Chung-Yi Li
Language Representation in Multilingual BERT and its applications to improve Cross-lingual Generalization
Oct 23, 2020



Abstract:A token embedding in multilingual BERT (m-BERT) contains both language and semantic information. We find that representation of a language can be obtained by simply averaging the embeddings of the tokens of the language. With the language representation, we can control the output languages of multilingual BERT by manipulating the token embeddings and achieve unsupervised token translation. We further propose a computationally cheap but effective approach to improve the cross-lingual ability of m-BERT based on the observation.
What does a network layer hear? Analyzing hidden representations of end-to-end ASR through speech synthesis
Nov 04, 2019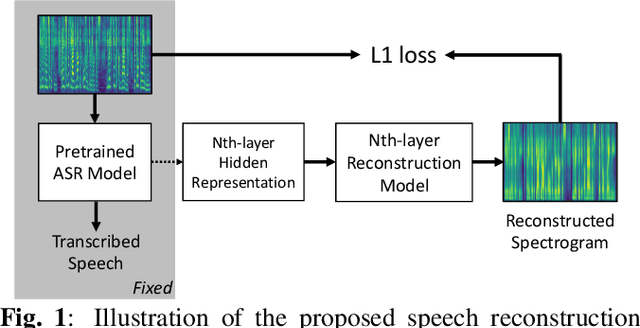
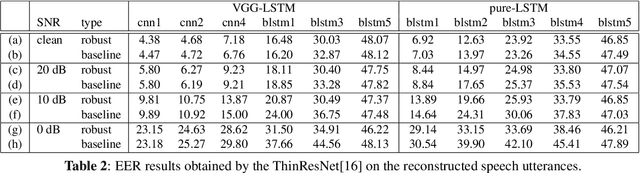
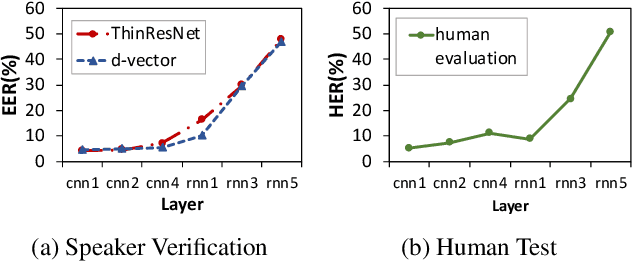
Abstract:End-to-end speech recognition systems have achieved competitive results compared to traditional systems. However, the complex transformations involved between layers given highly variable acoustic signals are hard to analyze. In this paper, we present our ASR probing model, which synthesizes speech from hidden representations of end-to-end ASR to examine the information maintain after each layer calculation. Listening to the synthesized speech, we observe gradual removal of speaker variability and noise as the layer goes deeper, which aligns with the previous studies on how deep network functions in speech recognition. This paper is the first study analyzing the end-to-end speech recognition model by demonstrating what each layer hears. Speaker verification and speech enhancement measurements on synthesized speech are also conducted to confirm our observation further.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge