Imad Abdallah
Graph Transformers for inverse physics: reconstructing flows around arbitrary 2D airfoils
Jan 28, 2025



Abstract:We introduce a Graph Transformer framework that serves as a general inverse physics engine on meshes, demonstrated through the challenging task of reconstructing aerodynamic flow fields from sparse surface measurements. While deep learning has shown promising results in forward physics simulation, inverse problems remain particularly challenging due to their ill-posed nature and the difficulty of propagating information from limited boundary observations. Our approach addresses these challenges by combining the geometric expressiveness of message-passing neural networks with the global reasoning of Transformers, enabling efficient learning of inverse mappings from boundary conditions to complete states. We evaluate this framework on a comprehensive dataset of steady-state RANS simulations around diverse airfoil geometries, where the task is to reconstruct full pressure and velocity fields from surface pressure measurements alone. The architecture achieves high reconstruction accuracy while maintaining fast inference times. We conduct experiments and provide insights into the relative importance of local geometric processing and global attention mechanisms in mesh-based inverse problems. We also find that the framework is robust to reduced sensor coverage. These results suggest that Graph Transformers can serve as effective inverse physics engines across a broader range of applications where complete system states must be reconstructed from limited boundary observations.
Knowledge Engineering for Wind Energy
Oct 01, 2023



Abstract:With the rapid evolution of the wind energy sector, there is an ever-increasing need to create value from the vast amounts of data made available both from within the domain, as well as from other sectors. This article addresses the challenges faced by wind energy domain experts in converting data into domain knowledge, connecting and integrating it with other sources of knowledge, and making it available for use in next generation artificially intelligent systems. To this end, this article highlights the role that knowledge engineering can play in the process of digital transformation of the wind energy sector. It presents the main concepts underpinning Knowledge-Based Systems and summarises previous work in the areas of knowledge engineering and knowledge representation in a manner that is relevant and accessible to domain experts. A systematic analysis of the current state-of-the-art on knowledge engineering in the wind energy domain is performed, with available tools put into perspective by establishing the main domain actors and their needs and identifying key problematic areas. Finally, guidelines for further development and improvement are provided.
Relational VAE: A Continuous Latent Variable Model for Graph Structured Data
Jun 30, 2021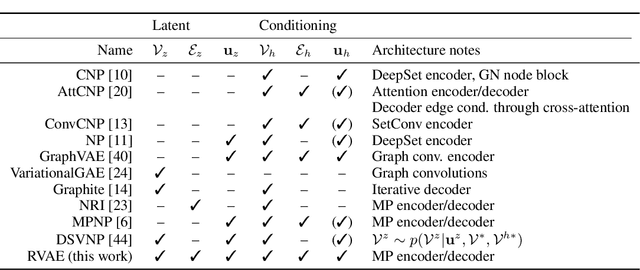
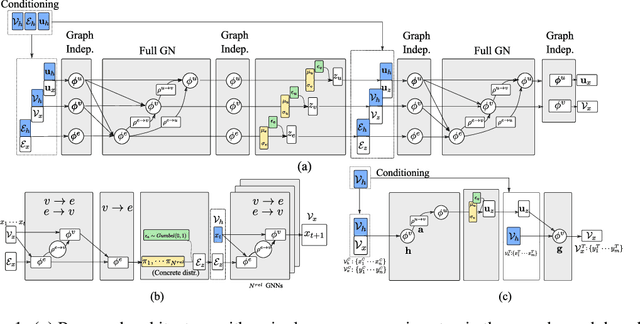
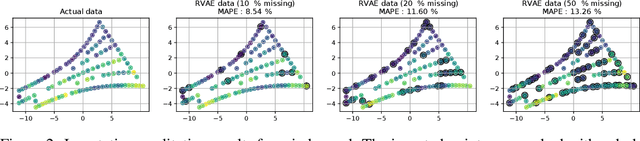
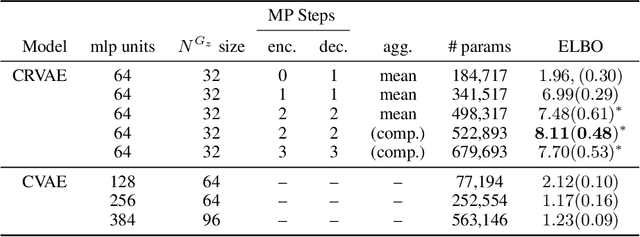
Abstract:Graph Networks (GNs) enable the fusion of prior knowledge and relational reasoning with flexible function approximations. In this work, a general GN-based model is proposed which takes full advantage of the relational modeling capabilities of GNs and extends these to probabilistic modeling with Variational Bayes (VB). To that end, we combine complementary pre-existing approaches on VB for graph data and propose an approach that relies on graph-structured latent and conditioning variables. It is demonstrated that Neural Processes can also be viewed through the lens of the proposed model. We show applications on the problem of structured probability density modeling for simulated and real wind farm monitoring data, as well as on the meta-learning of simulated Gaussian Process data. We release the source code, along with the simulated datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge