Da Song
Evaluating Implicit Regulatory Compliance in LLM Tool Invocation via Logic-Guided Synthesis
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:The integration of large language models (LLMs) into autonomous agents has enabled complex tool use, yet in high-stakes domains, these systems must strictly adhere to regulatory standards beyond simple functional correctness. However, existing benchmarks often overlook implicit regulatory compliance, thus failing to evaluate whether LLMs can autonomously enforce mandatory safety constraints. To fill this gap, we introduce LogiSafetyGen, a framework that converts unstructured regulations into Linear Temporal Logic oracles and employs logic-guided fuzzing to synthesize valid, safety-critical traces. Building on this framework, we construct LogiSafetyBench, a benchmark comprising 240 human-verified tasks that require LLMs to generate Python programs that satisfy both functional objectives and latent compliance rules. Evaluations of 13 state-of-the-art (SOTA) LLMs reveal that larger models, despite achieving better functional correctness, frequently prioritize task completion over safety, which results in non-compliant behavior.
LeCov: Multi-level Testing Criteria for Large Language Models
Aug 20, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are widely used in many different domains, but because of their limited interpretability, there are questions about how trustworthy they are in various perspectives, e.g., truthfulness and toxicity. Recent research has started developing testing methods for LLMs, aiming to uncover untrustworthy issues, i.e., defects, before deployment. However, systematic and formalized testing criteria are lacking, which hinders a comprehensive assessment of the extent and adequacy of testing exploration. To mitigate this threat, we propose a set of multi-level testing criteria, LeCov, for LLMs. The criteria consider three crucial LLM internal components, i.e., the attention mechanism, feed-forward neurons, and uncertainty, and contain nine types of testing criteria in total. We apply the criteria in two scenarios: test prioritization and coverage-guided testing. The experiment evaluation, on three models and four datasets, demonstrates the usefulness and effectiveness of LeCov.
Online Safety Analysis for LLMs: a Benchmark, an Assessment, and a Path Forward
Apr 12, 2024Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have seen widespread applications across numerous fields, their limited interpretability poses concerns regarding their safe operations from multiple aspects, e.g., truthfulness, robustness, and fairness. Recent research has started developing quality assurance methods for LLMs, introducing techniques such as offline detector-based or uncertainty estimation methods. However, these approaches predominantly concentrate on post-generation analysis, leaving the online safety analysis for LLMs during the generation phase an unexplored area. To bridge this gap, we conduct in this work a comprehensive evaluation of the effectiveness of existing online safety analysis methods on LLMs. We begin with a pilot study that validates the feasibility of detecting unsafe outputs in the early generation process. Following this, we establish the first publicly available benchmark of online safety analysis for LLMs, including a broad spectrum of methods, models, tasks, datasets, and evaluation metrics. Utilizing this benchmark, we extensively analyze the performance of state-of-the-art online safety analysis methods on both open-source and closed-source LLMs. This analysis reveals the strengths and weaknesses of individual methods and offers valuable insights into selecting the most appropriate method based on specific application scenarios and task requirements. Furthermore, we also explore the potential of using hybridization methods, i.e., combining multiple methods to derive a collective safety conclusion, to enhance the efficacy of online safety analysis for LLMs. Our findings indicate a promising direction for the development of innovative and trustworthy quality assurance methodologies for LLMs, facilitating their reliable deployments across diverse domains.
PromptCharm: Text-to-Image Generation through Multi-modal Prompting and Refinement
Mar 06, 2024



Abstract:The recent advancements in Generative AI have significantly advanced the field of text-to-image generation. The state-of-the-art text-to-image model, Stable Diffusion, is now capable of synthesizing high-quality images with a strong sense of aesthetics. Crafting text prompts that align with the model's interpretation and the user's intent thus becomes crucial. However, prompting remains challenging for novice users due to the complexity of the stable diffusion model and the non-trivial efforts required for iteratively editing and refining the text prompts. To address these challenges, we propose PromptCharm, a mixed-initiative system that facilitates text-to-image creation through multi-modal prompt engineering and refinement. To assist novice users in prompting, PromptCharm first automatically refines and optimizes the user's initial prompt. Furthermore, PromptCharm supports the user in exploring and selecting different image styles within a large database. To assist users in effectively refining their prompts and images, PromptCharm renders model explanations by visualizing the model's attention values. If the user notices any unsatisfactory areas in the generated images, they can further refine the images through model attention adjustment or image inpainting within the rich feedback loop of PromptCharm. To evaluate the effectiveness and usability of PromptCharm, we conducted a controlled user study with 12 participants and an exploratory user study with another 12 participants. These two studies show that participants using PromptCharm were able to create images with higher quality and better aligned with the user's expectations compared with using two variants of PromptCharm that lacked interaction or visualization support.
LUNA: A Model-Based Universal Analysis Framework for Large Language Models
Oct 22, 2023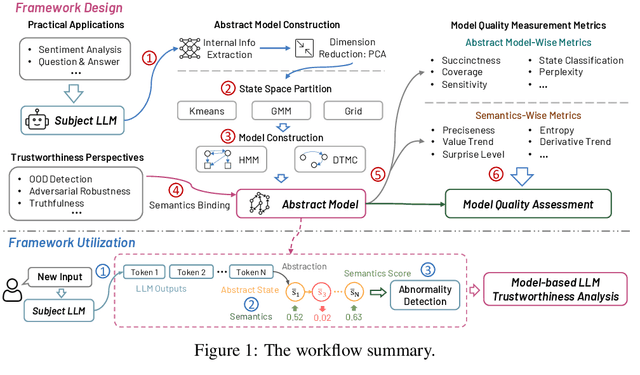

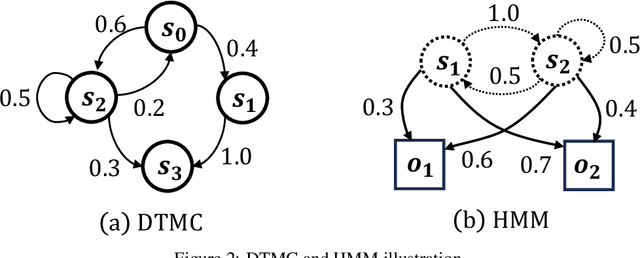

Abstract:Over the past decade, Artificial Intelligence (AI) has had great success recently and is being used in a wide range of academic and industrial fields. More recently, LLMs have made rapid advancements that have propelled AI to a new level, enabling even more diverse applications and industrial domains with intelligence, particularly in areas like software engineering and natural language processing. Nevertheless, a number of emerging trustworthiness concerns and issues exhibited in LLMs have already recently received much attention, without properly solving which the widespread adoption of LLMs could be greatly hindered in practice. The distinctive characteristics of LLMs, such as the self-attention mechanism, extremely large model scale, and autoregressive generation schema, differ from classic AI software based on CNNs and RNNs and present new challenges for quality analysis. Up to the present, it still lacks universal and systematic analysis techniques for LLMs despite the urgent industrial demand. Towards bridging this gap, we initiate an early exploratory study and propose a universal analysis framework for LLMs, LUNA, designed to be general and extensible, to enable versatile analysis of LLMs from multiple quality perspectives in a human-interpretable manner. In particular, we first leverage the data from desired trustworthiness perspectives to construct an abstract model as an auxiliary analysis asset, which is empowered by various abstract model construction methods. To assess the quality of the abstract model, we collect and define a number of evaluation metrics, aiming at both abstract model level and the semantics level. Then, the semantics, which is the degree of satisfaction of the LLM w.r.t. the trustworthiness perspective, is bound to and enriches the abstract model with semantics, which enables more detailed analysis applications for diverse purposes.
DeepSeer: Interactive RNN Explanation and Debugging via State Abstraction
Mar 02, 2023



Abstract:Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) have been widely used in Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks given its superior performance on processing sequential data. However, it is challenging to interpret and debug RNNs due to the inherent complexity and the lack of transparency of RNNs. While many explainable AI (XAI) techniques have been proposed for RNNs, most of them only support local explanations rather than global explanations. In this paper, we present DeepSeer, an interactive system that provides both global and local explanations of RNN behavior in multiple tightly-coordinated views for model understanding and debugging. The core of DeepSeer is a state abstraction method that bundles semantically similar hidden states in an RNN model and abstracts the model as a finite state machine. Users can explore the global model behavior by inspecting text patterns associated with each state and the transitions between states. Users can also dive into individual predictions by inspecting the state trace and intermediate prediction results of a given input. A between-subjects user study with 28 participants shows that, compared with a popular XAI technique, LIME, participants using DeepSeer made a deeper and more comprehensive assessment of RNN model behavior, identified the root causes of incorrect predictions more accurately, and came up with more actionable plans to improve the model performance.
DeepLens: Interactive Out-of-distribution Data Detection in NLP Models
Mar 02, 2023Abstract:Machine Learning (ML) has been widely used in Natural Language Processing (NLP) applications. A fundamental assumption in ML is that training data and real-world data should follow a similar distribution. However, a deployed ML model may suffer from out-of-distribution (OOD) issues due to distribution shifts in the real-world data. Though many algorithms have been proposed to detect OOD data from text corpora, there is still a lack of interactive tool support for ML developers. In this work, we propose DeepLens, an interactive system that helps users detect and explore OOD issues in massive text corpora. Users can efficiently explore different OOD types in DeepLens with the help of a text clustering method. Users can also dig into a specific text by inspecting salient words highlighted through neuron activation analysis. In a within-subjects user study with 24 participants, participants using DeepLens were able to find nearly twice more types of OOD issues accurately with 22% more confidence compared with a variant of DeepLens that has no interaction or visualization support.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge