Chenqi Guo
Crossmodal Knowledge Distillation with WordNet-Relaxed Text Embeddings for Robust Image Classification
Mar 31, 2025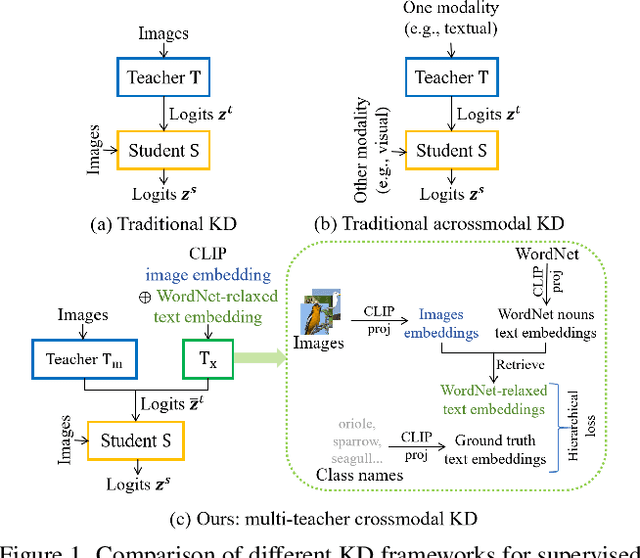
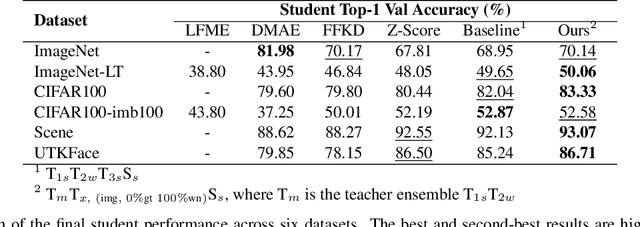
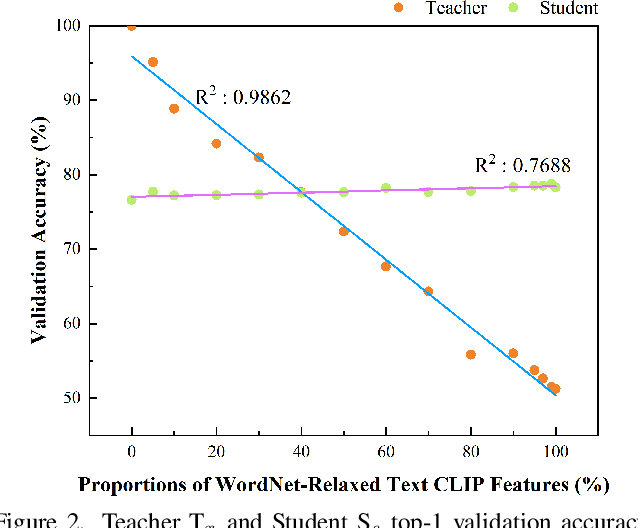
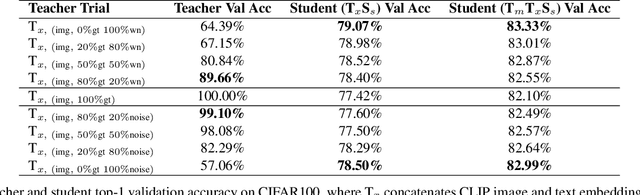
Abstract:Crossmodal knowledge distillation (KD) aims to enhance a unimodal student using a multimodal teacher model. In particular, when the teacher's modalities include the student's, additional complementary information can be exploited to improve knowledge transfer. In supervised image classification, image datasets typically include class labels that represent high-level concepts, suggesting a natural avenue to incorporate textual cues for crossmodal KD. However, these labels rarely capture the deeper semantic structures in real-world visuals and can lead to label leakage if used directly as inputs, ultimately limiting KD performance. To address these issues, we propose a multi-teacher crossmodal KD framework that integrates CLIP image embeddings with learnable WordNet-relaxed text embeddings under a hierarchical loss. By avoiding direct use of exact class names and instead using semantically richer WordNet expansions, we mitigate label leakage and introduce more diverse textual cues. Experiments show that this strategy significantly boosts student performance, whereas noisy or overly precise text embeddings hinder distillation efficiency. Interpretability analyses confirm that WordNet-relaxed prompts encourage heavier reliance on visual features over textual shortcuts, while still effectively incorporating the newly introduced textual cues. Our method achieves state-of-the-art or second-best results on six public datasets, demonstrating its effectiveness in advancing crossmodal KD.
Why does Knowledge Distillation Work? Rethink its Attention and Fidelity Mechanism
Apr 30, 2024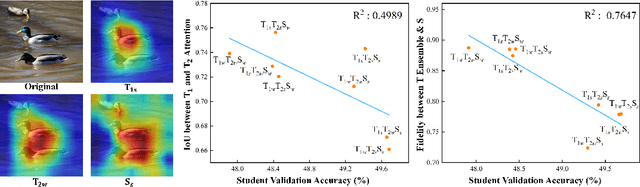
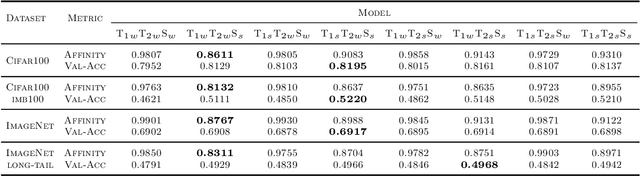
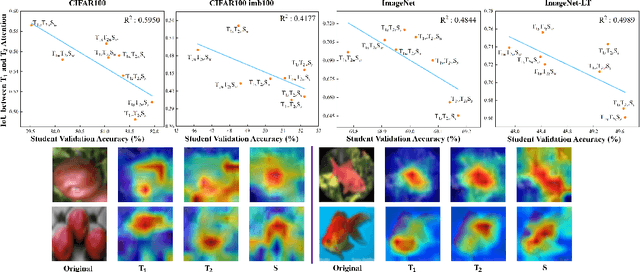
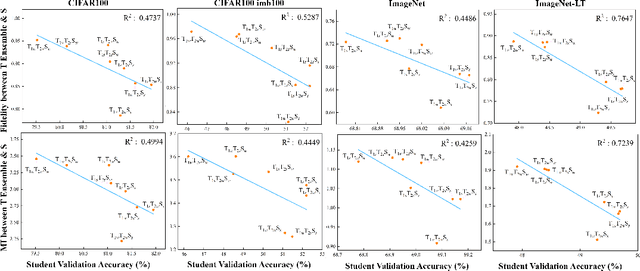
Abstract:Does Knowledge Distillation (KD) really work? Conventional wisdom viewed it as a knowledge transfer procedure where a perfect mimicry of the student to its teacher is desired. However, paradoxical studies indicate that closely replicating the teacher's behavior does not consistently improve student generalization, posing questions on its possible causes. Confronted with this gap, we hypothesize that diverse attentions in teachers contribute to better student generalization at the expense of reduced fidelity in ensemble KD setups. By increasing data augmentation strengths, our key findings reveal a decrease in the Intersection over Union (IoU) of attentions between teacher models, leading to reduced student overfitting and decreased fidelity. We propose this low-fidelity phenomenon as an underlying characteristic rather than a pathology when training KD. This suggests that stronger data augmentation fosters a broader perspective provided by the divergent teacher ensemble and lower student-teacher mutual information, benefiting generalization performance. These insights clarify the mechanism on low-fidelity phenomenon in KD. Thus, we offer new perspectives on optimizing student model performance, by emphasizing increased diversity in teacher attentions and reduced mimicry behavior between teachers and student.
Structural Similarity: When to Use Deep Generative Models on Imbalanced Image Dataset Augmentation
Mar 08, 2023



Abstract:Improving the performance on an imbalanced training set is one of the main challenges in nowadays Machine Learning. One way to augment and thus re-balance the image dataset is through existing deep generative models, like class-conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (cGAN) or Diffusion Models by synthesizing images on each of the tail-class. Our experiments on imbalanced image dataset classification show that, the validation accuracy improvement with such re-balancing method is related to the image similarity between different classes. Thus, to quantify this image dataset class similarity, we propose a measurement called Super-Sub Class Structural Similarity (SSIM-supSubCls) based on Structural Similarity (SSIM). A deep generative model data augmentation classification (GM-augCls) pipeline is also provided to verify this metric correlates with the accuracy enhancement. We further quantify the relationship between them, discovering that the accuracy improvement decays exponentially with respect to SSIM-supSubCls values.
When do GANs replicate? On the choice of dataset size
Feb 23, 2022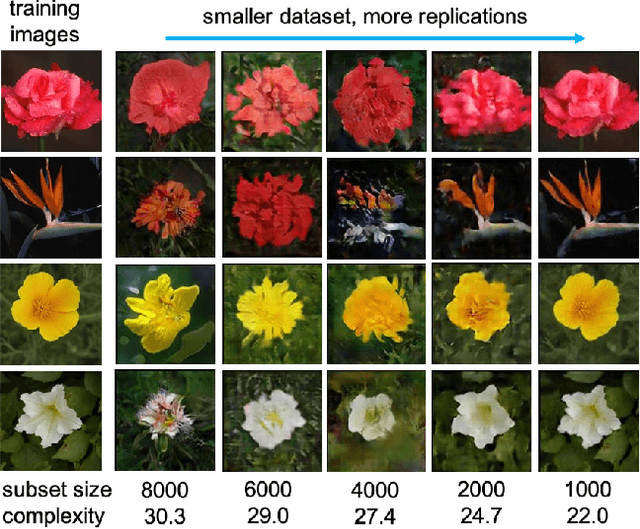



Abstract:Do GANs replicate training images? Previous studies have shown that GANs do not seem to replicate training data without significant change in the training procedure. This leads to a series of research on the exact condition needed for GANs to overfit to the training data. Although a number of factors has been theoretically or empirically identified, the effect of dataset size and complexity on GANs replication is still unknown. With empirical evidence from BigGAN and StyleGAN2, on datasets CelebA, Flower and LSUN-bedroom, we show that dataset size and its complexity play an important role in GANs replication and perceptual quality of the generated images. We further quantify this relationship, discovering that replication percentage decays exponentially with respect to dataset size and complexity, with a shared decaying factor across GAN-dataset combinations. Meanwhile, the perceptual image quality follows a U-shape trend w.r.t dataset size. This finding leads to a practical tool for one-shot estimation on minimal dataset size to prevent GAN replication which can be used to guide datasets construction and selection.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge