Daniel Carlos Guimarães Pedronette
Person Re-ID through Unsupervised Hypergraph Rank Selection and Fusion
Apr 27, 2023
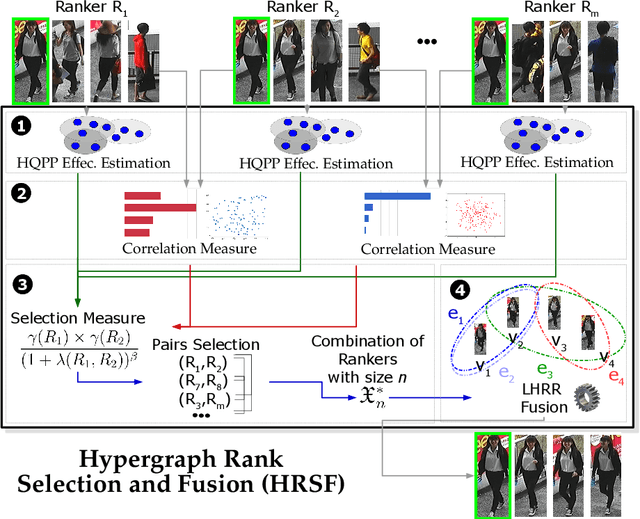
Abstract:Person Re-ID has been gaining a lot of attention and nowadays is of fundamental importance in many camera surveillance applications. The task consists of identifying individuals across multiple cameras that have no overlapping views. Most of the approaches require labeled data, which is not always available, given the huge amount of demanded data and the difficulty of manually assigning a class for each individual. Recently, studies have shown that re-ranking methods are capable of achieving significant gains, especially in the absence of labeled data. Besides that, the fusion of feature extractors and multiple-source training is another promising research direction not extensively exploited. We aim to fill this gap through a manifold rank aggregation approach capable of exploiting the complementarity of different person Re-ID rankers. In this work, we perform a completely unsupervised selection and fusion of diverse ranked lists obtained from multiple and diverse feature extractors. Among the contributions, this work proposes a query performance prediction measure that models the relationship among images considering a hypergraph structure and does not require the use of any labeled data. Expressive gains were obtained in four datasets commonly used for person Re-ID. We achieved results competitive to the state-of-the-art in most of the scenarios.
Rank Flow Embedding for Unsupervised and Semi-Supervised Manifold Learning
Apr 24, 2023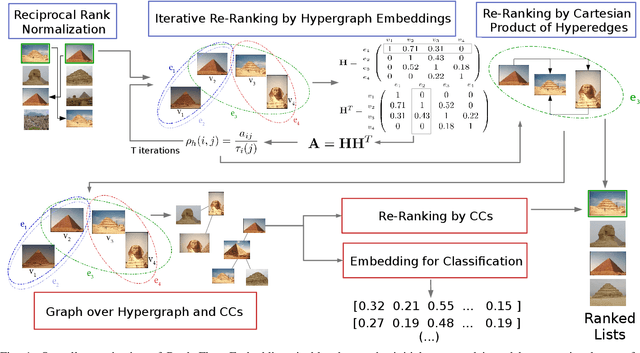
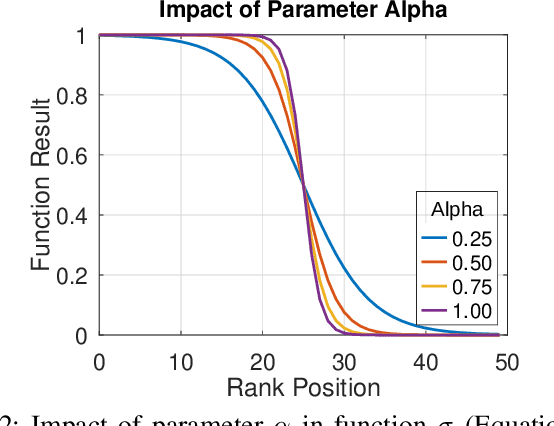
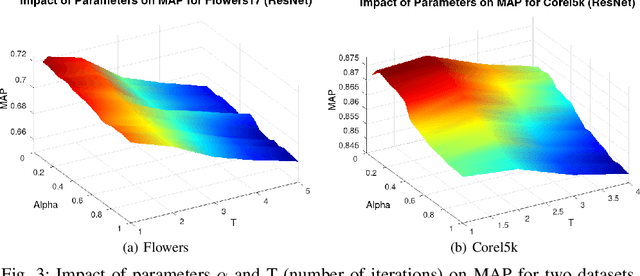
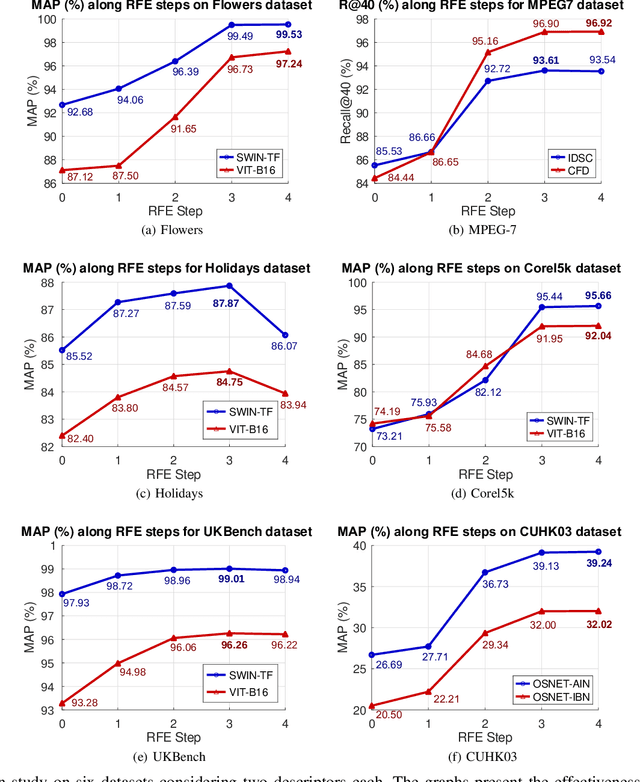
Abstract:Impressive advances in acquisition and sharing technologies have made the growth of multimedia collections and their applications almost unlimited. However, the opposite is true for the availability of labeled data, which is needed for supervised training, since such data is often expensive and time-consuming to obtain. While there is a pressing need for the development of effective retrieval and classification methods, the difficulties faced by supervised approaches highlight the relevance of methods capable of operating with few or no labeled data. In this work, we propose a novel manifold learning algorithm named Rank Flow Embedding (RFE) for unsupervised and semi-supervised scenarios. The proposed method is based on ideas recently exploited by manifold learning approaches, which include hypergraphs, Cartesian products, and connected components. The algorithm computes context-sensitive embeddings, which are refined following a rank-based processing flow, while complementary contextual information is incorporated. The generated embeddings can be exploited for more effective unsupervised retrieval or semi-supervised classification based on Graph Convolutional Networks. Experimental results were conducted on 10 different collections. Various features were considered, including the ones obtained with recent Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and Vision Transformer (ViT) models. High effective results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method on different tasks: unsupervised image retrieval, semi-supervised classification, and person Re-ID. The results demonstrate that RFE is competitive or superior to the state-of-the-art in diverse evaluated scenarios.
Graph Convolutional Networks based on Manifold Learning for Semi-Supervised Image Classification
Apr 24, 2023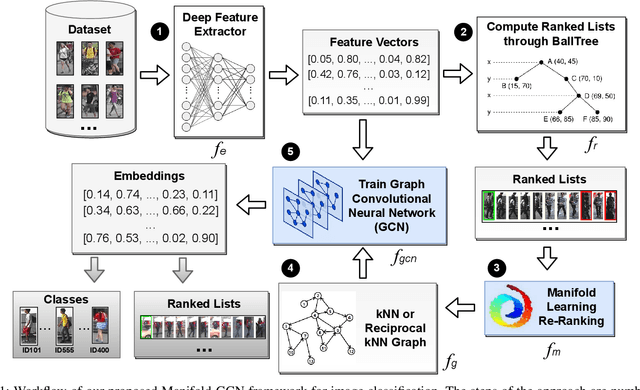
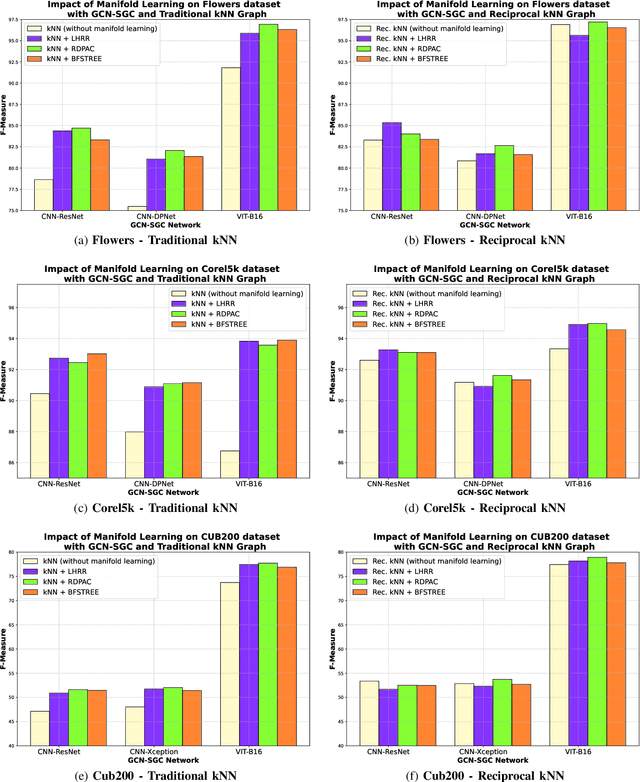
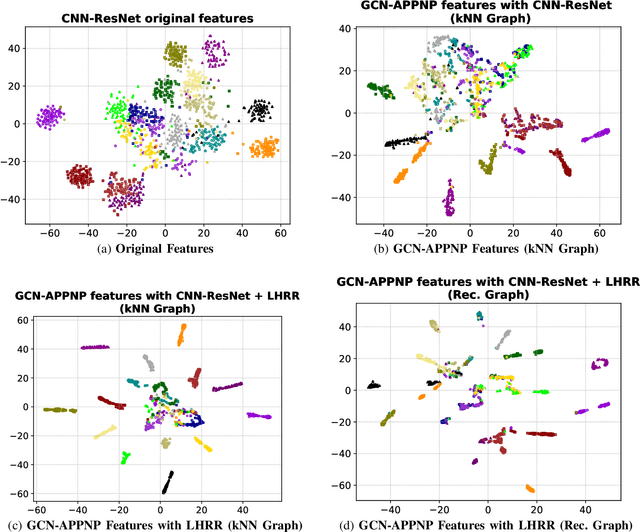
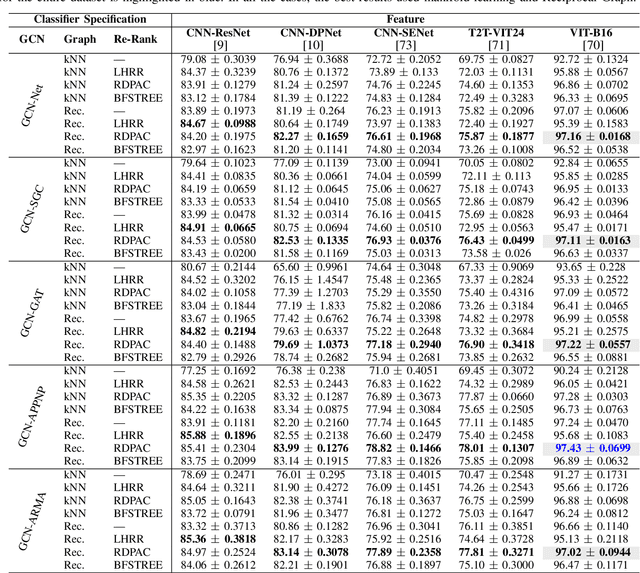
Abstract:Due to a huge volume of information in many domains, the need for classification methods is imperious. In spite of many advances, most of the approaches require a large amount of labeled data, which is often not available, due to costs and difficulties of manual labeling processes. In this scenario, unsupervised and semi-supervised approaches have been gaining increasing attention. The GCNs (Graph Convolutional Neural Networks) represent a promising solution since they encode the neighborhood information and have achieved state-of-the-art results on scenarios with limited labeled data. However, since GCNs require graph-structured data, their use for semi-supervised image classification is still scarce in the literature. In this work, we propose a novel approach, the Manifold-GCN, based on GCNs for semi-supervised image classification. The main hypothesis of this paper is that the use of manifold learning to model the graph structure can further improve the GCN classification. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first framework that allows the combination of GCNs with different types of manifold learning approaches for image classification. All manifold learning algorithms employed are completely unsupervised, which is especially useful for scenarios where the availability of labeled data is a concern. A broad experimental evaluation was conducted considering 5 GCN models, 3 manifold learning approaches, 3 image datasets, and 5 deep features. The results reveal that our approach presents better accuracy than traditional and recent state-of-the-art methods with very efficient run times for both training and testing.
Improving Transferability of Domain Adaptation Networks Through Domain Alignment Layers
Sep 06, 2021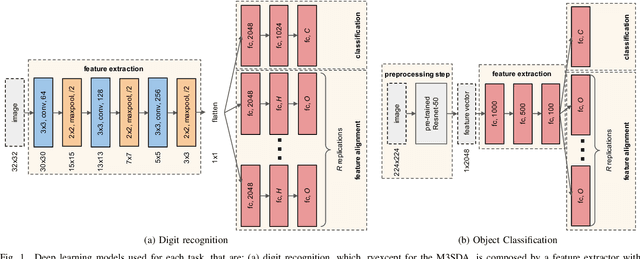
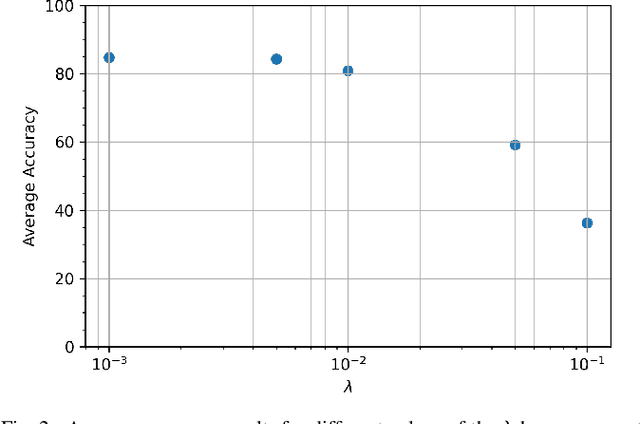

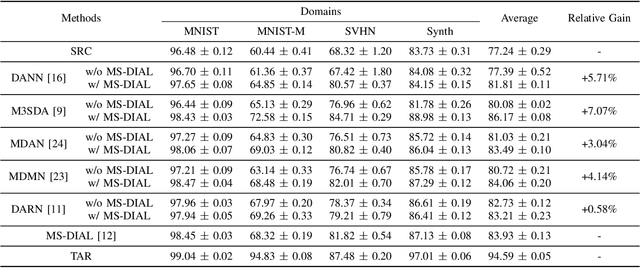
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) has been the primary approach used in various computer vision tasks due to its relevant results achieved on many tasks. However, on real-world scenarios with partially or no labeled data, DL methods are also prone to the well-known domain shift problem. Multi-source unsupervised domain adaptation (MSDA) aims at learning a predictor for an unlabeled domain by assigning weak knowledge from a bag of source models. However, most works conduct domain adaptation leveraging only the extracted features and reducing their domain shift from the perspective of loss function designs. In this paper, we argue that it is not sufficient to handle domain shift only based on domain-level features, but it is also essential to align such information on the feature space. Unlike previous works, we focus on the network design and propose to embed Multi-Source version of DomaIn Alignment Layers (MS-DIAL) at different levels of the predictor. These layers are designed to match the feature distributions between different domains and can be easily applied to various MSDA methods. To show the robustness of our approach, we conducted an extensive experimental evaluation considering two challenging scenarios: digit recognition and object classification. The experimental results indicated that our approach can improve state-of-the-art MSDA methods, yielding relative gains of up to +30.64% on their classification accuracies.
Unsupervised Graph-based Rank Aggregation for Improved Retrieval
Jan 17, 2019
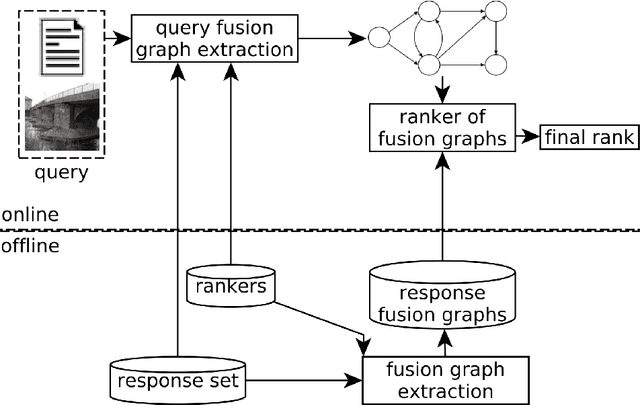
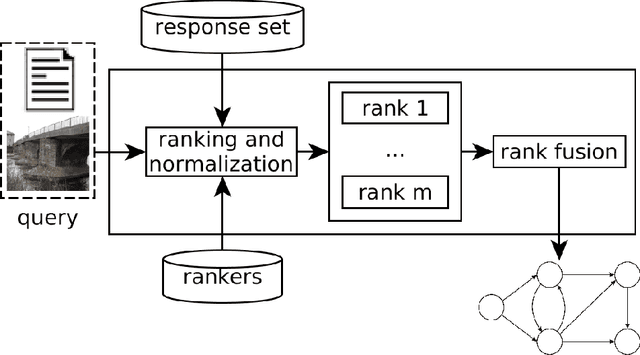
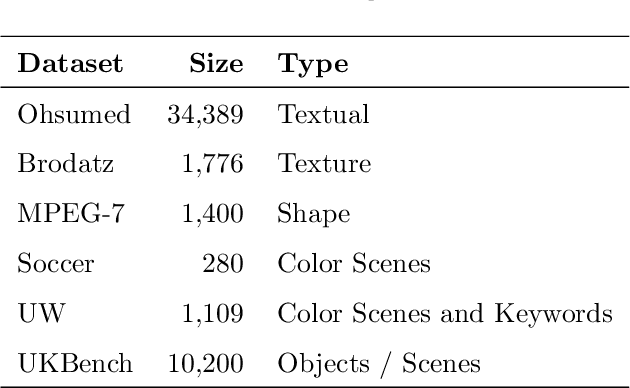
Abstract:This paper presents a robust and comprehensive graph-based rank aggregation approach, used to combine results of isolated ranker models in retrieval tasks. The method follows an unsupervised scheme, which is independent of how the isolated ranks are formulated. Our approach is able to combine arbitrary models, defined in terms of different ranking criteria, such as those based on textual, image or hybrid content representations. We reformulate the ad-hoc retrieval problem as a document retrieval of their fusion graph, which we propose as a new unified representation model capable of merging multiple ranks and expressing inter-relationships of retrieval results automatically. By doing so, we claim that the retrieval system can benefit from learning the manifold structure of datasets, thus leading to more effective results. Another contribution is that our graph-based aggregation formulation, unlike existing approaches, allows for encapsulating contextual information encoded from multiple ranks, which can be directly used for ranking, without further computations and processing steps over the graphs. Based on the graphs, a novel similarity retrieval score is formulated using an efficient computation of minimum common subgraphs. Finally, another benefit over existing approaches is the absence of hyperparameters. A comprehensive experimental evaluation was conducted considering diverse well-known public datasets, composed of textual, image, and multimodal documents. Performed experiments demonstrate that our method reaches top performance, yielding better effectiveness scores than state-of-the-art baseline methods and promoting large gains over the rankers being fused, thus showing the successful capability of the proposal in representing queries based on a unified graph-based model of rank fusions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge