Charilaos Mylonas
Relational VAE: A Continuous Latent Variable Model for Graph Structured Data
Jun 30, 2021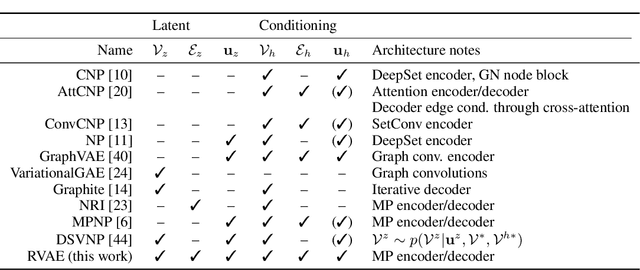
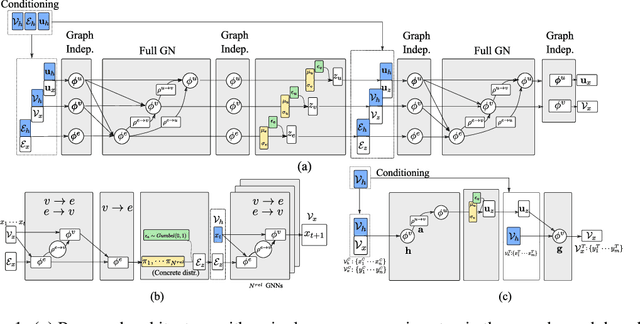
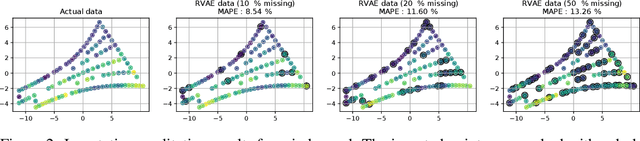
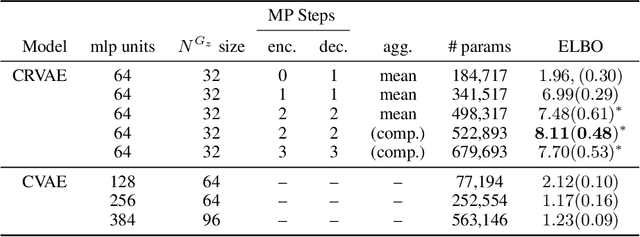
Abstract:Graph Networks (GNs) enable the fusion of prior knowledge and relational reasoning with flexible function approximations. In this work, a general GN-based model is proposed which takes full advantage of the relational modeling capabilities of GNs and extends these to probabilistic modeling with Variational Bayes (VB). To that end, we combine complementary pre-existing approaches on VB for graph data and propose an approach that relies on graph-structured latent and conditioning variables. It is demonstrated that Neural Processes can also be viewed through the lens of the proposed model. We show applications on the problem of structured probability density modeling for simulated and real wind farm monitoring data, as well as on the meta-learning of simulated Gaussian Process data. We release the source code, along with the simulated datasets.
Foundations of Population-Based SHM, Part IV: The Geometry of Spaces of Structures and their Feature Spaces
Mar 05, 2021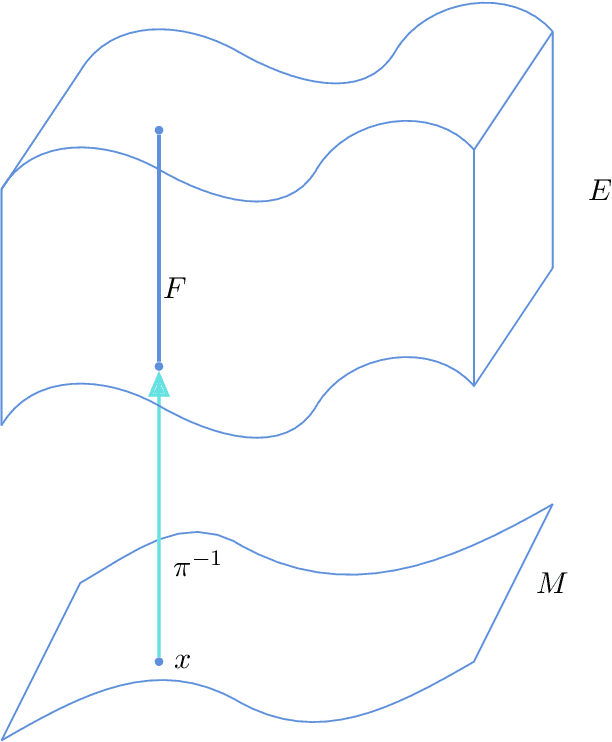
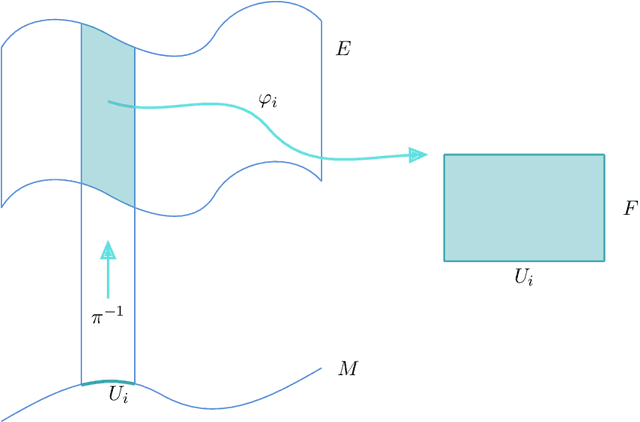
Abstract:One of the requirements of the population-based approach to Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) proposed in the earlier papers in this sequence, is that structures be represented by points in an abstract space. Furthermore, these spaces should be metric spaces in a loose sense; i.e. there should be some measure of distance applicable to pairs of points; similar structures should then be close in the metric. However, this geometrical construction is not enough for the framing of problems in data-based SHM, as it leaves undefined the notion of feature spaces. Interpreting the feature values on a structure-by-structure basis as a type of field over the space of structures, it seems sensible to borrow an idea from modern theoretical physics, and define feature assignments as sections in a vector bundle over the structure space. With this idea in place, one can interpret the effect of environmental and operational variations as gauge degrees of freedom, as in modern gauge field theories. This paper will discuss the various geometrical structures required for an abstract theory of feature spaces in SHM, and will draw analogies with how these structures have shown their power in modern physics. In the second part of the paper, the problem of determining the normal condition cross section of a feature bundle is addressed. The solution is provided by the application of Graph Neural Networks (GNN), a versatile non-Euclidean machine learning algorithm which is not restricted to inputs and outputs from vector spaces. In particular, the algorithm is well suited to operating directly on the sort of graph structures which are an important part of the proposed framework for PBSHM. The solution of the normal section problem is demonstrated for a heterogeneous population of truss structures for which the feature of interest is the first natural frequency.
Remaining Useful Life Estimation Under Uncertainty with Causal GraphNets
Nov 23, 2020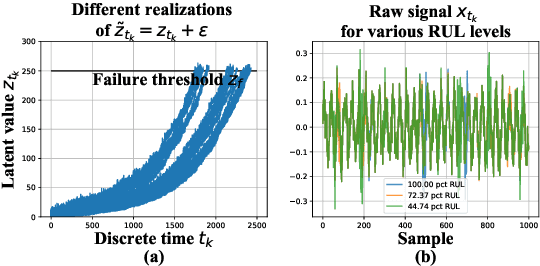
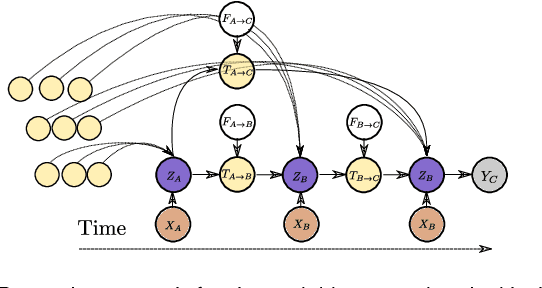
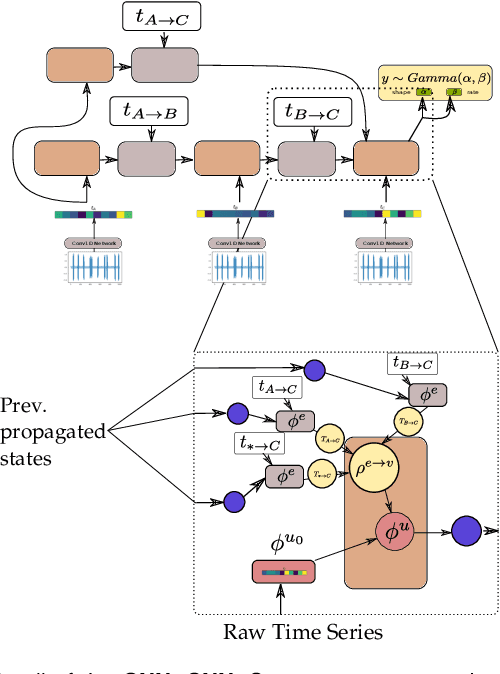
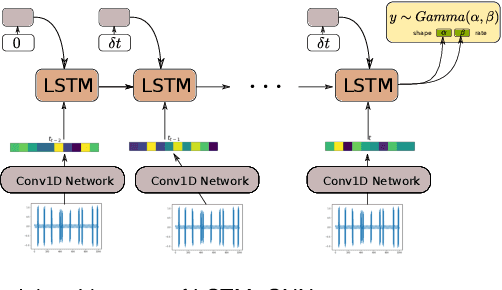
Abstract:In this work, a novel approach for the construction and training of time series models is presented that deals with the problem of learning on large time series with non-equispaced observations, which at the same time may possess features of interest that span multiple scales. The proposed method is appropriate for constructing predictive models for non-stationary stochastic time series.The efficacy of the method is demonstrated on a simulated stochastic degradation dataset and on a real-world accelerated life testing dataset for ball-bearings. The proposed method, which is based on GraphNets, implicitly learns a model that describes the evolution of the system at the level of a state-vector rather than of a raw observation. The proposed approach is compared to a recurrent network with a temporal convolutional feature extractor head (RNN-tCNN) which forms a known viable alternative for the problem context considered. Finally, by taking advantage of recent advances in the computation of reparametrization gradients for learning probability distributions, a simple yet effective technique for representing prediction uncertainty as a Gamma distribution over remaining useful life predictions is employed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge