Claudio Vairo
A Communication Layer for Integrated Sensors and Robotic ecology Solutions to Ambient Intelligence
Jun 09, 2021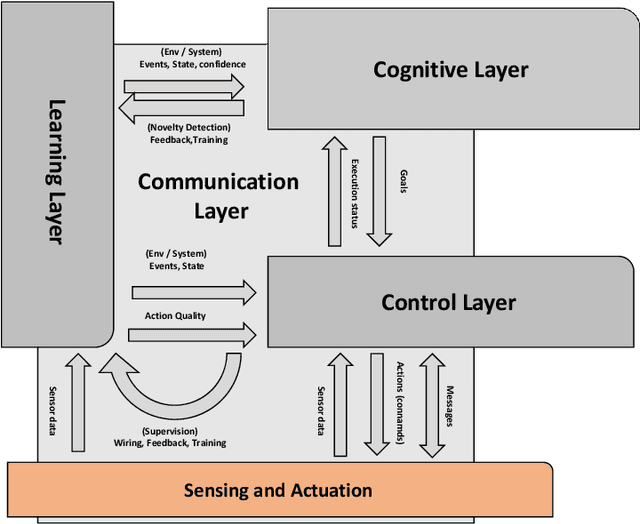
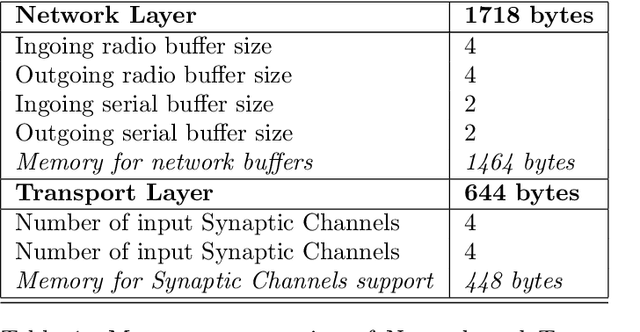
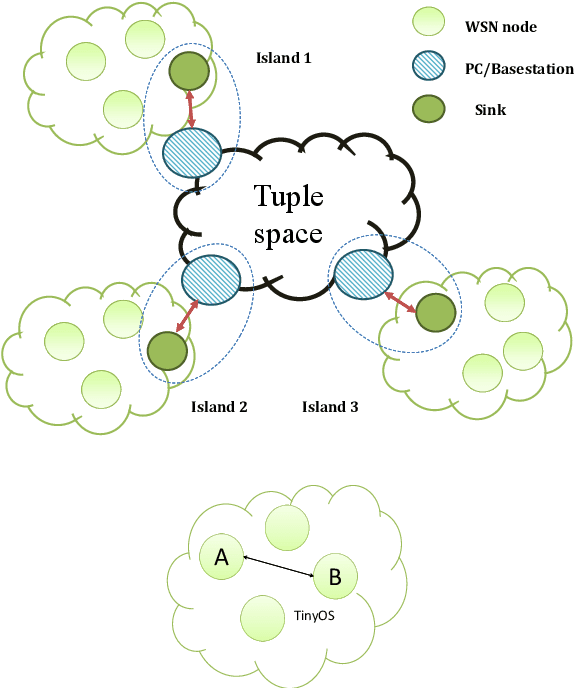
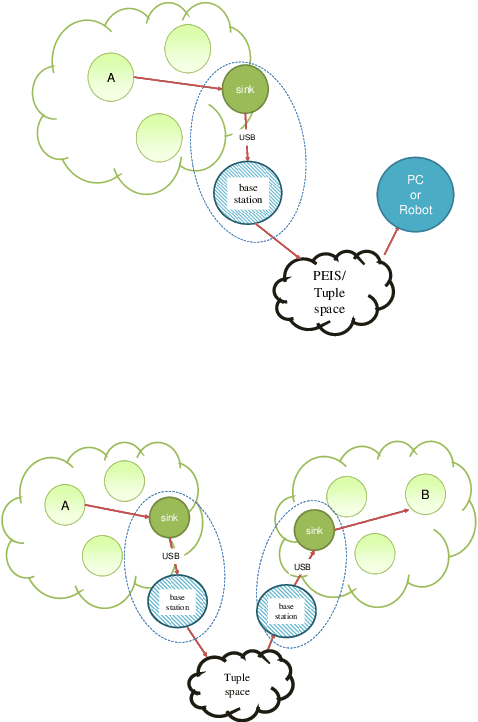
Abstract:This paper presents a communication framework built to simplify the construction of robotic ecologies, i.e., networks of heterogeneous computational nodes interfaced with sensors, actuators, and mobile robots. Building integrated ambient intelligence (AmI) solutions out of such a wide range of heterogeneous devices is a key requirement for a range of application domains, such as home automation, logistic, security and Ambient Assisted Living (AAL). This goal is challenging since these ecologies need to adapt to changing environments and especially when they include tiny embedded devices with limited computational resources. We discuss a number of requirements characterizing this type of systems and illustrate how they have been addressed in the design of the new communication framework. The most distinguishing aspect of our frameworks is the transparency with which the same communication features are offered across heterogeneous programming languages and operating systems under a consistent API. Finally, we illustrate how the framework has been used to bind together and to support the operations of all the components of adaptive robotic ecologies in two real-world test-beds.
Multi-Camera Vehicle Counting Using Edge-AI
Jun 05, 2021



Abstract:This paper presents a novel solution to automatically count vehicles in a parking lot using images captured by smart cameras. Unlike most of the literature on this task, which focuses on the analysis of single images, this paper proposes the use of multiple visual sources to monitor a wider parking area from different perspectives. The proposed multi-camera system is capable of automatically estimate the number of cars present in the entire parking lot directly on board the edge devices. It comprises an on-device deep learning-based detector that locates and counts the vehicles from the captured images and a decentralized geometric-based approach that can analyze the inter-camera shared areas and merge the data acquired by all the devices. We conduct the experimental evaluation on an extended version of the CNRPark-EXT dataset, a collection of images taken from the parking lot on the campus of the National Research Council (CNR) in Pisa, Italy. We show that our system is robust and takes advantage of the redundant information deriving from the different cameras, improving the overall performance without requiring any extra geometrical information of the monitored scene.
The VISIONE Video Search System: Exploiting Off-the-Shelf Text Search Engines for Large-Scale Video Retrieval
Aug 06, 2020



Abstract:In this paper, we describe VISIONE, a video search system that allows users to search for videos using textual keywords, occurrence of objects and their spatial relationships, occurrence of colors and their spatial relationships, and image similarity. These modalities can be combined together to express complex queries and satisfy user needs. The peculiarity of our approach is that we encode all the information extracted from the keyframes, such as visual deep features, tags, color and object locations, using a convenient textual encoding indexed in a single text retrieval engine. This offers great flexibility when results corresponding to various parts of the query needs to be merged. We report an extensive analysis of the system retrieval performance, using the query logs generated during the Video Browser Showdown (VBS) 2019 competition. This allowed us to fine-tune the system by choosing the optimal parameters and strategies among the ones that we tested.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge