Congcong Miao
Internalizing LLM Reasoning via Discovery and Replay of Latent Actions
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:The internalization of chain-of-thought processes into hidden states has emerged as a highly efficient paradigm for scaling test-time compute. However, existing activation steering methods rely on static control vectors that fail to adapt to the non-stationary evolution of complex reasoning tasks. To address this limitation, we propose STIR (Self-Distilled Tools for Internal Reasoning), a framework that reformulates reasoning enhancement as a dynamic latent trajectory control problem. STIR introduces a synergistic three-stage pipeline: (1) differential intrinsic action induction harvests latent reasoning successes to crystallize steering primitives; (2) sparse control basis construction curates a compact, geometrically diverse tool library; and (3) value-modulated trajectory intervention dynamically injects context-specific impulses via anchor-based gating. Extensive experiments on six arithmetic and logical benchmarks across four representative models demonstrate that STIR improves average accuracy by 1.9% to 7.5% while reducing average token consumption by up to 35% compared to vanilla decoding. These findings demonstrate that the benefits of explicit chain-of-thought can be realized through dynamic latent trajectory control, internalizing the reasoning process to bypass the explicit generation while achieving superior fidelity. Our code is available at https://github.com/sznnzs/LLM-Latent-Action.
Self-supervised Representation Learning for Trip Recommendation
Sep 08, 2021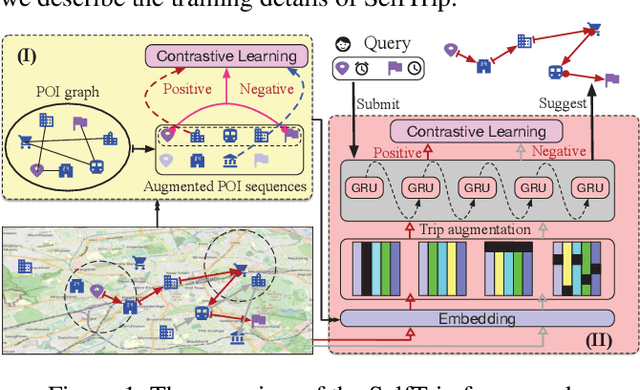
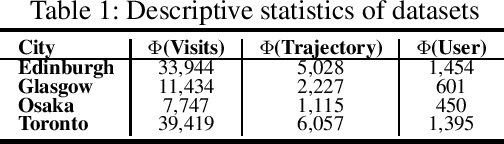
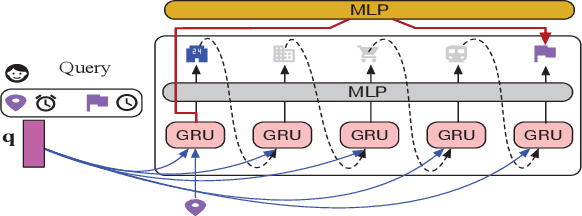
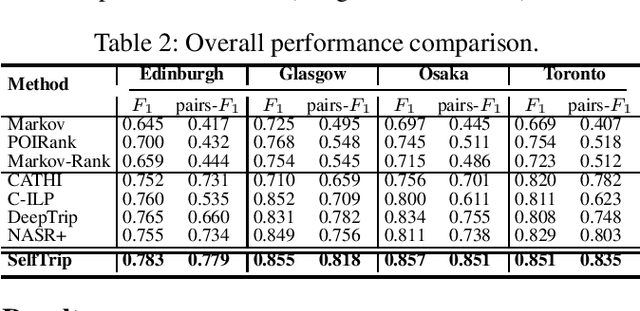
Abstract:Trip recommendation is a significant and engaging location-based service that can help new tourists make more customized travel plans. It often attempts to suggest a sequence of point of interests (POIs) for a user who requests a personalized travel demand. Conventional methods either leverage the heuristic algorithms (e.g., dynamic programming) or statistical analysis (e.g., Markov models) to search or rank a POI sequence. These procedures may fail to capture the diversity of human needs and transitional regularities. They even provide recommendations that deviate from tourists' real travel intention when the trip data is sparse. Although recent deep recursive models (e.g., RNN) are capable of alleviating these concerns, existing solutions hardly recognize the practical reality, such as the diversity of tourist demands, uncertainties in the trip generation, and the complex visiting preference. Inspired by the advance in deep learning, we introduce a novel self-supervised representation learning framework for trip recommendation -- SelfTrip, aiming at tackling the aforementioned challenges. Specifically, we propose a two-step contrastive learning mechanism concerning the POI representation, as well as trip representation. Furthermore, we present four trip augmentation methods to capture the visiting uncertainties in trip planning. We evaluate our SelfTrip on four real-world datasets, and extensive results demonstrate the promising gain compared with several cutting-edge benchmarks, e.g., up to 4% and 12% on F1 and pair-F1, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge