Craig B. Engstrom
Explainable Semantic Medical Image Segmentation with Style
Mar 10, 2023Abstract:Semantic medical image segmentation using deep learning has recently achieved high accuracy, making it appealing to clinical problems such as radiation therapy. However, the lack of high-quality semantically labelled data remains a challenge leading to model brittleness to small shifts to input data. Most works require extra data for semi-supervised learning and lack the interpretability of the boundaries of the training data distribution during training, which is essential for model deployment in clinical practice. We propose a fully supervised generative framework that can achieve generalisable segmentation with only limited labelled data by simultaneously constructing an explorable manifold during training. The proposed approach creates medical image style paired with a segmentation task driven discriminator incorporating end-to-end adversarial training. The discriminator is generalised to small domain shifts as much as permissible by the training data, and the generator automatically diversifies the training samples using a manifold of input features learnt during segmentation. All the while, the discriminator guides the manifold learning by supervising the semantic content and fine-grained features separately during the image diversification. After training, visualisation of the learnt manifold from the generator is available to interpret the model limits. Experiments on a fully semantic, publicly available pelvis dataset demonstrated that our method is more generalisable to shifts than other state-of-the-art methods while being more explainable using an explorable manifold.
CAN3D: Fast 3D Medical Image Segmentation via Compact Context Aggregation
Sep 22, 2021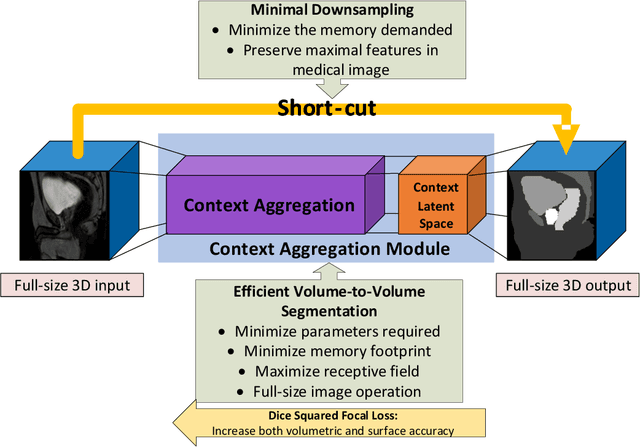
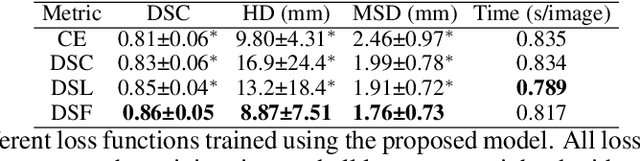
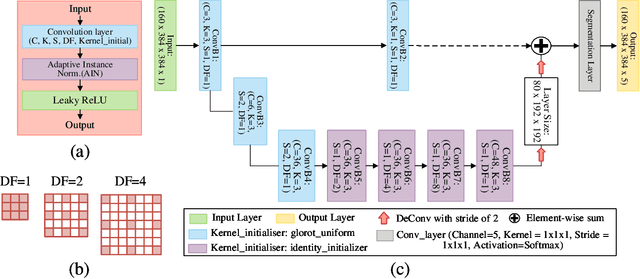
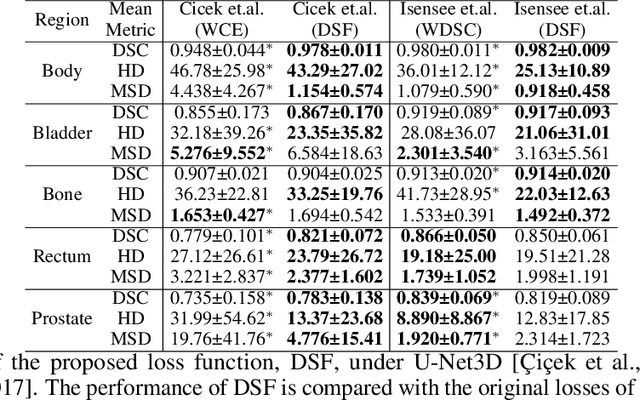
Abstract:Direct automatic segmentation of objects from 3D medical imaging, such as magnetic resonance (MR) imaging, is challenging as it often involves accurately identifying a number of individual objects with complex geometries within a large volume under investigation. To address these challenges, most deep learning approaches typically enhance their learning capability by substantially increasing the complexity or the number of trainable parameters within their models. Consequently, these models generally require long inference time on standard workstations operating clinical MR systems and are restricted to high-performance computing hardware due to their large memory requirement. Further, to fit 3D dataset through these large models using limited computer memory, trade-off techniques such as patch-wise training are often used which sacrifice the fine-scale geometric information from input images which could be clinically significant for diagnostic purposes. To address these challenges, we present a compact convolutional neural network with a shallow memory footprint to efficiently reduce the number of model parameters required for state-of-art performance. This is critical for practical employment as most clinical environments only have low-end hardware with limited computing power and memory. The proposed network can maintain data integrity by directly processing large full-size 3D input volumes with no patches required and significantly reduces the computational time required for both training and inference. We also propose a novel loss function with extra shape constraint to improve the accuracy for imbalanced classes in 3D MR images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge