Chenliang Zhou
Quartet of Diffusions: Structure-Aware Point Cloud Generation through Part and Symmetry Guidance
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:We introduce the Quartet of Diffusions, a structure-aware point cloud generation framework that explicitly models part composition and symmetry. Unlike prior methods that treat shape generation as a holistic process or only support part composition, our approach leverages four coordinated diffusion models to learn distributions of global shape latents, symmetries, semantic parts, and their spatial assembly. This structured pipeline ensures guaranteed symmetry, coherent part placement, and diverse, high-quality outputs. By disentangling the generative process into interpretable components, our method supports fine-grained control over shape attributes, enabling targeted manipulation of individual parts while preserving global consistency. A central global latent further reinforces structural coherence across assembled parts. Our experiments show that the Quartet achieves state-of-the-art performance. To our best knowledge, this is the first 3D point cloud generation framework that fully integrates and enforces both symmetry and part priors throughout the generative process.
Features Emerge as Discrete States: The First Application of SAEs to 3D Representations
Dec 15, 2025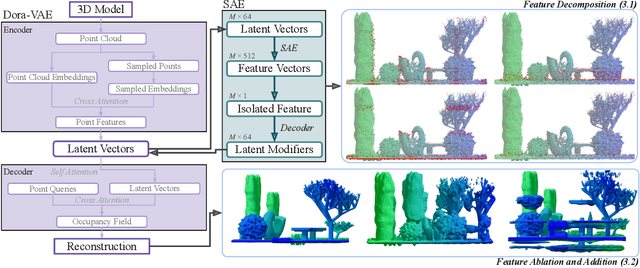
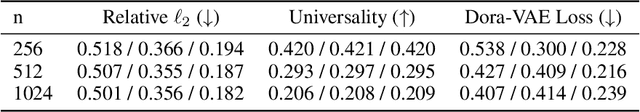
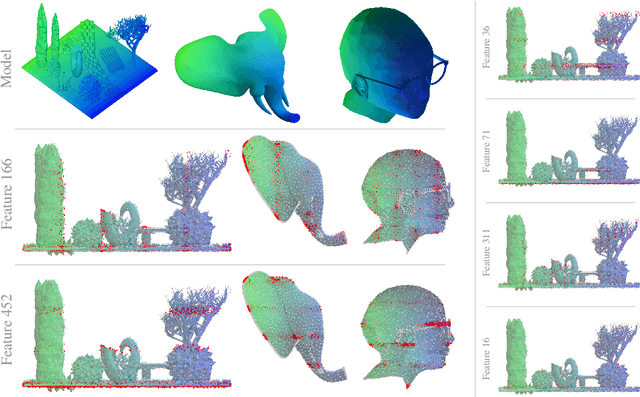
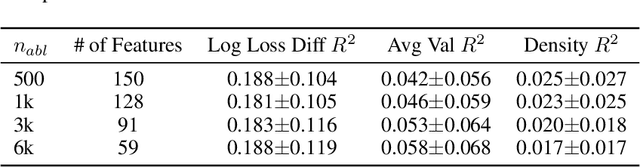
Abstract:Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) are a powerful dictionary learning technique for decomposing neural network activations, translating the hidden state into human ideas with high semantic value despite no external intervention or guidance. However, this technique has rarely been applied outside of the textual domain, limiting theoretical explorations of feature decomposition. We present the first application of SAEs to the 3D domain, analyzing the features used by a state-of-the-art 3D reconstruction VAE applied to 53k 3D models from the Objaverse dataset. We observe that the network encodes discrete rather than continuous features, leading to our key finding: such models approximate a discrete state space, driven by phase-like transitions from feature activations. Through this state transition framework, we address three otherwise unintuitive behaviors - the inclination of the reconstruction model towards positional encoding representations, the sigmoidal behavior of reconstruction loss from feature ablation, and the bimodality in the distribution of phase transition points. This final observation suggests the model redistributes the interference caused by superposition to prioritize the saliency of different features. Our work not only compiles and explains unexpected phenomena regarding feature decomposition, but also provides a framework to explain the model's feature learning dynamics. The code and dataset of encoded 3D objects will be available on release.
RETRO: REthinking Tactile Representation Learning with Material PriOrs
May 20, 2025
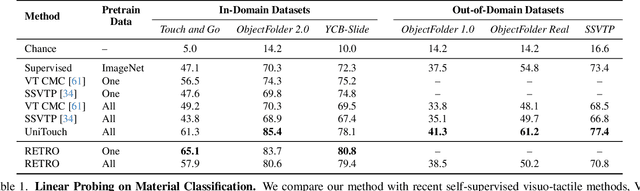
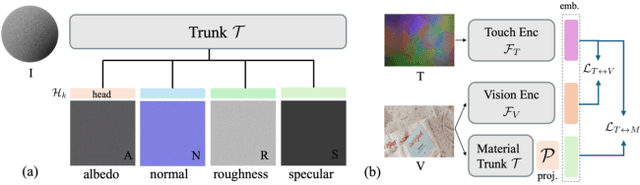
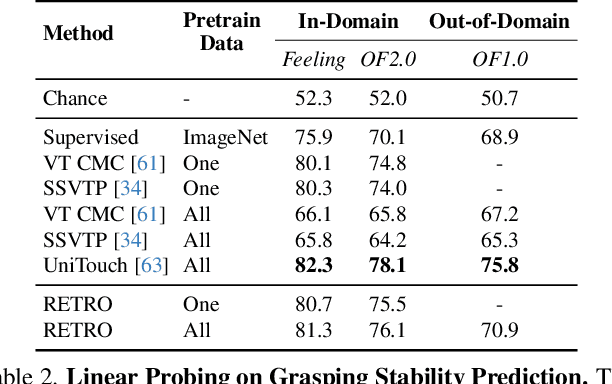
Abstract:Tactile perception is profoundly influenced by the surface properties of objects in contact. However, despite their crucial role in shaping tactile experiences, these material characteristics have been largely neglected in existing tactile representation learning methods. Most approaches primarily focus on aligning tactile data with visual or textual information, overlooking the richness of tactile feedback that comes from understanding the materials' inherent properties. In this work, we address this gap by revisiting the tactile representation learning framework and incorporating material-aware priors into the learning process. These priors, which represent pre-learned characteristics specific to different materials, allow tactile models to better capture and generalize the nuances of surface texture. Our method enables more accurate, contextually rich tactile feedback across diverse materials and textures, improving performance in real-world applications such as robotics, haptic feedback systems, and material editing.
Physically Based Neural Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function
Nov 04, 2024Abstract:We introduce the physically based neural bidirectional reflectance distribution function (PBNBRDF), a novel, continuous representation for material appearance based on neural fields. Our model accurately reconstructs real-world materials while uniquely enforcing physical properties for realistic BRDFs, specifically Helmholtz reciprocity via reparametrization and energy passivity via efficient analytical integration. We conduct a systematic analysis demonstrating the benefits of adhering to these physical laws on the visual quality of reconstructed materials. Additionally, we enhance the color accuracy of neural BRDFs by introducing chromaticity enforcement supervising the norms of RGB channels. Through both qualitative and quantitative experiments on multiple databases of measured real-world BRDFs, we show that adhering to these physical constraints enables neural fields to more faithfully and stably represent the original data and achieve higher rendering quality.
XQSV: A Structurally Variable Network to Imitate Human Play in Xiangqi
Jul 05, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce an innovative deep learning architecture, termed Xiangqi Structurally Variable (XQSV), designed to emulate the behavioral patterns of human players in Xiangqi, or Chinese Chess. The unique attribute of XQSV is its capacity to alter its structural configuration dynamically, optimizing performance for the task based on the particular subset of data on which it is trained. We have incorporated several design improvements to significantly enhance the network's predictive accuracy, including a local illegal move filter, an Elo range partitioning, a sequential one-dimensional input, and a simulation of imperfect memory capacity. Empirical evaluations reveal that XQSV attains a predictive accuracy of approximately 40%, with its performance peaking within the trained Elo range. This indicates the model's success in mimicking the play behavior of individuals within that specific range. A three-terminal Turing Test was employed to demonstrate that the XQSV model imitates human behavior more accurately than conventional Xiangqi engines, rendering it indistinguishable from actual human opponents. Given the inherent nondeterminism in human gameplay, we propose two supplementary relaxed evaluation metrics. To our knowledge, XQSV represents the first model to mimic Xiangqi players.
FrePolad: Frequency-Rectified Point Latent Diffusion for Point Cloud Generation
Nov 20, 2023



Abstract:We propose FrePolad: frequency-rectified point latent diffusion, a point cloud generation pipeline integrating a variational autoencoder (VAE) with a denoising diffusion probabilistic model (DDPM) for the latent distribution. FrePolad simultaneously achieves high quality, diversity, and flexibility in point cloud cardinality for generation tasks while maintaining high computational efficiency. The improvement in generation quality and diversity is achieved through (1) a novel frequency rectification module via spherical harmonics designed to retain high-frequency content while learning the point cloud distribution; and (2) a latent DDPM to learn the regularized yet complex latent distribution. In addition, FrePolad supports variable point cloud cardinality by formulating the sampling of points as conditional distributions over a latent shape distribution. Finally, the low-dimensional latent space encoded by the VAE contributes to FrePolad's fast and scalable sampling. Our quantitative and qualitative results demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of FrePolad in terms of quality, diversity, and computational efficiency.
CLIP-PAE: Projection-Augmentation Embedding to Extract Relevant Features for a Disentangled, Interpretable, and Controllable Text-Guided Image Manipulation
Oct 08, 2022



Abstract:Recently introduced Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) bridges images and text by embedding them into a joint latent space. This opens the door to ample literature that aims to manipulate an input image by providing a textual explanation. However, due to the discrepancy between image and text embeddings in the joint space, using text embeddings as the optimization target often introduces undesired artifacts in the resulting images. Disentanglement, interpretability, and controllability are also hard to guarantee for manipulation. To alleviate these problems, we propose to define corpus subspaces spanned by relevant prompts to capture specific image characteristics. We introduce CLIP Projection-Augmentation Embedding (PAE) as an optimization target to improve the performance of text-guided image manipulation. Our method is a simple and general paradigm that can be easily computed and adapted, and smoothly incorporated into any CLIP-based image manipulation algorithm. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, we conduct several theoretical and empirical studies. As a case study, we utilize the method for text-guided semantic face editing. We quantitatively and qualitatively demonstrate that PAE facilitates a more disentangled, interpretable, and controllable image manipulation with state-of-the-art quality and accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge