Chloe M. Barnes
Enhancing Pollinator Conservation towards Agriculture 4.0: Monitoring of Bees through Object Recognition
May 24, 2024



Abstract:In an era of rapid climate change and its adverse effects on food production, technological intervention to monitor pollinator conservation is of paramount importance for environmental monitoring and conservation for global food security. The survival of the human species depends on the conservation of pollinators. This article explores the use of Computer Vision and Object Recognition to autonomously track and report bee behaviour from images. A novel dataset of 9664 images containing bees is extracted from video streams and annotated with bounding boxes. With training, validation and testing sets (6722, 1915, and 997 images, respectively), the results of the COCO-based YOLO model fine-tuning approaches show that YOLOv5m is the most effective approach in terms of recognition accuracy. However, YOLOv5s was shown to be the most optimal for real-time bee detection with an average processing and inference time of 5.1ms per video frame at the cost of slightly lower ability. The trained model is then packaged within an explainable AI interface, which converts detection events into timestamped reports and charts, with the aim of facilitating use by non-technical users such as expert stakeholders from the apiculture industry towards informing responsible consumption and production.
Fruit Quality and Defect Image Classification with Conditional GAN Data Augmentation
Apr 12, 2021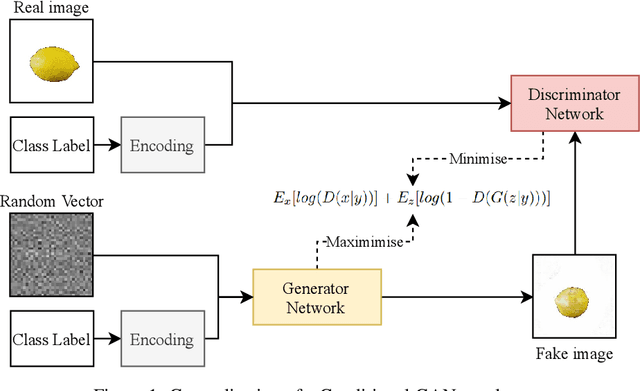
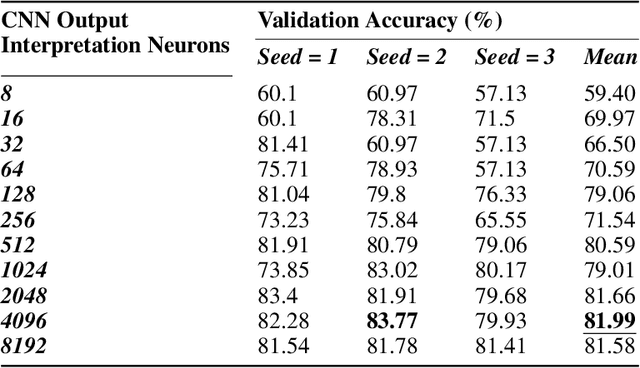
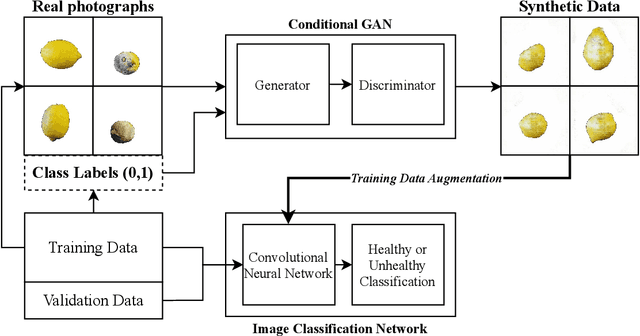
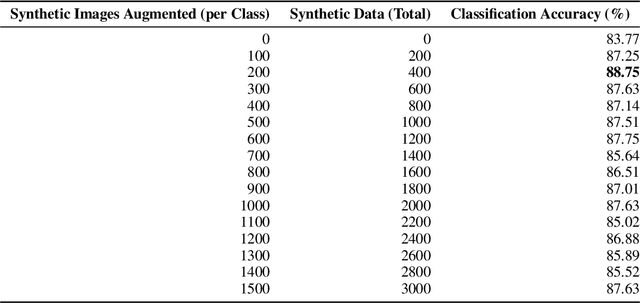
Abstract:Contemporary Artificial Intelligence technologies allow for the employment of Computer Vision to discern good crops from bad, providing a step in the pipeline of selecting healthy fruit from undesirable fruit, such as those which are mouldy or gangrenous. State-of-the-art works in the field report high accuracy results on small datasets (<1000 images), which are not representative of the population regarding real-world usage. The goals of this study are to further enable real-world usage by improving generalisation with data augmentation as well as to reduce overfitting and energy usage through model pruning. In this work, we suggest a machine learning pipeline that combines the ideas of fine-tuning, transfer learning, and generative model-based training data augmentation towards improving fruit quality image classification. A linear network topology search is performed to tune a VGG16 lemon quality classification model using a publicly-available dataset of 2690 images. We find that appending a 4096 neuron fully connected layer to the convolutional layers leads to an image classification accuracy of 83.77%. We then train a Conditional Generative Adversarial Network on the training data for 2000 epochs, and it learns to generate relatively realistic images. Grad-CAM analysis of the model trained on real photographs shows that the synthetic images can exhibit classifiable characteristics such as shape, mould, and gangrene. A higher image classification accuracy of 88.75% is then attained by augmenting the training with synthetic images, arguing that Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks have the ability to produce new data to alleviate issues of data scarcity. Finally, model pruning is performed via polynomial decay, where we find that the Conditional GAN-augmented classification network can retain 81.16% classification accuracy when compressed to 50% of its original size.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge