Chihiro Noguchi
Left-Right Symmetry Breaking in CLIP-style Vision-Language Models Trained on Synthetic Spatial-Relation Data
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Spatial understanding remains a key challenge in vision-language models. Yet it is still unclear whether such understanding is truly acquired, and if so, through what mechanisms. We present a controllable 1D image-text testbed to probe how left-right relational understanding emerges in Transformer-based vision and text encoders trained with a CLIP-style contrastive objective. We train lightweight Transformer-based vision and text encoders end-to-end on paired descriptions of one- and two-object scenes and evaluate generalization to unseen object pairs while systematically varying label and layout diversity. We find that contrastive training learns left-right relations and that label diversity, more than layout diversity, is the primary driver of generalization in this setting. To gain the mechanistic understanding, we perform an attention decomposition and show that interactions between positional and token embeddings induce a horizontal attention gradient that breaks left-right symmetry in the encoders; ablating this contribution substantially reduces left-right discrimination. Our results provide a mechanistic insight of when and how CLIP-style models acquire relational competence.
Offline Reinforcement Learning for End-to-End Autonomous Driving
Dec 21, 2025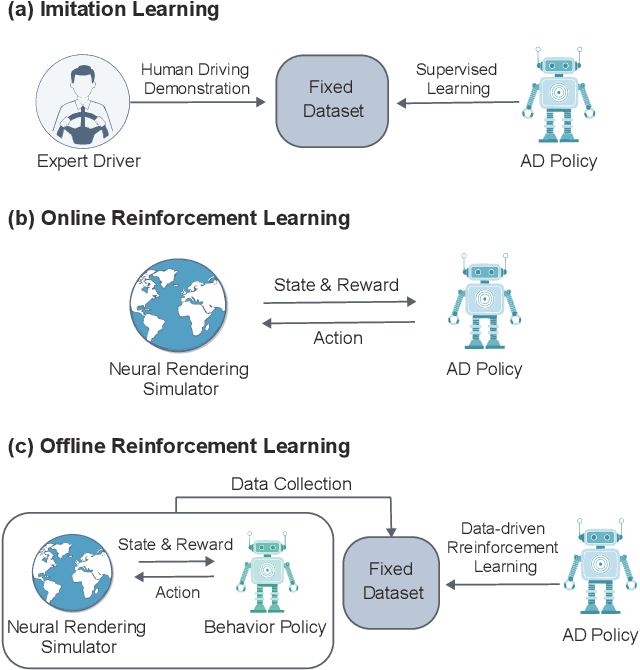
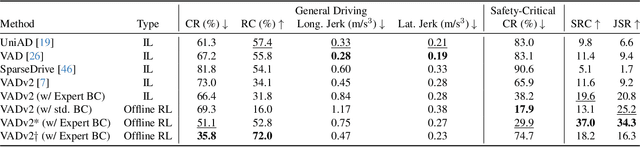
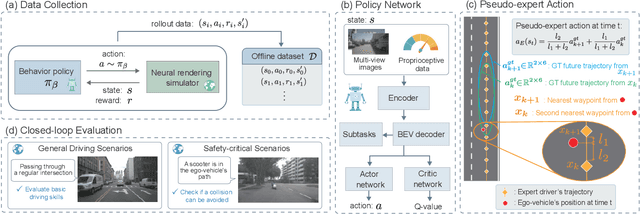
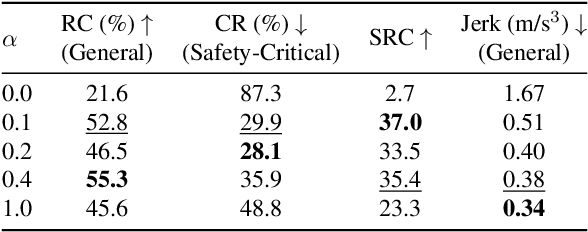
Abstract:End-to-end (E2E) autonomous driving models that take only camera images as input and directly predict a future trajectory are appealing for their computational efficiency and potential for improved generalization via unified optimization; however, persistent failure modes remain due to reliance on imitation learning (IL). While online reinforcement learning (RL) could mitigate IL-induced issues, the computational burden of neural rendering-based simulation and large E2E networks renders iterative reward and hyperparameter tuning costly. We introduce a camera-only E2E offline RL framework that performs no additional exploration and trains solely on a fixed simulator dataset. Offline RL offers strong data efficiency and rapid experimental iteration, yet is susceptible to instability from overestimation on out-of-distribution (OOD) actions. To address this, we construct pseudo ground-truth trajectories from expert driving logs and use them as a behavior regularization signal, suppressing imitation of unsafe or suboptimal behavior while stabilizing value learning. Training and closed-loop evaluation are conducted in a neural rendering environment learned from the public nuScenes dataset. Empirically, the proposed method achieves substantial improvements in collision rate and route completion compared with IL baselines. Our code will be available at [URL].
Text Image Generation for Low-Resource Languages with Dual Translation Learning
Sep 26, 2024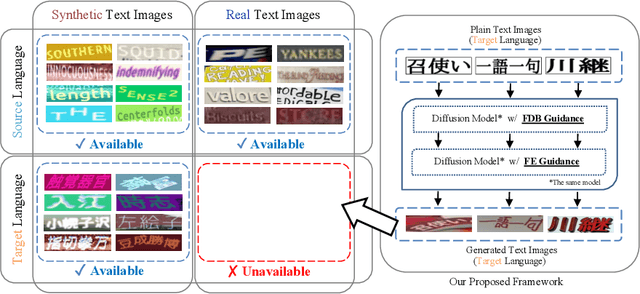
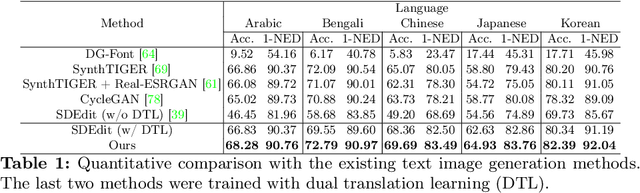
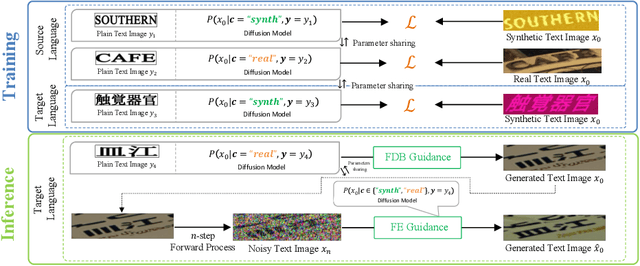
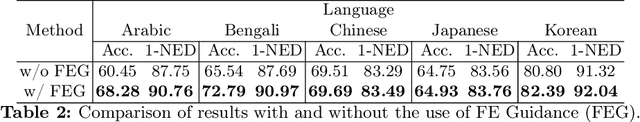
Abstract:Scene text recognition in low-resource languages frequently faces challenges due to the limited availability of training datasets derived from real-world scenes. This study proposes a novel approach that generates text images in low-resource languages by emulating the style of real text images from high-resource languages. Our approach utilizes a diffusion model that is conditioned on binary states: ``synthetic'' and ``real.'' The training of this model involves dual translation tasks, where it transforms plain text images into either synthetic or real text images, based on the binary states. This approach not only effectively differentiates between the two domains but also facilitates the model's explicit recognition of characters in the target language. Furthermore, to enhance the accuracy and variety of generated text images, we introduce two guidance techniques: Fidelity-Diversity Balancing Guidance and Fidelity Enhancement Guidance. Our experimental results demonstrate that the text images generated by our proposed framework can significantly improve the performance of scene text recognition models for low-resource languages.
Road Obstacle Detection based on Unknown Objectness Scores
Mar 27, 2024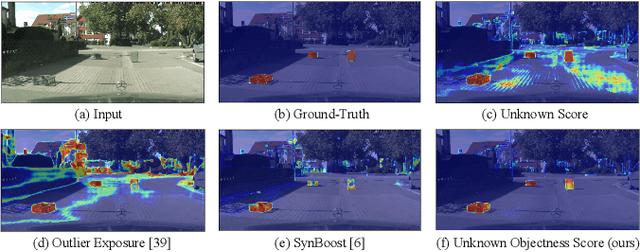
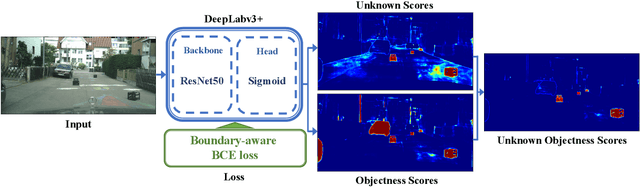
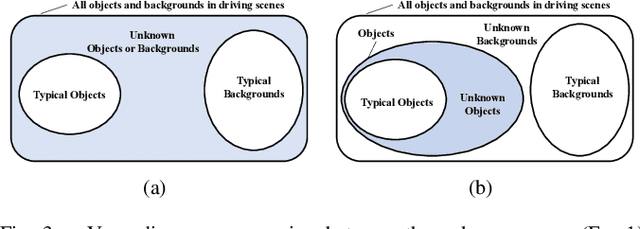

Abstract:The detection of unknown traffic obstacles is vital to ensure safe autonomous driving. The standard object-detection methods cannot identify unknown objects that are not included under predefined categories. This is because object-detection methods are trained to assign a background label to pixels corresponding to the presence of unknown objects. To address this problem, the pixel-wise anomaly-detection approach has attracted increased research attention. Anomaly-detection techniques, such as uncertainty estimation and perceptual difference from reconstructed images, make it possible to identify pixels of unknown objects as out-of-distribution (OoD) samples. However, when applied to images with many unknowns and complex components, such as driving scenes, these methods often exhibit unstable performance. The purpose of this study is to achieve stable performance for detecting unknown objects by incorporating the object-detection fashions into the pixel-wise anomaly detection methods. To achieve this goal, we adopt a semantic-segmentation network with a sigmoid head that simultaneously provides pixel-wise anomaly scores and objectness scores. Our experimental results show that the objectness scores play an important role in improving the detection performance. Based on these results, we propose a novel anomaly score by integrating these two scores, which we term as unknown objectness score. Quantitative evaluations show that the proposed method outperforms state-of-the-art methods when applied to the publicly available datasets.
Scene Text Image Super-resolution based on Text-conditional Diffusion Models
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:Scene Text Image Super-resolution (STISR) has recently achieved great success as a preprocessing method for scene text recognition. STISR aims to transform blurred and noisy low-resolution (LR) text images in real-world settings into clear high-resolution (HR) text images suitable for scene text recognition. In this study, we leverage text-conditional diffusion models (DMs), known for their impressive text-to-image synthesis capabilities, for STISR tasks. Our experimental results revealed that text-conditional DMs notably surpass existing STISR methods. Especially when texts from LR text images are given as input, the text-conditional DMs are able to produce superior quality super-resolution text images. Utilizing this capability, we propose a novel framework for synthesizing LR-HR paired text image datasets. This framework consists of three specialized text-conditional DMs, each dedicated to text image synthesis, super-resolution, and image degradation. These three modules are vital for synthesizing distinct LR and HR paired images, which are more suitable for training STISR methods. Our experiments confirmed that these synthesized image pairs significantly enhance the performance of STISR methods in the TextZoom evaluation.
Ego-Vehicle Action Recognition based on Semi-Supervised Contrastive Learning
Mar 02, 2023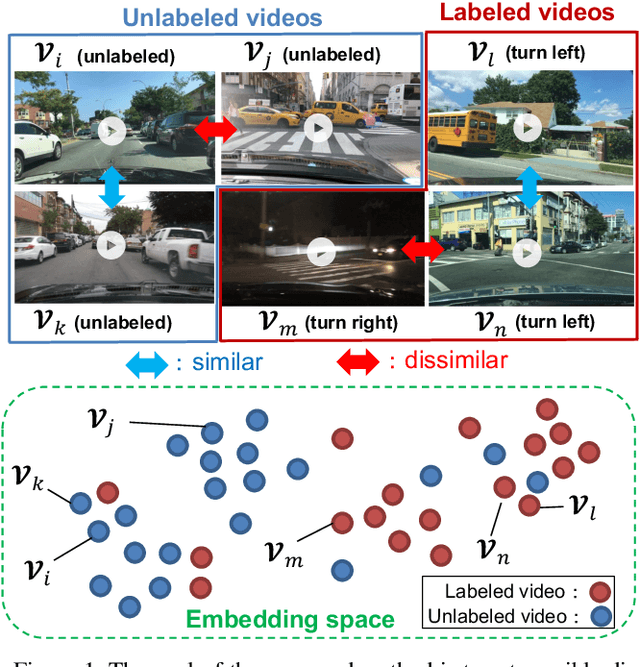
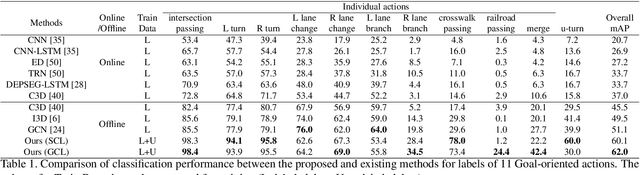
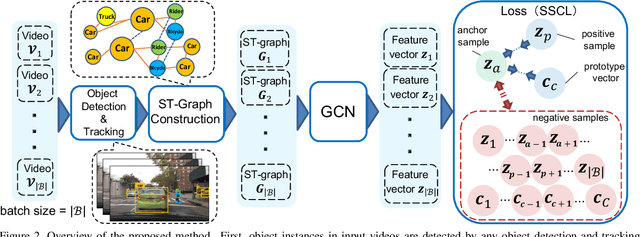
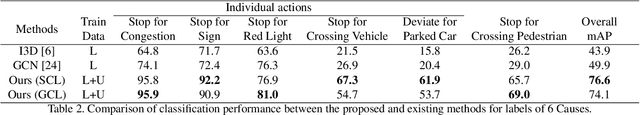
Abstract:In recent years, many automobiles have been equipped with cameras, which have accumulated an enormous amount of video footage of driving scenes. Autonomous driving demands the highest level of safety, for which even unimaginably rare driving scenes have to be collected in training data to improve the recognition accuracy for specific scenes. However, it is prohibitively costly to find very few specific scenes from an enormous amount of videos. In this article, we show that proper video-to-video distances can be defined by focusing on ego-vehicle actions. It is well known that existing methods based on supervised learning cannot handle videos that do not fall into predefined classes, though they work well in defining video-to-video distances in the embedding space between labeled videos. To tackle this problem, we propose a method based on semi-supervised contrastive learning. We consider two related but distinct contrastive learning: standard graph contrastive learning and our proposed SOIA-based contrastive learning. We observe that the latter approach can provide more sensible video-to-video distances between unlabeled videos. Next, the effectiveness of our method is quantified by evaluating the classification performance of the ego-vehicle action recognition using HDD dataset, which shows that our method including unlabeled data in training significantly outperforms the existing methods using only labeled data in training.
* 19 pages, 17 figures
Approximate matrix completion based on cavity method
Jun 29, 2019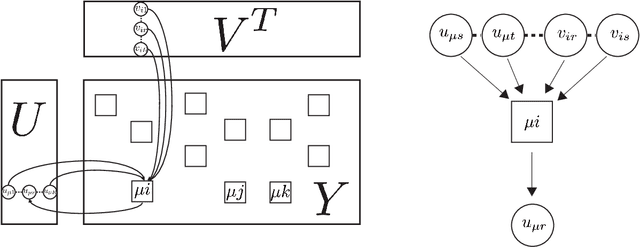
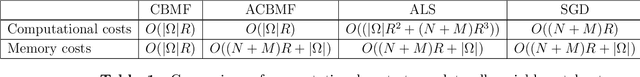
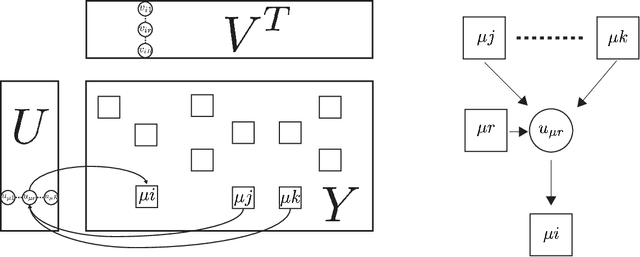
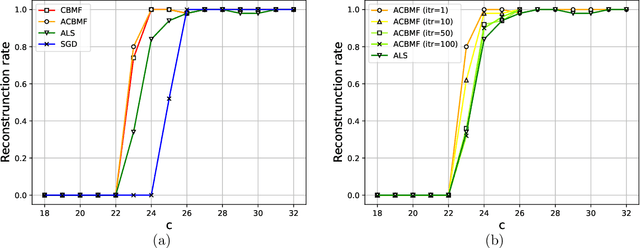
Abstract:In order to solve large matrix completion problems with practical computational cost, an approximate approach based on matrix factorization has been widely used. Alternating least squares (ALS) and stochastic gradient descent (SGD) are two major algorithms to this end. In this study, we propose a new algorithm, namely cavity-based matrix factorization (CBMF) and approximate cavity-based matrix factorization (ACBMF), which are developed based on the cavity method from statistical mechanics. ALS yields solutions with less iterations when compared to those of SGD. This is because its update rules are described in a closed form although it entails higher computational cost. CBMF can also write its update rules in a closed form, and its computational cost is lower than that of ALS. ACBMF is proposed to compensate a disadvantage of CBMF in terms of relatively high memory cost. We experimentally illustrate that the proposed methods outperform the two existing algorithms in terms of convergence speed per iteration, and it can work under the condition where observed entries are relatively fewer. Additionally, in contrast to SGD, (A)CBMF does not require scheduling of the learning rate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge