Camilo Sarmiento
An action language-based formalisation of an abstract argumentation framework
Sep 29, 2024
Abstract:An abstract argumentation framework is a commonly used formalism to provide a static representation of a dialogue. However, the order of enunciation of the arguments in an argumentative dialogue is very important and can affect the outcome of this dialogue. In this paper, we propose a new framework for modelling abstract argumentation graphs, a model that incorporates the order of enunciation of arguments. By taking this order into account, we have the means to deduce a unique outcome for each dialogue, called an extension. We also establish several properties, such as termination and correctness, and discuss two notions of completeness. In particular, we propose a modification of the previous transformation based on a "last enunciated last updated" strategy, which verifies the second form of completeness.
Action Languages Based Actual Causality in Ethical Decision Making Contexts
May 05, 2022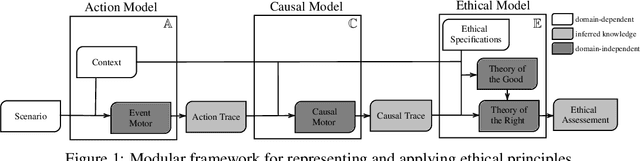
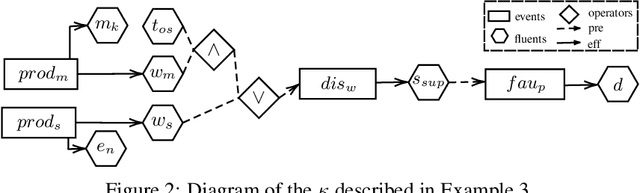
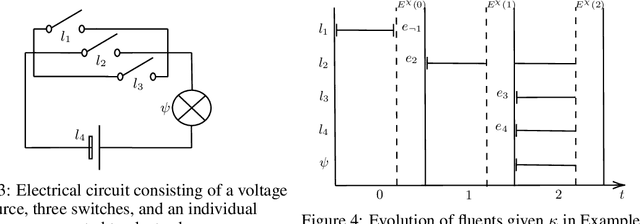
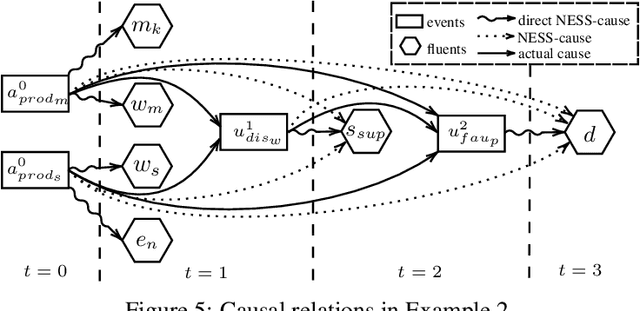
Abstract:Moral responsibility is closely intermixed with causality, even if it cannot be reduced to it. Besides, rationally understanding the evolution of the physical world is inherently linked with the idea of causality. It follows that decision making applications based on automated planning, especially if they integrate references to ethical norms, have inevitably to deal with causality. Despite these considerations, much of the work in computational ethics relegates causality to the background, if not ignores it completely. This paper contribution is double. The first one is to link up two research topics$\unicode{x2014}$automated planning and causality$\unicode{x2014}$by proposing an actual causation definition suitable for action languages. This definition is a formalisation of Wright's NESS test of causation. The second is to link up computational ethics and causality by showing the importance of causality in the simulation of ethical reasoning and by enabling the domain to deal with situations that were previously out of reach thanks to the actual causation definition proposed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge