Daniel J. Hoeppner
Object-Guided Instance Segmentation With Auxiliary Feature Refinement for Biological Images
Jun 14, 2021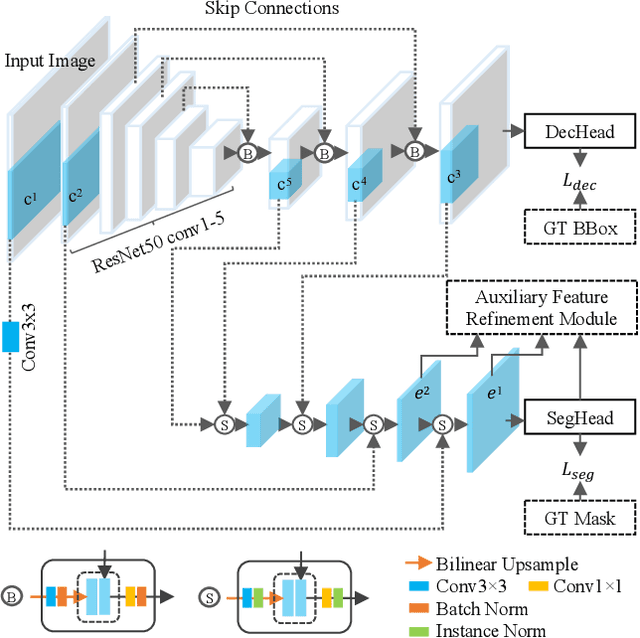
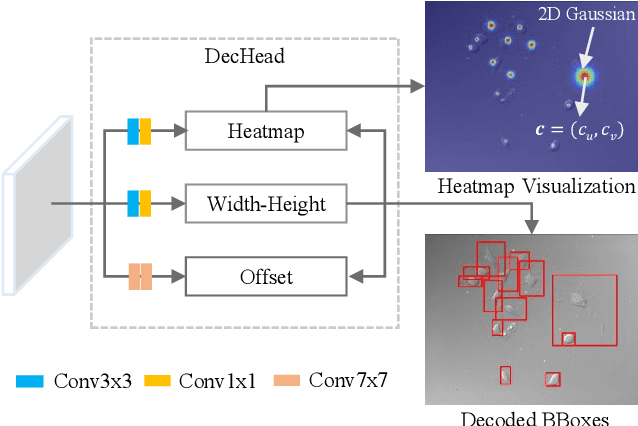
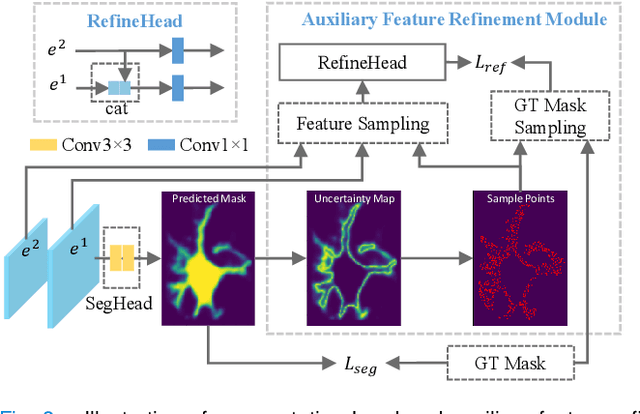
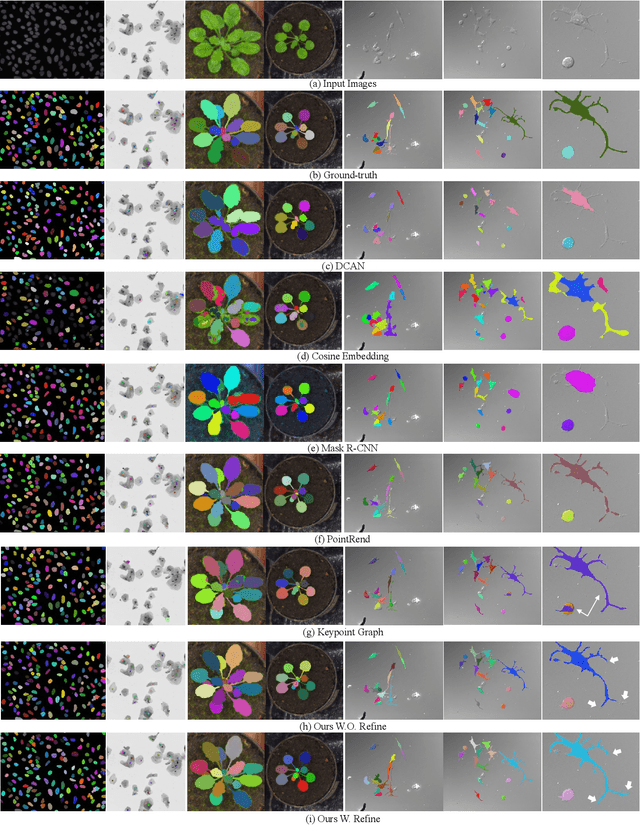
Abstract:Instance segmentation is of great importance for many biological applications, such as study of neural cell interactions, plant phenotyping, and quantitatively measuring how cells react to drug treatment. In this paper, we propose a novel box-based instance segmentation method. Box-based instance segmentation methods capture objects via bounding boxes and then perform individual segmentation within each bounding box region. However, existing methods can hardly differentiate the target from its neighboring objects within the same bounding box region due to their similar textures and low-contrast boundaries. To deal with this problem, in this paper, we propose an object-guided instance segmentation method. Our method first detects the center points of the objects, from which the bounding box parameters are then predicted. To perform segmentation, an object-guided coarse-to-fine segmentation branch is built along with the detection branch. The segmentation branch reuses the object features as guidance to separate target object from the neighboring ones within the same bounding box region. To further improve the segmentation quality, we design an auxiliary feature refinement module that densely samples and refines point-wise features in the boundary regions. Experimental results on three biological image datasets demonstrate the advantages of our method. The code will be available at https://github.com/yijingru/ObjGuided-Instance-Segmentation.
Object-Guided Instance Segmentation for Biological Images
Nov 20, 2019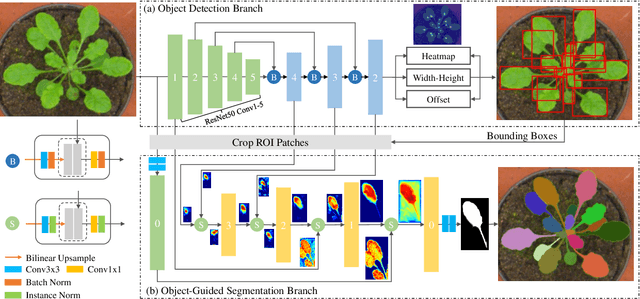
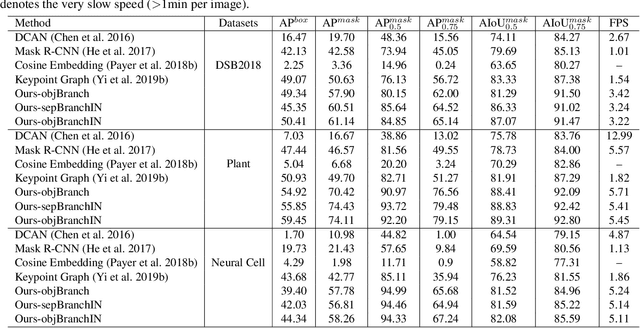
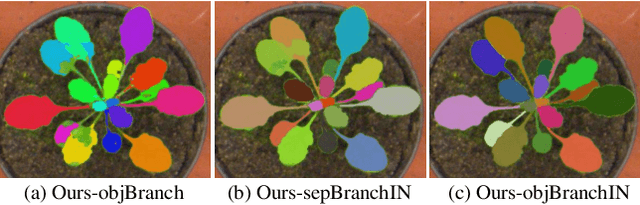
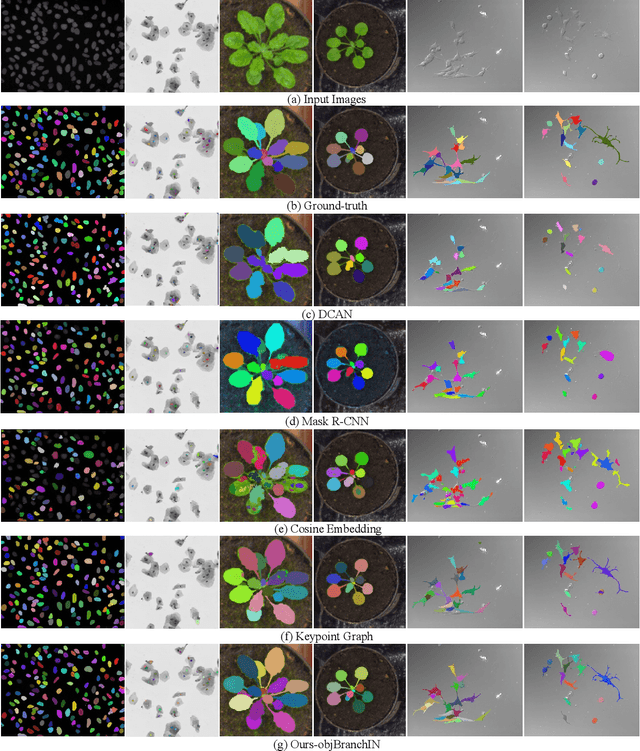
Abstract:Instance segmentation of biological images is essential for studying object behaviors and properties. The challenges, such as clustering, occlusion, and adhesion problems of the objects, make instance segmentation a non-trivial task. Current box-free instance segmentation methods typically rely on local pixel-level information. Due to a lack of global object view, these methods are prone to over- or under-segmentation. On the contrary, the box-based instance segmentation methods incorporate object detection into the segmentation, performing better in identifying the individual instances. In this paper, we propose a new box-based instance segmentation method. Mainly, we locate the object bounding boxes from their center points. The object features are subsequently reused in the segmentation branch as a guide to separate the clustered instances within an RoI patch. Along with the instance normalization, the model is able to recover the target object distribution and suppress the distribution of neighboring attached objects. Consequently, the proposed model performs excellently in segmenting the clustered objects while retaining the target object details. The proposed method achieves state-of-the-art performances on three biological datasets: cell nuclei, plant phenotyping dataset, and neural cells.
Multi-scale Cell Instance Segmentation with Keypoint Graph based Bounding Boxes
Jul 25, 2019



Abstract:Most existing methods handle cell instance segmentation problems directly without relying on additional detection boxes. These methods generally fails to separate touching cells due to the lack of global understanding of the objects. In contrast, box-based instance segmentation solves this problem by combining object detection with segmentation. However, existing methods typically utilize anchor box-based detectors, which would lead to inferior instance segmentation performance due to the class imbalance issue. In this paper, we propose a new box-based cell instance segmentation method. In particular, we first detect the five pre-defined points of a cell via keypoints detection. Then we group these points according to a keypoint graph and subsequently extract the bounding box for each cell. Finally, cell segmentation is performed on feature maps within the bounding boxes. We validate our method on two cell datasets with distinct object shapes, and empirically demonstrate the superiority of our method compared to other instance segmentation techniques. Code is available at: https://github.com/yijingru/KG_Instance_Segmentation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge