Can Jiang
HyperCLOVA X Technical Report
Apr 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce HyperCLOVA X, a family of large language models (LLMs) tailored to the Korean language and culture, along with competitive capabilities in English, math, and coding. HyperCLOVA X was trained on a balanced mix of Korean, English, and code data, followed by instruction-tuning with high-quality human-annotated datasets while abiding by strict safety guidelines reflecting our commitment to responsible AI. The model is evaluated across various benchmarks, including comprehensive reasoning, knowledge, commonsense, factuality, coding, math, chatting, instruction-following, and harmlessness, in both Korean and English. HyperCLOVA X exhibits strong reasoning capabilities in Korean backed by a deep understanding of the language and cultural nuances. Further analysis of the inherent bilingual nature and its extension to multilingualism highlights the model's cross-lingual proficiency and strong generalization ability to untargeted languages, including machine translation between several language pairs and cross-lingual inference tasks. We believe that HyperCLOVA X can provide helpful guidance for regions or countries in developing their sovereign LLMs.
A Multilayer Perceptron-based Fast Sunlight Assessment for the Conceptual Design of Residential Neighborhoods under Chinese Policy
Aug 15, 2023Abstract:In Chinese building codes, it is required that residential buildings receive a minimum number of hours of natural, direct sunlight on a specified winter day, which represents the worst sunlight condition in a year. This requirement is a prerequisite for obtaining a building permit during the conceptual design of a residential project. Thus, officially sanctioned software is usually used to assess the sunlight performance of buildings. These software programs predict sunlight hours based on repeated shading calculations, which is time-consuming. This paper proposed a multilayer perceptron-based method, a one-stage prediction approach, which outputs a shading time interval caused by the inputted cuboid-form building. The sunlight hours of a site can be obtained by calculating the union of the sunlight time intervals (complement of shading time interval) of all the buildings. Three numerical experiments, i.e., horizontal level and slope analysis, and simulation-based optimization are carried out; the results show that the method reduces the computation time to 1/84~1/50 with 96.5%~98% accuracies. A residential neighborhood layout planning plug-in for Rhino 7/Grasshopper is also developed based on the proposed model. This paper indicates that deep learning techniques can be adopted to accelerate sunlight hour simulations at the conceptual design phase.
Adaptive Control of Resource Flow to Optimize Construction Work and Cash Flow via Online Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jul 20, 2023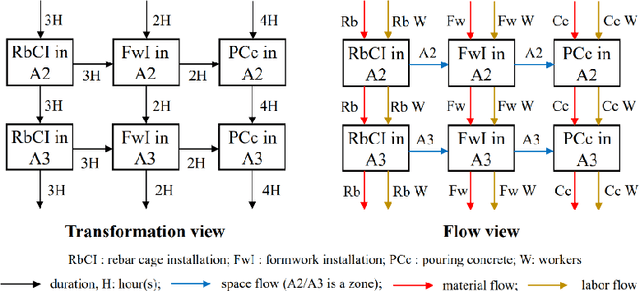
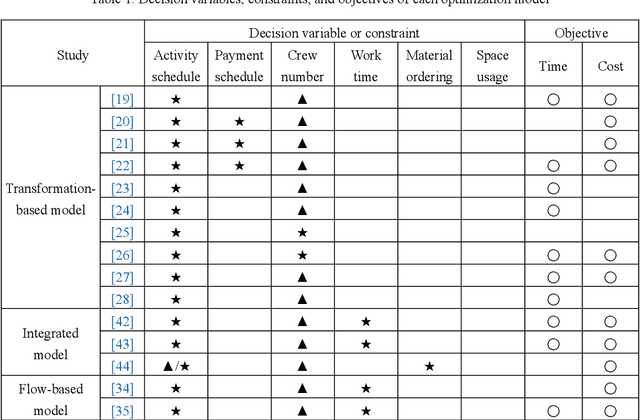
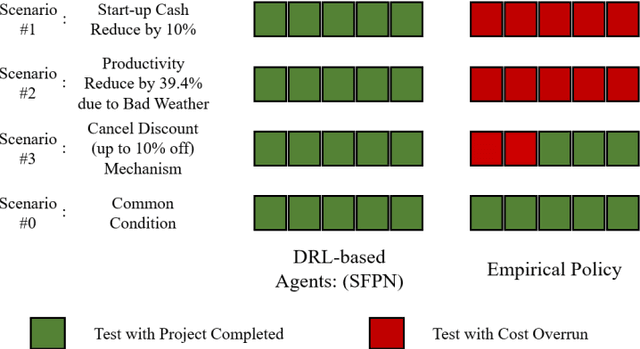
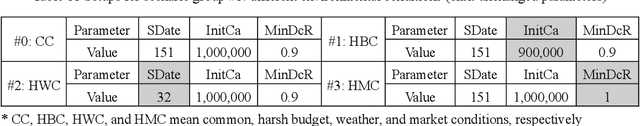
Abstract:Due to complexity and dynamics of construction work, resource, and cash flows, poor management of them usually leads to time and cost overruns, bankruptcy, even project failure. Existing approaches in construction failed to achieve optimal control of resource flow in a dynamic environment with uncertainty. Therefore, this paper introducess a model and method to adaptive control the resource flows to optimize the work and cash flows of construction projects. First, a mathematical model based on a partially observable Markov decision process is established to formulate the complex interactions of construction work, resource, and cash flows as well as uncertainty and variability of diverse influence factors. Meanwhile, to efficiently find the optimal solutions, a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) based method is introduced to realize the continuous adaptive optimal control of labor and material flows, thereby optimizing the work and cash flows. To assist the training process of DRL, a simulator based on discrete event simulation is also developed to mimic the dynamic features and external environments of a project. Experiments in simulated scenarios illustrate that our method outperforms the vanilla empirical method and genetic algorithm, possesses remarkable capability in diverse projects and external environments, and a hybrid agent of DRL and empirical method leads to the best result. This paper contributes to adaptive control and optimization of coupled work, resource, and cash flows, and may serve as a step stone for adopting DRL technology in construction project management.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge