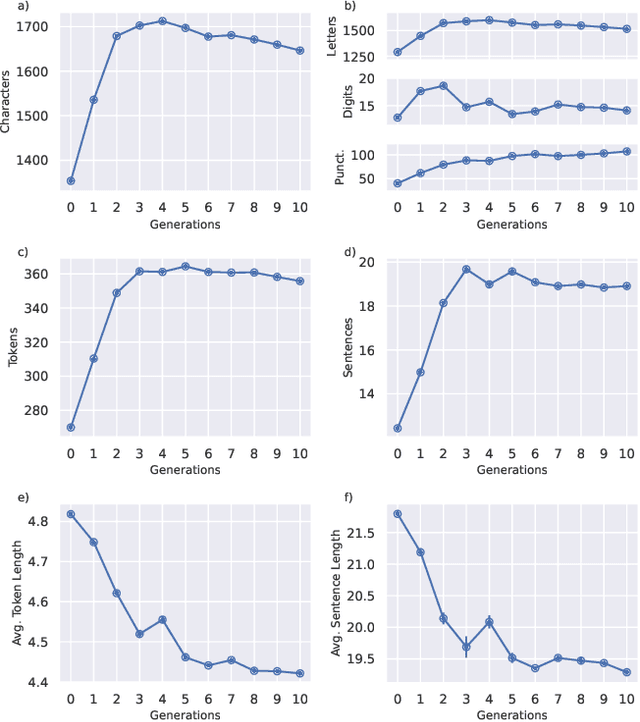
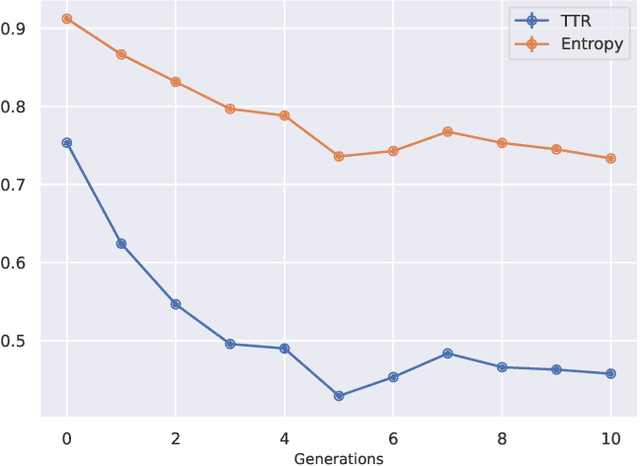
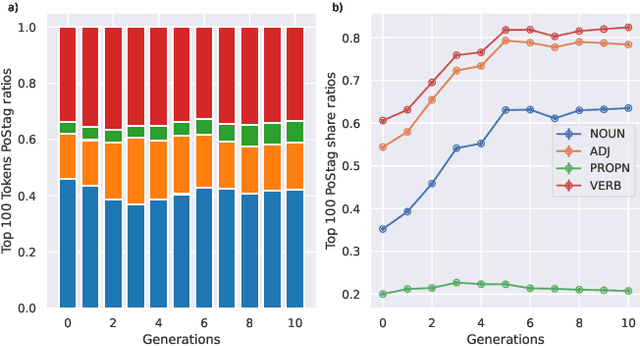
Abstract:Recent research has focused on the medium and long-term impacts of generative AI, posing scientific and societal challenges mainly due to the detection and reliability of machine-generated information, which is projected to form the major content on the Web soon. Prior studies show that LLMs exhibit a lower performance in generation tasks (model collapse) as they undergo a fine-tuning process across multiple generations on their own generated content (self-consuming loop). In this paper, we present a comprehensive simulation framework built upon the chat version of LLama2, focusing particularly on the linguistic aspects of the generated content, which has not been fully examined in existing studies. Our results show that the model produces less lexical rich content across generations, reducing diversity. The lexical richness has been measured using the linguistic measures of entropy and TTR as well as calculating the POSTags frequency. The generated content has also been examined with an $n$-gram analysis, which takes into account the word order, and semantic networks, which consider the relation between different words. These findings suggest that the model collapse occurs not only by decreasing the content diversity but also by distorting the underlying linguistic patterns of the generated text, which both highlight the critical importance of carefully choosing and curating the initial input text, which can alleviate the model collapse problem. Furthermore, we conduct a qualitative analysis of the fine-tuned models of the pipeline to compare their performances on generic NLP tasks to the original model. We find that autophagy transforms the initial model into a more creative, doubtful and confused one, which might provide inaccurate answers and include conspiracy theories in the model responses, spreading false and biased information on the Web.
A survey on the impact of AI-based recommenders on human behaviours: methodologies, outcomes and future directions
Jun 29, 2024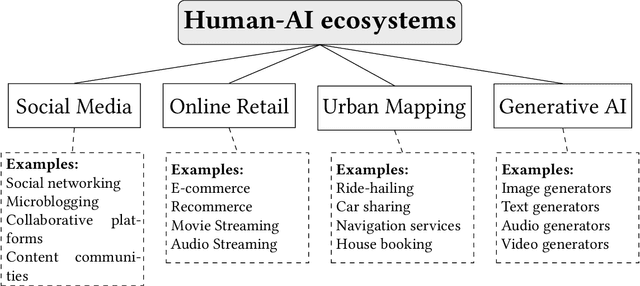
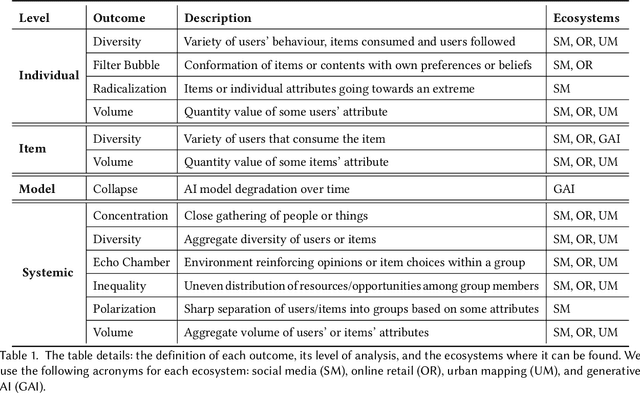
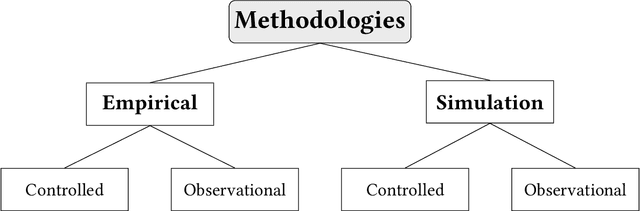
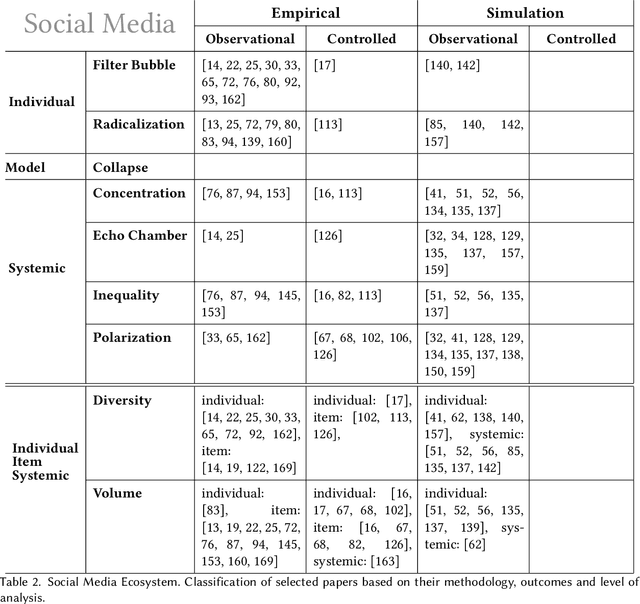
Abstract:Recommendation systems and assistants (in short, recommenders) are ubiquitous in online platforms and influence most actions of our day-to-day lives, suggesting items or providing solutions based on users' preferences or requests. This survey analyses the impact of recommenders in four human-AI ecosystems: social media, online retail, urban mapping and generative AI ecosystems. Its scope is to systematise a fast-growing field in which terminologies employed to classify methodologies and outcomes are fragmented and unsystematic. We follow the customary steps of qualitative systematic review, gathering 144 articles from different disciplines to develop a parsimonious taxonomy of: methodologies employed (empirical, simulation, observational, controlled), outcomes observed (concentration, model collapse, diversity, echo chamber, filter bubble, inequality, polarisation, radicalisation, volume), and their level of analysis (individual, item, model, and systemic). We systematically discuss all findings of our survey substantively and methodologically, highlighting also potential avenues for future research. This survey is addressed to scholars and practitioners interested in different human-AI ecosystems, policymakers and institutional stakeholders who want to understand better the measurable outcomes of recommenders, and tech companies who wish to obtain a systematic view of the impact of their recommenders.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge