Colin Klein
Exploring Major Transitions in the Evolution of Biological Cognition With Artificial Neural Networks
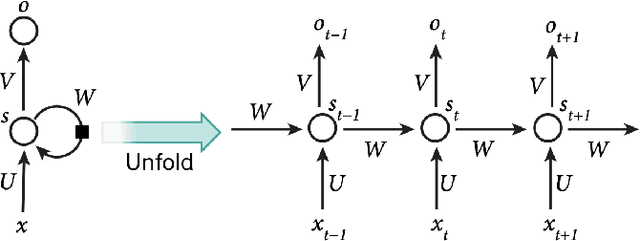
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Transitional accounts of evolution emphasise a few changes that shape what is evolvable, with dramatic consequences for derived lineages. More recently it has been proposed that cognition might also have evolved via a series of major transitions that manipulate the structure of biological neural networks, fundamentally changing the flow of information. We used idealised models of information flow, artificial neural networks (ANNs), to evaluate whether changes in information flow in a network can yield a transitional change in cognitive performance. We compared networks with feed-forward, recurrent and laminated topologies, and tested their performance learning artificial grammars that differed in complexity, controlling for network size and resources. We documented a qualitative expansion in the types of input that recurrent networks can process compared to feed-forward networks, and a related qualitative increase in performance for learning the most complex grammars. We also noted how the difficulty in training recurrent networks poses a form of transition barrier and contingent irreversibility -- other key features of evolutionary transitions. Not all changes in network topology confer a performance advantage in this task set. Laminated networks did not outperform non-laminated networks in grammar learning. Overall, our findings show how some changes in information flow can yield transitions in cognitive performance.
Consciousness in Artificial Intelligence: Insights from the Science of Consciousness
Aug 22, 2023
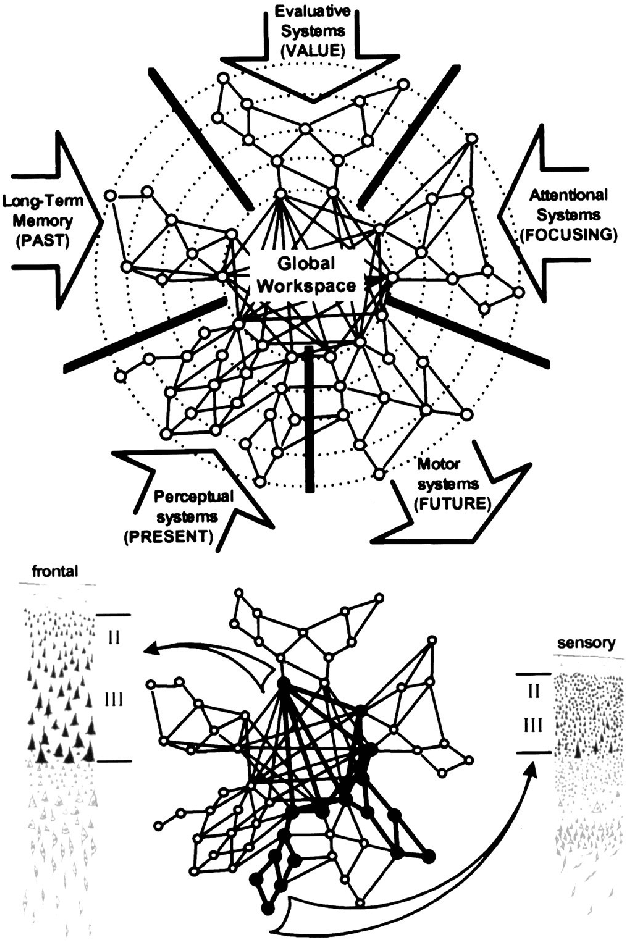

Abstract:Whether current or near-term AI systems could be conscious is a topic of scientific interest and increasing public concern. This report argues for, and exemplifies, a rigorous and empirically grounded approach to AI consciousness: assessing existing AI systems in detail, in light of our best-supported neuroscientific theories of consciousness. We survey several prominent scientific theories of consciousness, including recurrent processing theory, global workspace theory, higher-order theories, predictive processing, and attention schema theory. From these theories we derive "indicator properties" of consciousness, elucidated in computational terms that allow us to assess AI systems for these properties. We use these indicator properties to assess several recent AI systems, and we discuss how future systems might implement them. Our analysis suggests that no current AI systems are conscious, but also suggests that there are no obvious technical barriers to building AI systems which satisfy these indicators.
Automated clustering of COVID-19 anti-vaccine discourse on Twitter
Mar 03, 2022



Abstract:Attitudes about vaccination have become more polarized; it is common to see vaccine disinformation and fringe conspiracy theories online. An observational study of Twitter vaccine discourse is found in Ojea Quintana et al. (2021): the authors analyzed approximately six months' of Twitter discourse -- 1.3 million original tweets and 18 million retweets between December 2019 and June 2020, ranging from before to after the establishment of Covid-19 as a pandemic. This work expands upon Ojea Quintana et al. (2021) with two main contributions from data science. First, based on the authors' initial network clustering and qualitative analysis techniques, we are able to clearly demarcate and visualize the language patterns used in discourse by Antivaxxers (anti-vaccination campaigners and vaccine deniers) versus other clusters (collectively, Others). Second, using the characteristics of Antivaxxers' tweets, we develop text classifiers to determine the likelihood a given user is employing anti-vaccination language, ultimately contributing to an early-warning mechanism to improve the health of our epistemic environment and bolster (and not hinder) public health initiatives.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge