Can Xiao
Beyond GEMM-Centric NPUs: Enabling Efficient Diffusion LLM Sampling
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Diffusion Large Language Models (dLLMs) introduce iterative denoising to enable parallel token generation, but their sampling phase displays fundamentally different characteristics compared to GEMM-centric transformer layers. Profiling on modern GPUs reveals that sampling can account for up to 70% of total model inference latency-primarily due to substantial memory loads and writes from vocabulary-wide logits, reduction-based token selection, and iterative masked updates. These processes demand large on-chip SRAM and involve irregular memory accesses that conventional NPUs struggle to handle efficiently. To address this, we identify a set of critical instructions that an NPU architecture must specifically optimize for dLLM sampling. Our design employs lightweight non-GEMM vector primitives, in-place memory reuse strategies, and a decoupled mixed-precision memory hierarchy. Together, these optimizations deliver up to a 2.53x speedup over the NVIDIA RTX A6000 GPU under an equivalent nm technology node. We also open-source our cycle-accurate simulation and post-synthesis RTL verification code, confirming functional equivalence with current dLLM PyTorch implementations.
QERA: an Analytical Framework for Quantization Error Reconstruction
Oct 08, 2024



Abstract:he growing number of parameters and computational demands of large language models (LLMs) present significant challenges for their efficient deployment. Recently, there is an increasing interest in quantizing weights to extremely low precision while offsetting the resulting error with low-rank, high-precision error reconstruction terms. The combination of quantization and low-rank approximation is now popular in both adapter-based, parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods such as LoftQ and low-precision inference techniques including ZeroQuant-V2. Usually, the low-rank terms are calculated via the singular value decomposition (SVD) of the weight quantization error, minimizing the Frobenius and spectral norms of the weight approximation error. Recent methods like LQ-LoRA and LQER introduced hand-crafted heuristics to minimize errors in layer outputs (activations) rather than weights, resulting improved quantization results. However, these heuristic methods lack an analytical solution to guide the design of quantization error reconstruction terms. In this paper, we revisit this problem and formulate an analytical framework, named Quantization Error Reconstruction Analysis (QERA), and offer a closed-form solution to the problem. We show QERA benefits both existing low-precision fine-tuning and inference methods -- QERA achieves a fine-tuned accuracy gain of $\Delta_{\text{acc}}$ = 6.05% of 2-bit RoBERTa-base on GLUE compared to LoftQ; and obtains $\Delta_{\text{acc}}$ = 2.97% higher post-training quantization accuracy of 4-bit Llama-3.1-70B on average than ZeroQuant-V2 and $\Delta_{\text{ppl}}$ = - 0.28 lower perplexity on WikiText2 than LQER.
CAN: Revisiting Feature Co-Action for Click-Through Rate Prediction
Nov 11, 2020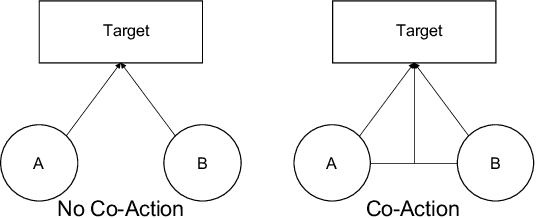
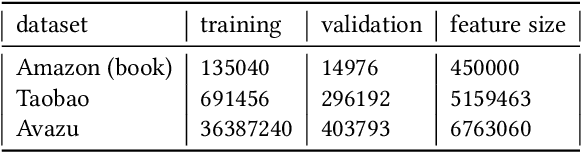
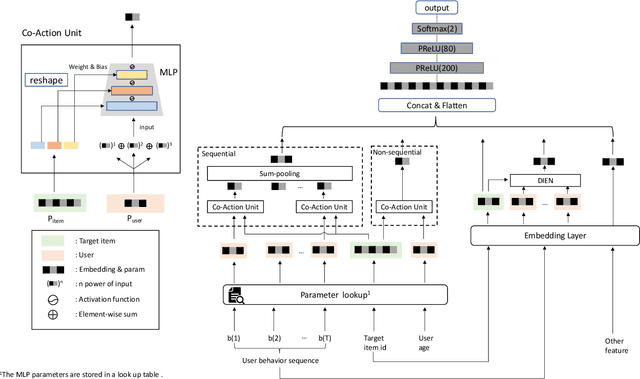
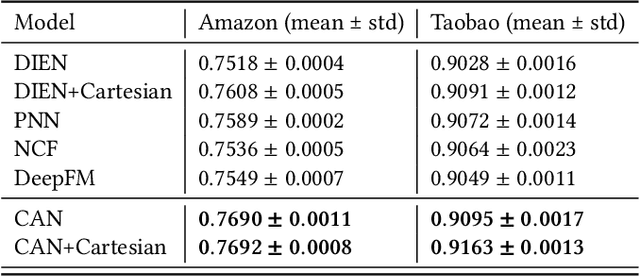
Abstract:Inspired by the success of deep learning, recent industrial Click-Through Rate (CTR) prediction models have made the transition from traditional shallow approaches to deep approaches. Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are known for its ability to learn non-linear interactions from raw feature automatically, however, the non-linear feature interaction is learned in an implicit manner. The non-linear interaction may be hard to capture and explicitly model the \textit{co-action} of raw feature is beneficial for CTR prediction. \textit{Co-action} refers to the collective effects of features toward final prediction. In this paper, we argue that current CTR models do not fully explore the potential of feature co-action. We conduct experiments and show that the effect of feature co-action is underestimated seriously. Motivated by our observation, we propose feature Co-Action Network (CAN) to explore the potential of feature co-action. The proposed model can efficiently and effectively capture the feature co-action, which improves the model performance while reduce the storage and computation consumption. Experiment results on public and industrial datasets show that CAN outperforms state-of-the-art CTR models by a large margin. Up to now, CAN has been deployed in the Alibaba display advertisement system, obtaining averaging 12\% improvement on CTR and 8\% on RPM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge