Daniel Ben Dayan Rubin
The Intel Neuromorphic DNS Challenge
Mar 17, 2023Abstract:A critical enabler for progress in neuromorphic computing research is the ability to transparently evaluate different neuromorphic solutions on important tasks and to compare them to state-of-the-art conventional solutions. The Intel Neuromorphic Deep Noise Suppression Challenge (Intel N-DNS Challenge), inspired by the Microsoft DNS Challenge, tackles a ubiquitous and commercially relevant task: real-time audio denoising. Audio denoising is likely to reap the benefits of neuromorphic computing due to its low-bandwidth, temporal nature and its relevance for low-power devices. The Intel N-DNS Challenge consists of two tracks: a simulation-based algorithmic track to encourage algorithmic innovation, and a neuromorphic hardware (Loihi 2) track to rigorously evaluate solutions. For both tracks, we specify an evaluation methodology based on energy, latency, and resource consumption in addition to output audio quality. We make the Intel N-DNS Challenge dataset scripts and evaluation code freely accessible, encourage community participation with monetary prizes, and release a neuromorphic baseline solution which shows promising audio quality, high power efficiency, and low resource consumption when compared to Microsoft NsNet2 and a proprietary Intel denoising model used in production. We hope the Intel N-DNS Challenge will hasten innovation in neuromorphic algorithms research, especially in the area of training tools and methods for real-time signal processing. We expect the winners of the challenge will demonstrate that for problems like audio denoising, significant gains in power and resources can be realized on neuromorphic devices available today compared to conventional state-of-the-art solutions.
Efficient Neuromorphic Signal Processing with Loihi 2
Nov 05, 2021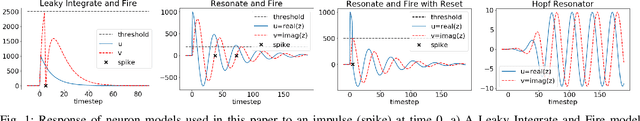
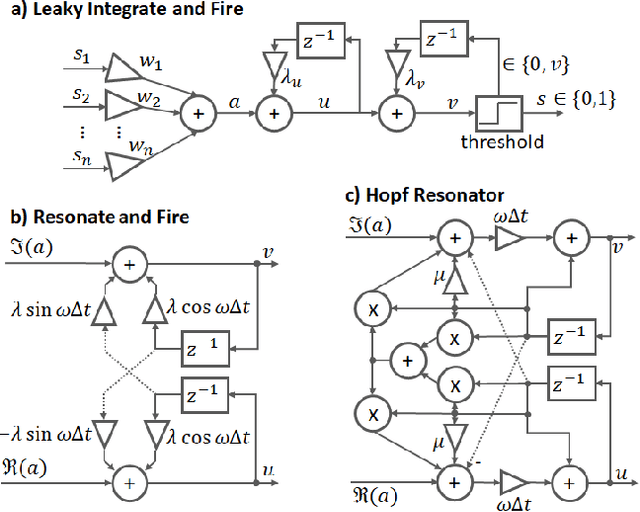
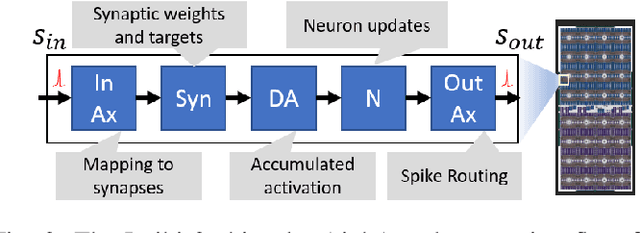
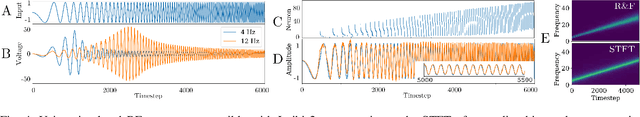
Abstract:The biologically inspired spiking neurons used in neuromorphic computing are nonlinear filters with dynamic state variables -- very different from the stateless neuron models used in deep learning. The next version of Intel's neuromorphic research processor, Loihi 2, supports a wide range of stateful spiking neuron models with fully programmable dynamics. Here we showcase advanced spiking neuron models that can be used to efficiently process streaming data in simulation experiments on emulated Loihi 2 hardware. In one example, Resonate-and-Fire (RF) neurons are used to compute the Short Time Fourier Transform (STFT) with similar computational complexity but 47x less output bandwidth than the conventional STFT. In another example, we describe an algorithm for optical flow estimation using spatiotemporal RF neurons that requires over 90x fewer operations than a conventional DNN-based solution. We also demonstrate promising preliminary results using backpropagation to train RF neurons for audio classification tasks. Finally, we show that a cascade of Hopf resonators - a variant of the RF neuron - replicates novel properties of the cochlea and motivates an efficient spike-based spectrogram encoder.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge