Chuping Qu
Optimizing Neural Networks with Learnable Non-Linear Activation Functions via Lookup-Based FPGA Acceleration
Aug 23, 2025Abstract:Learned activation functions in models like Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) outperform fixed-activation architectures in terms of accuracy and interpretability; however, their computational complexity poses critical challenges for energy-constrained edge AI deployments. Conventional CPUs/GPUs incur prohibitive latency and power costs when evaluating higher order activations, limiting deployability under ultra-tight energy budgets. We address this via a reconfigurable lookup architecture with edge FPGAs. By coupling fine-grained quantization with adaptive lookup tables, our design minimizes energy-intensive arithmetic operations while preserving activation fidelity. FPGA reconfigurability enables dynamic hardware specialization for learned functions, a key advantage for edge systems that require post-deployment adaptability. Evaluations using KANs - where unique activation functions play a critical role - demonstrate that our FPGA-based design achieves superior computational speed and over $10^4$ times higher energy efficiency compared to edge CPUs and GPUs, while maintaining matching accuracy and minimal footprint overhead. This breakthrough positions our approach as a practical enabler for energy-critical edge AI, where computational intensity and power constraints traditionally preclude the use of adaptive activation networks.
DeepFire2: A Convolutional Spiking Neural Network Accelerator on FPGAs
May 09, 2023Abstract:Brain-inspired spiking neural networks (SNNs) replace the multiply-accumulate operations of traditional neural networks by integrate-and-fire neurons, with the goal of achieving greater energy efficiency. Specialized hardware implementations of those neurons clearly have advantages over general-purpose devices in terms of power and performance, but exhibit poor scalability when it comes to accelerating large neural networks. DeepFire2 introduces a hardware architecture which can map large network layers efficiently across multiple super logic regions in a multi-die FPGA. That gives more control over resource allocation and parallelism, benefiting both throughput and energy consumption. Avoiding the use of lookup tables to implement the AND operations of an SNN, prevents the layer size to be limited by logic resources. A deep pipeline does not only lead to an increased clock speed of up to 600 MHz. We double the throughput and power efficiency compared to our previous version of DeepFire, which equates to an almost 10-fold improvement over other previous implementations. Importantly, we are able to deploy a large ImageNet model, while maintaining a throughput of over 1500 frames per second.
DTNN: Energy-efficient Inference with Dendrite Tree Inspired Neural Networks for Edge Vision Applications
May 25, 2021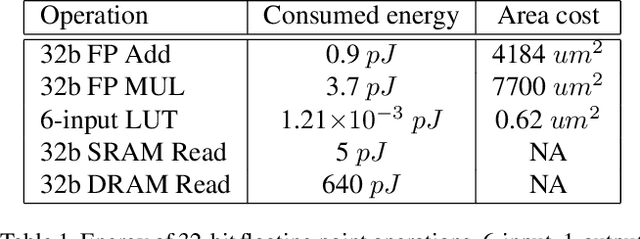
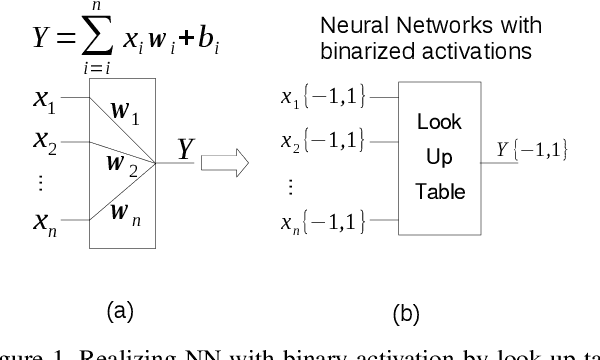
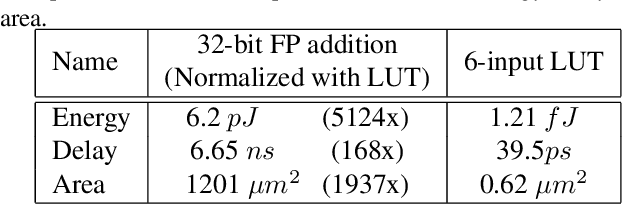
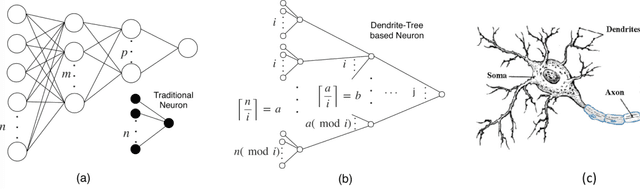
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNN) have achieved remarkable success in computer vision (CV). However, training and inference of DNN models are both memory and computation intensive, incurring significant overhead in terms of energy consumption and silicon area. In particular, inference is much more cost-sensitive than training because training can be done offline with powerful platforms, while inference may have to be done on battery powered devices with constrained form factors, especially for mobile or edge vision applications. In order to accelerate DNN inference, model quantization was proposed. However previous works only focus on the quantization rate without considering the efficiency of operations. In this paper, we propose Dendrite-Tree based Neural Network (DTNN) for energy-efficient inference with table lookup operations enabled by activation quantization. In DTNN both costly weight access and arithmetic computations are eliminated for inference. We conducted experiments on various kinds of DNN models such as LeNet-5, MobileNet, VGG, and ResNet with different datasets, including MNIST, Cifar10/Cifar100, SVHN, and ImageNet. DTNN achieved significant energy saving (19.4X and 64.9X improvement on ResNet-18 and VGG-11 with ImageNet, respectively) with negligible loss of accuracy. To further validate the effectiveness of DTNN and compare with state-of-the-art low energy implementation for edge vision, we design and implement DTNN based MLP image classifiers using off-the-shelf FPGAs. The results show that DTNN on the FPGA, with higher accuracy, could achieve orders of magnitude better energy consumption and latency compared with the state-of-the-art low energy approaches reported that use ASIC chips.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge