Chung Hee Kim
Autonomous Robotic Pepper Harvesting: Imitation Learning in Unstructured Agricultural Environments
Nov 15, 2024


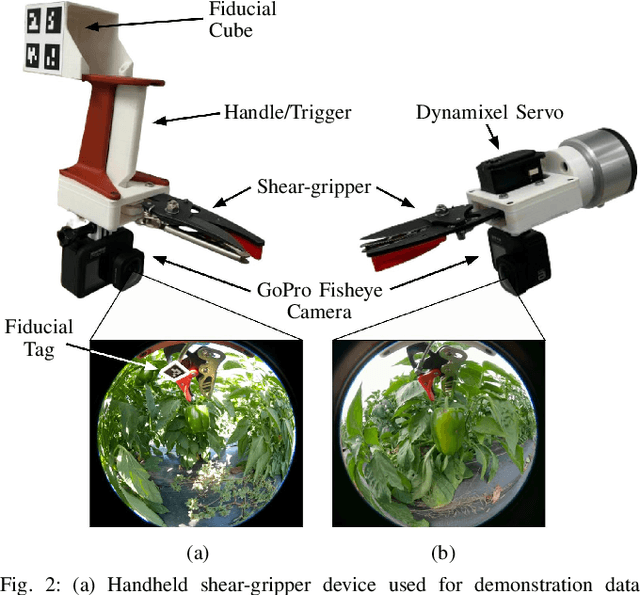
Abstract:Automating tasks in outdoor agricultural fields poses significant challenges due to environmental variability, unstructured terrain, and diverse crop characteristics. We present a robotic system for autonomous pepper harvesting designed to operate in these unprotected, complex settings. Utilizing a custom handheld shear-gripper, we collected 300 demonstrations to train a visuomotor policy, enabling the system to adapt to varying field conditions and crop diversity. We achieved a success rate of 28.95% with a cycle time of 31.71 seconds, comparable to existing systems tested under more controlled conditions like greenhouses. Our system demonstrates the feasibility and effectiveness of leveraging imitation learning for automated harvesting in unstructured agricultural environments. This work aims to advance scalable, automated robotic solutions for agriculture in natural settings.
Towards Robotic Tree Manipulation: Leveraging Graph Representations
Nov 13, 2023



Abstract:There is growing interest in automating agricultural tasks that require intricate and precise interaction with specialty crops, such as trees and vines. However, developing robotic solutions for crop manipulation remains a difficult challenge due to complexities involved in modeling their deformable behavior. In this study, we present a framework for learning the deformation behavior of tree-like crops under contact interaction. Our proposed method involves encoding the state of a spring-damper modeled tree crop as a graph. This representation allows us to employ graph networks to learn both a forward model for predicting resulting deformations, and a contact policy for inferring actions to manipulate tree crops. We conduct a comprehensive set of experiments in a simulated environment and demonstrate generalizability of our method on previously unseen trees. Videos can be found on the project website: https://kantor-lab.github.io/tree_gnn
Occlusion Reasoning for Skeleton Extraction of Self-Occluded Tree Canopies
Jan 20, 2023



Abstract:In this work, we present a method to extract the skeleton of a self-occluded tree canopy by estimating the unobserved structures of the tree. A tree skeleton compactly describes the topological structure and contains useful information such as branch geometry, positions and hierarchy. This can be critical to planning contact interactions for agricultural manipulation, yet is difficult to gain due to occlusion by leaves, fruits and other branches. Our method uses an instance segmentation network to detect visible trunk, branches, and twigs. Then, based on the observed tree structures, we build a custom 3D likelihood map in the form of an occupancy grid to hypothesize on the presence of occluded skeletons through a series of minimum cost path searches. We show that our method outperforms baseline methods in highly occluded scenes, demonstrated through a set of experiments on a synthetic tree dataset. Qualitative results are also presented on a real tree dataset collected from the field.
3D Reconstruction-Based Seed Counting of Sorghum Panicles for Agricultural Inspection
Nov 14, 2022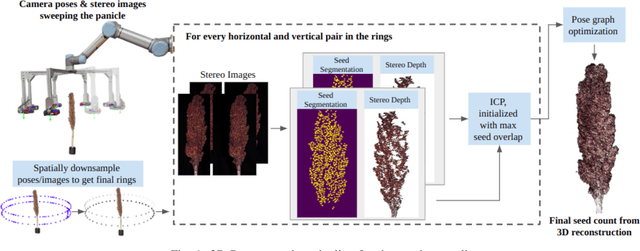

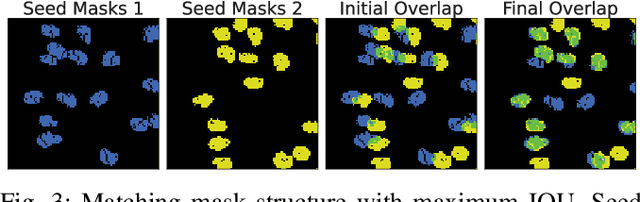
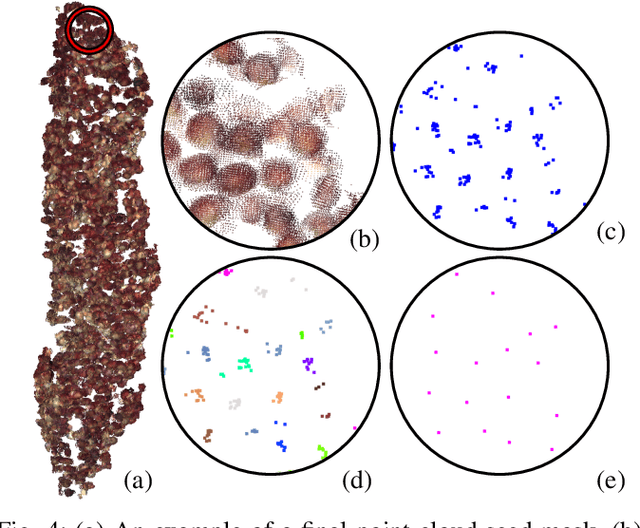
Abstract:In this paper, we present a method for creating high-quality 3D models of sorghum panicles for phenotyping in breeding experiments. This is achieved with a novel reconstruction approach that uses seeds as semantic landmarks in both 2D and 3D. To evaluate the performance, we develop a new metric for assessing the quality of reconstructed point clouds without having a ground-truth point cloud. Finally, a counting method is presented where the density of seed centers in the 3D model allows 2D counts from multiple views to be effectively combined into a whole-panicle count. We demonstrate that using this method to estimate seed count and weight for sorghum outperforms count extrapolation from 2D images, an approach used in most state of the art methods for seeds and grains of comparable size.
Planning for Dexterous Ungrasping: Secure Ungrasping through Dexterous Manipulation
Aug 31, 2021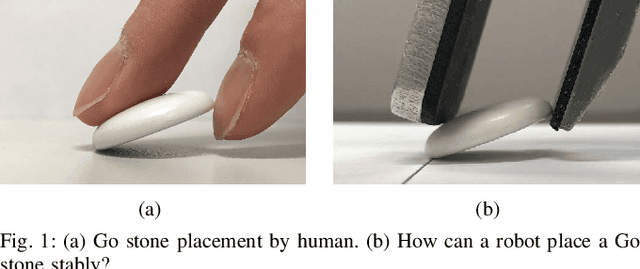

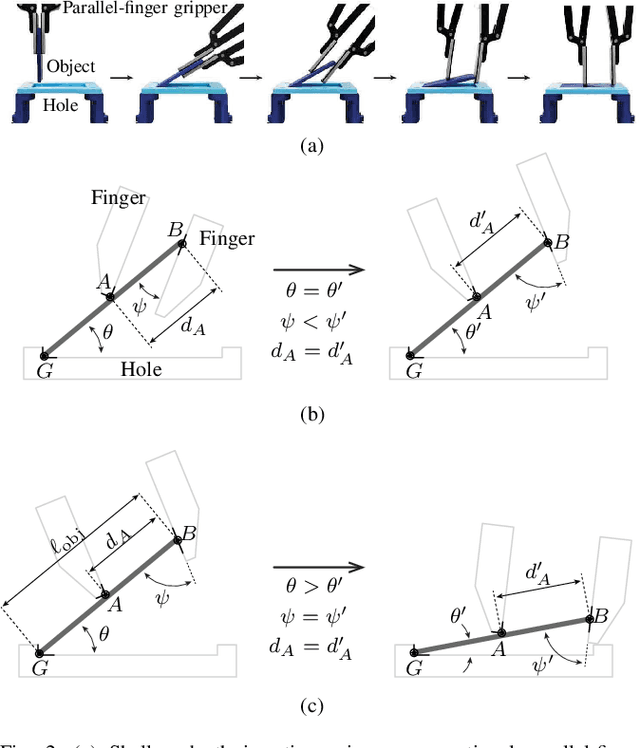
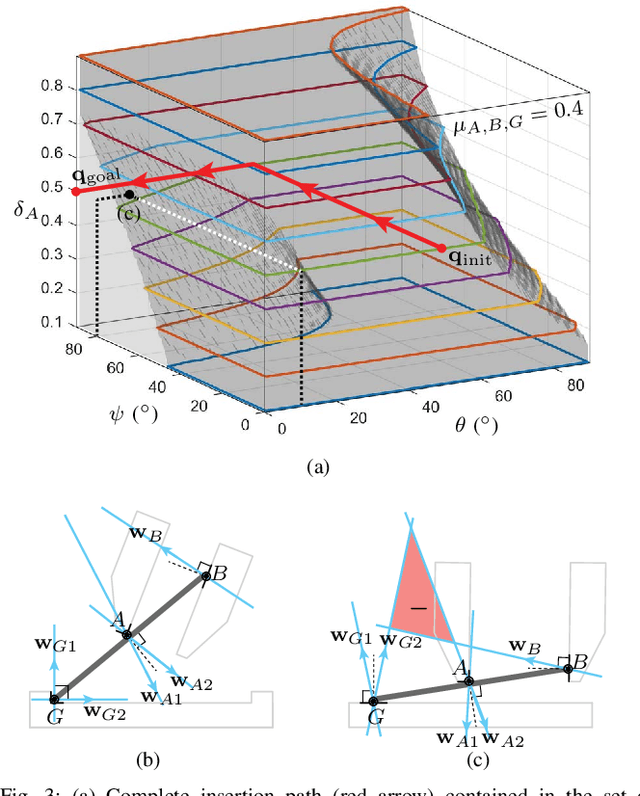
Abstract:This paper presents a robotic manipulation technique for dexterous ungrasping. It refers to the capability of securely transferring a grasped object from the gripper to the robot's environment, i.e. the inverse of grasping or picking, through dexterous manipulation. The game of Go offers an example: consider how the player would typically place an initially pinch-grasped stone onto the board through the dexterous interaction between the fingers, the stone, and the board. Likewise, dexterous ungrasping addresses the necessity of changing the object's configuration relative to the gripper or the environment in order to securely keep hold of the object. In particular, we present a planning framework for determining a feasible minimum-cost motion path that completes dexterous ungrasping. Digit asymmetry in a gripper, i.e. difference in digit lengths, is discovered as the key to feasible and secure ungrasping. A set of experiments show the effectiveness of dexterous ungrasping in practical placement tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge