Changxu Zhang
Leveraging Transformer Decoder for Automotive Radar Object Detection
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we present a Transformer-based architecture for 3D radar object detection that uses a novel Transformer Decoder as the prediction head to directly regress 3D bounding boxes and class scores from radar feature representations. To bridge multi-scale radar features and the decoder, we propose Pyramid Token Fusion (PTF), a lightweight module that converts a feature pyramid into a unified, scale-aware token sequence. By formulating detection as a set prediction problem with learnable object queries and positional encodings, our design models long-range spatial-temporal correlations and cross-feature interactions. This approach eliminates dense proposal generation and heuristic post-processing such as extensive non-maximum suppression (NMS) tuning. We evaluate the proposed framework on the RADDet, where it achieves significant improvements over state-of-the-art radar-only baselines.
Synthetic FMCW Radar Range Azimuth Maps Augmentation with Generative Diffusion Model
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:The scarcity and low diversity of well-annotated automotive radar datasets often limit the performance of deep-learning-based environmental perception. To overcome these challenges, we propose a conditional generative framework for synthesizing realistic Frequency-Modulated Continuous-Wave radar Range-Azimuth Maps. Our approach leverages a generative diffusion model to generate radar data for multiple object categories, including pedestrians, cars, and cyclists. Specifically, conditioning is achieved via Confidence Maps, where each channel represents a semantic class and encodes Gaussian-distributed annotations at target locations. To address radar-specific characteristics, we incorporate Geometry Aware Conditioning and Temporal Consistency Regularization into the generative process. Experiments on the ROD2021 dataset demonstrate that signal reconstruction quality improves by \SI{3.6}{dB} in Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio over baseline methods, while training with a combination of real and synthetic datasets improves overall mean Average Precision by 4.15% compared with conventional image-processing-based augmentation. These results indicate that our generative framework not only produces physically plausible and diverse radar spectrum but also substantially improves model generalization in downstream tasks.
High-Resolution Range-Doppler Imaging from One-Bit PMCW Radar via Generative Adversarial Networks
Mar 17, 2025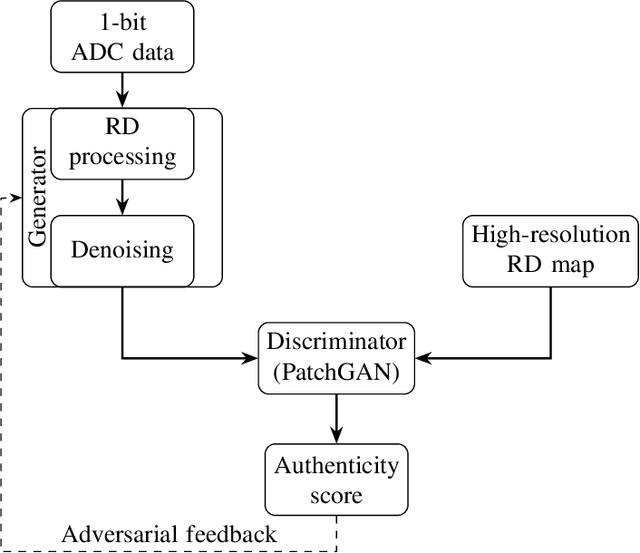
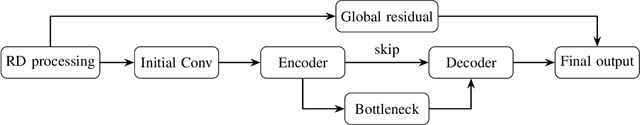
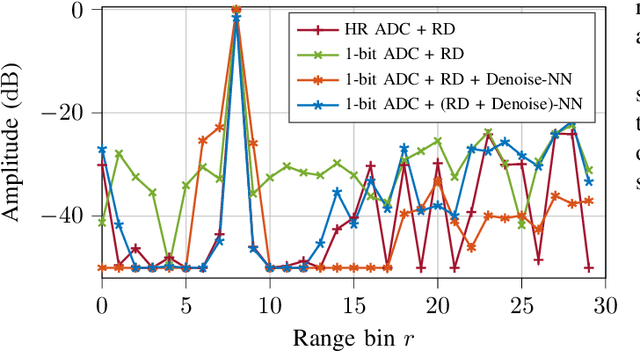
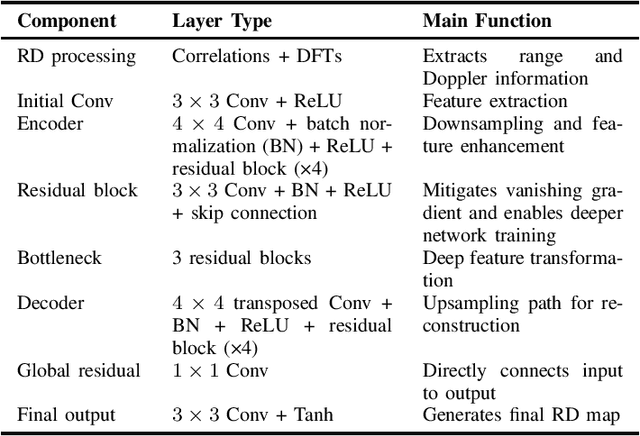
Abstract:Digital modulation schemes such as PMCW have recently attracted increasing attention as possible replacements for FMCW modulation in future automotive radar systems. A significant obstacle to their widespread adoption is the expensive and power-consuming ADC required at gigahertz frequencies. To mitigate these challenges, employing low-resolution ADC, such as one-bit, has been suggested. Nonetheless, using one-bit sampling results in the loss of essential information. This study explores two RD imaging methods in PMCW radar systems utilizing NN. The first method merges standard RD signal processing with a GAN, whereas the second method uses an E2E strategy in which traditional signal processing is substituted with an NN-based RD module. The findings indicate that these methods can substantially improve the probability of detecting targets in the range-Doppler domain.
TSIT: A Simple and Versatile Framework for Image-to-Image Translation
Jul 25, 2020



Abstract:We introduce a simple and versatile framework for image-to-image translation. We unearth the importance of normalization layers, and provide a carefully designed two-stream generative model with newly proposed feature transformations in a coarse-to-fine fashion. This allows multi-scale semantic structure information and style representation to be effectively captured and fused by the network, permitting our method to scale to various tasks in both unsupervised and supervised settings. No additional constraints (e.g., cycle consistency) are needed, contributing to a very clean and simple method. Multi-modal image synthesis with arbitrary style control is made possible. A systematic study compares the proposed method with several state-of-the-art task-specific baselines, verifying its effectiveness in both perceptual quality and quantitative evaluations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge