Cheuk Tung Shadow Yiu
Automatic Speech Recognition Datasets in Cantonese: A Survey and New Dataset
Jan 17, 2022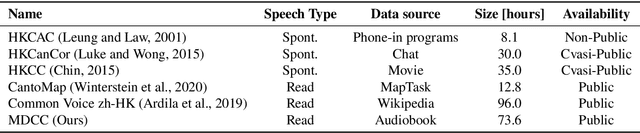
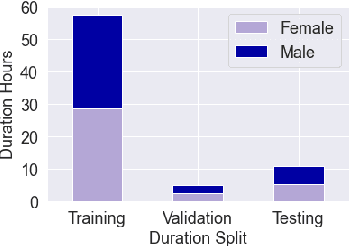
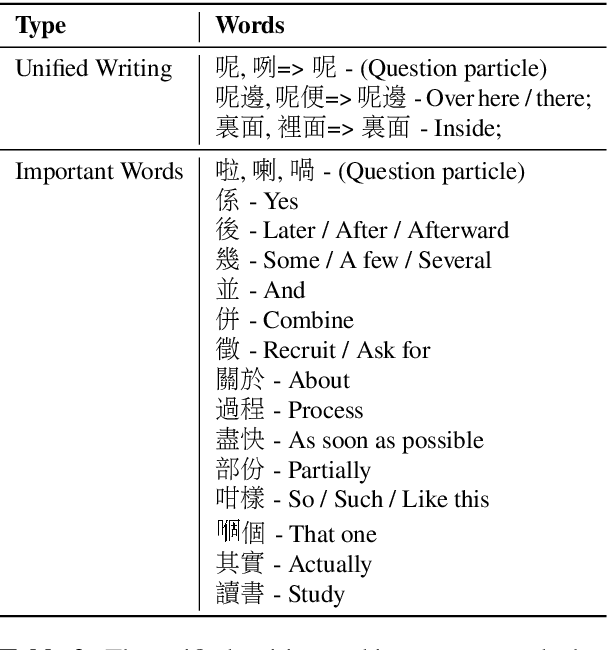
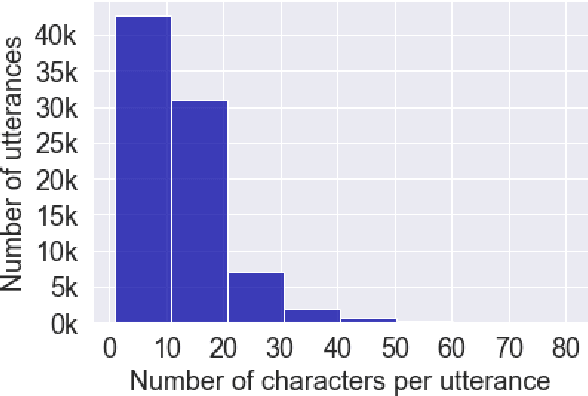
Abstract:Automatic speech recognition (ASR) on low resource languages improves the access of linguistic minorities to technological advantages provided by artificial intelligence (AI). In this paper, we address the problem of data scarcity for the Hong Kong Cantonese language by creating a new Cantonese dataset. Our dataset, Multi-Domain Cantonese Corpus (MDCC), consists of 73.6 hours of clean read speech paired with transcripts, collected from Cantonese audiobooks from Hong Kong. It comprises philosophy, politics, education, culture, lifestyle and family domains, covering a wide range of topics. We also review all existing Cantonese datasets and analyze them according to their speech type, data source, total size and availability. We further conduct experiments with Fairseq S2T Transformer, a state-of-the-art ASR model, on the biggest existing dataset, Common Voice zh-HK, and our proposed MDCC, and the results show the effectiveness of our dataset. In addition, we create a powerful and robust Cantonese ASR model by applying multi-dataset learning on MDCC and Common Voice zh-HK.
CI-AVSR: A Cantonese Audio-Visual Speech Dataset for In-car Command Recognition
Jan 11, 2022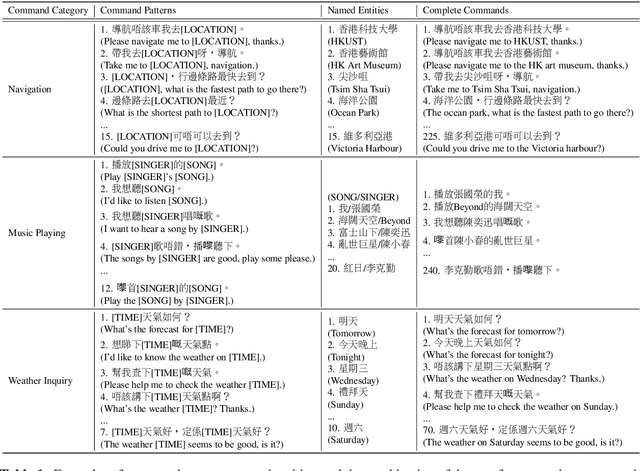
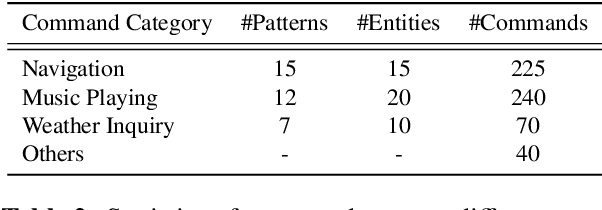
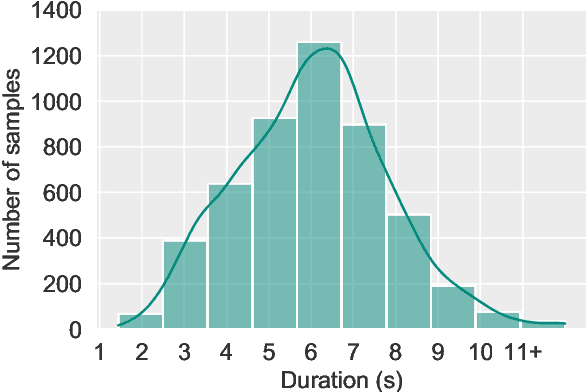
Abstract:With the rise of deep learning and intelligent vehicle, the smart assistant has become an essential in-car component to facilitate driving and provide extra functionalities. In-car smart assistants should be able to process general as well as car-related commands and perform corresponding actions, which eases driving and improves safety. However, there is a data scarcity issue for low resource languages, hindering the development of research and applications. In this paper, we introduce a new dataset, Cantonese In-car Audio-Visual Speech Recognition (CI-AVSR), for in-car command recognition in the Cantonese language with both video and audio data. It consists of 4,984 samples (8.3 hours) of 200 in-car commands recorded by 30 native Cantonese speakers. Furthermore, we augment our dataset using common in-car background noises to simulate real environments, producing a dataset 10 times larger than the collected one. We provide detailed statistics of both the clean and the augmented versions of our dataset. Moreover, we implement two multimodal baselines to demonstrate the validity of CI-AVSR. Experiment results show that leveraging the visual signal improves the overall performance of the model. Although our best model can achieve a considerable quality on the clean test set, the speech recognition quality on the noisy data is still inferior and remains as an extremely challenging task for real in-car speech recognition systems. The dataset and code will be released at https://github.com/HLTCHKUST/CI-AVSR.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge